Related Research Articles

The Kingdom of the East Saxons, referred to as the Kingdom of Essex, was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex, Middlesex, much of Hertfordshire and west Kent. The last king of Essex was Sigered of Essex, who in 825 ceded the kingdom to Ecgberht, King of Wessex.

The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group that inhabited much of what is now England in the Early Middle Ages, and spoke Old English. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. Although the details are not clear, their cultural identity developed out of the interaction of incoming groups of Germanic peoples, with the pre-existing Romano-British culture. Over time, most of the people of what is now southern and eastern England came to identify as Anglo-Saxon and speak Old English. Danish and Norman invasions later changed the situation significantly, but their language and political structures are the direct predecessors of the medieval Kingdom of England, and the medieval English language. Although the modern English language owes somewhat less than 26% of its words to Old English, this includes the vast majority of words used in everyday speech.

Mercia was one of the three notable Anglic kingdoms founded after Sub-Roman Britain was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred around the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlands of England.

Wulfhere or Wulfar was King of Mercia from 658 until 675 AD. He was the first Christian king of all of Mercia, though it is not known when or how he converted from Anglo-Saxon paganism. His accession marked the end of Oswiu of Northumbria's overlordship of southern England, and Wulfhere extended his influence over much of that region. His campaigns against the West Saxons led to Mercian control of much of the Thames valley. He conquered the Isle of Wight and the Meon valley and gave them to King Æthelwealh of the South Saxons. He also had influence in Surrey, Essex, and Kent. He married Eormenhild, the daughter of King Eorcenberht of Kent.
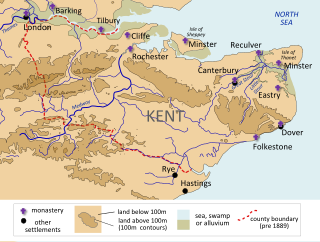
The Kingdom of the Kentish, today referred to as the Kingdom of Kent, was an early medieval kingdom in what is now South East England. It existed from either the fifth or the sixth century AD until it was fully absorbed into the Kingdom of Wessex in the late 9th century and later into the Kingdom of England in the early 10th century.
Cynegils was King of Wessex from c. 611 to c. 642. Cynegils is traditionally considered to have been King of Wessex, but the familiar kingdoms of the so-called Heptarchy had not yet formed from the patchwork of smaller kingdoms in his lifetime. The later kingdom of Wessex was centred on the counties of Hampshire, Dorset, Somerset and Wiltshire but the evidence of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is that the kingdom of Cynegils was located on the upper River Thames, extending into northern Wiltshire and Somerset, southern Gloucestershire and Oxfordshire, and western Berkshire, with Dorchester-on-Thames as one of the major royal sites. This region, probably connected to the early tribal grouping known as the Gewisse, a term used by Bede for the West Saxons, lay on the frontier between the later kingdoms of Wessex and Mercia.

The Tribal Hidage is a list of thirty-five tribes that was compiled in Anglo-Saxon England some time between the 7th and 9th centuries. It includes a number of independent kingdoms and other smaller territories, and assigns a number of hides to each one. The list is headed by Mercia and consists almost exclusively of peoples who lived south of the Humber estuary and territories that surrounded the Mercian kingdom, some of which have never been satisfactorily identified by scholars. The value of 100,000 hides for Wessex is by far the largest: it has been suggested that this was a deliberate exaggeration.

Medeshamstede was the name of Peterborough in the Anglo-Saxon period. It was the site of a monastery founded around the middle of the 7th century, which was an important feature in the kingdom of Mercia from the outset. Little is known of its founder and first abbot, Sexwulf, though he was himself an important figure, and later became bishop of Mercia. Medeshamstede soon acquired a string of daughter churches, and was a centre for an Anglo-Saxon sculptural style.
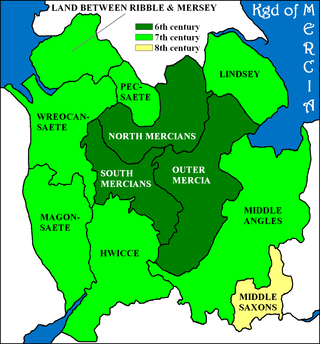
The Pecsætan, also called Peaklanders or Peakrills in modern English, were an Anglo-Saxon tribe who inhabited the central and northern parts of the Peak District area in England.

The Burghal Hidage is an Anglo-Saxon document providing a list of over thirty fortified places (burhs), the majority being in the ancient Kingdom of Wessex, and the taxes assigned for their maintenance. The document, so named by Frederic William Maitland in 1897, survives in two versions of medieval and early modern date. Version A, Cotton Otho B.xi was badly damaged in a fire at Ashburnham House in 1731 but the body of the text survives in a transcript made by the antiquary Laurence Nowell in 1562. Version B survives as a composite part of seven further manuscripts, usually given the title De numero hydarum Anglie in Britannia. There are several discrepancies in the lists recorded in the two versions of the document: Version A includes references to Burpham, Wareham and Bridport but omits Shaftesbury and Barnstaple which are listed in Version B. Version B also names Worcester and Warwick in an appended list.

The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain is the process which changed the language and culture of most of what became England from Romano-British to Germanic. The Germanic-speakers in Britain, themselves of diverse origins, eventually developed a common cultural identity as Anglo-Saxons. This process principally occurred from the mid-fifth to early seventh centuries, following the end of Roman rule in Britain around the year 410. The settlement was followed by the establishment of the Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms in the south and east of Britain, later followed by the rest of modern England, and the south-east of modern Scotland. The exact nature of this change is a topic of on-going research. Questions remain about the scale, timing and nature of the settlements, and also about what happened to the previous residents of what is now England.

Coinage in Anglo-Saxon England refers to the use of coins, either for monetary value or for other purposes, in Anglo-Saxon England.
Helena Francisca Hamerow, FSA is an American-born archaeologist, best known for her work on the archeology of early medieval communities in Northwestern Europe. She is Professor of Early Medieval archaeology and former Head of the School of Archaeology, University of Oxford.

Eorpeburnan is the first place identified in the Burghal Hidage, a document created in the late 9th or early 10th century, that provides a list of thirty one fortified places in Wessex. It details the location of fortifications designed to defend the West Saxon kingdom from the Vikings but also the relative size of burghal defences and their garrisons. Eorpeburnan is designated as having a hidage of 324, its precise location is lost in history, but scholars have suggested some possible sites.
Finglesham Anglo-Saxon cemetery is a place of burial that was used from the sixth to the eighth centuries CE. It is located adjacent to the village of Finglesham, near Sandwich in Kent, South East England. Belonging to the Anglo-Saxon period, it was part of the much wider tradition of burial in Early Anglo-Saxon England.
Buckland Anglo-Saxon cemetery was a place of burial. It is located on Long Hill in the town of Dover in Kent, South East England. Belonging to the Anglo-Saxon period, it was part of the much wider tradition of burial in Early Anglo-Saxon England.
Mill Hill Anglo-Saxon cemetery is a place of burial located close to the town of Deal in Kent, South-East England. Belonging to the Middle Anglo-Saxon period, it was part of the much wider tradition of burial in Early Anglo-Saxon England.

Sarre Anglo-Saxon cemetery is a place of burial that was used in the sixth and seventh centuries CE.
Urbs Iudeu was a city besieged in 655 AD by Penda, King of Mercia, and Cadafael, King of Gwynedd. The siege was an important episode in a long-running war between Mercia and Northumbria in the years 616–679. This war was fought in the area north of the River Trent, in particular in and around the Peak District (Wirksworth) also around Heathfield (Doncaster), Elmet (Aberford) and Lindsey (Lincoln), as these were provinces of Northumbria at the time.
Susan Marian Oosthuizen is Emeritus Professor of Medieval Archaeology at the University of Cambridge. She specialises in examining the origins and development of early medieval and medieval landscapes, and in the evolution of systems of governance.
References
- ↑ "Susan Harrington". UCL. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ↑ "Beyond the Tribal Hidage: Anglo-Saxon kingdoms in southern England AD 400-750". UCL. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ↑ "People and place: the making of the Kingdom of Northumbria AD 300-800" (PDF). Medieval Archaeology. Vol. 54. Autumn 2015.
- ↑ "Fellows Directory - Harrington". Society of Antiquaries of London. Retrieved 2 March 2020.