
Cheerleading is an activity in which the participants cheer for their team as a form of encouragement. It can range from chanting slogans to intense physical activity. It can be performed to motivate sports teams, to entertain the audience, or for competition. Cheerleading routines typically range anywhere from one to three minutes, and contain components of tumbling, dance, jumps, cheers, and stunting.

Parasports are sports played by people with a disability, including physical and intellectual disabilities. Some parasports are forms of adapted physical activities from existing able-bodied sports, while others have been specifically created for persons with a disability and do not have an able-bodied equivalent. Disability exists in four categories: physical, mental, permanent and temporary. At a competitive level, disability sport classifications are applied to allow people of varying abilities to face similar opposition.

Special Olympics is the world's largest sports organization for children and adults with intellectual disabilities and physical disabilities, providing year-round training and activities to 5 million participants and Unified Sports partners in 172 countries. Special Olympics competitions are held every day, all around the world—including local, national and regional competitions, adding up to more than 100,000 events a year. Like the International Paralympic Committee, the Special Olympics organization is recognized by the International Olympic Committee; however, unlike the Paralympic Games, Special Olympics World Games are not held in the same year nor in conjunction with the Olympic Games.
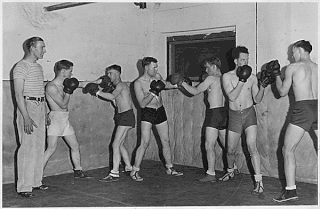
YMCA, sometimes regionally called the Y, is a worldwide youth organization based in Geneva, Switzerland, with more than 64 million beneficiaries in 120 countries. It was founded on 6 June 1844 by George Williams in London, originally as the Young Men's Christian Association, and aims to put Christian values into practice by developing a healthy "body, mind, and spirit".
Touch is a variant of rugby league that is conducted under the direction of the Federation of International Touch (FIT). Though it shares similarities and history with rugby league, it is recognised as a sport in its own right due to its differences which have been developed over the sport's lifetime.

Physical education, often abbreviated to Phys Ed. or P.E., is a subject taught in schools around the world. It is usually taught during primary and secondary education, and encourages psychomotor learning by using a play and movement exploration setting to promote health and physical fitness. Activities in P.E. include football, netball, hockey, rounders, cricket, four square, racing, and numerous other children's games. Physical education also teaches nutrition, healthy habits, and individuality of needs.
Sport Canada is a branch of the Department of Canadian Heritage that develops federal sport policy in Canada, provides funding programs in support of sport, and administers special projects related to sport. Its mission "to enhance opportunities for all Canadians to participate and excel in sport."

Sports days or field days are events staged by many schools and offices in which people participate in competitive sporting activities, often with the aim of winning trophies or prizes. Though they are often held at the beginning of summer, they are staged in the autumn or spring seasons, especially in countries where the summer is very harsh. Schools stage many sports days in which children participate in the sporting events. It is usually held in elementary schools.

The International Shooting Sport Federation (ISSF) is the governing body of the Olympic shooting events in rifle, pistol and shotgun disciplines, and of several non-Olympic shooting sport events. ISSF's activities include regulation of the sport, Olympic qualifications and organization of international competitions such as the ISSF World Cup Series, the ISSF World Cup Finals, the ISSF Separate World Championship in Shotgun events and the ISSF World Championship in all events.
Sport in China has been long associated with the martial arts. Today, China consists of a variety of competitive sports. Traditional Chinese culture regards physical fitness as an important characteristic. China has its own national quadrennial multi-sport event similar to the Olympic Games called the National Games.
The International Children's Games (ICG) is an International Olympic Committee-sanctioned event held every year where children from cities around the world and between the ages of 12 and 15 participate in a variety of sports and cultural activities.

Pahlevani and zourkhaneh rituals is the name inscribed by UNESCO for varzesh-e pahlavāni or varzesh-e bāstāni, a traditional system of athletics and a form of martial arts originally used to train warriors in Iran (Persia), and first appearing under this name and form in the Safavid era, with similarities to systems in adjacent lands under other names. Outside Iran, zoorkhanehs can now also be found in Azerbaijan, and Afghanistan, and were introduced into Iraq in the mid-19th century by the Iranian immigrants, where they seem to have existed until the 1980s before disappearing. This is most likely attributed to the genocide and exile of ethnic Persians in Iraq under Saddam Hussein. Where ethnic Persians were largely forcibly exiled out of Iraq and into Iran. It combines martial arts, calisthenics, strength training and music. It contains elements of pre-Islamic and post-Islamic culture of Iran with the spirituality of Persian Shia Islam and Sufism. Practiced in a domed structure called the zurkhāneh, training sessions consist mainly of ritual gymnastic movements and climax with the core of combat practice, a form of submission-grappling called koshti pahlavāni.
Special Olympics Canada is a national organization founded in 1969 to help people with intellectual disabilities develop self-confidence and social skills through sports training and competition.
Belt wrestling is a form of wrestling that is one of the oldest historically recorded sports. It involves two belted contestants aiming to take each other over by grappling with a belt. There are hundreds of national belt wrestling styles, but contemporary most widespread and internationally competed are Alysh and Kurash, developed by the previously nomadic Turkic peoples of Central Asia. United World Wrestling recognized Alysh wrestling as the primary international belt wrestling style. It is regulated globally by the International Federation of Wrestling on Belts Alysh, the sport's governing body. Although the sport has been practiced for millennia, and local championships were held in various places of the world, it was until 2001 when Bayaman Erkinbayev started its international version, and it was called "Alysh". Until 2005, Rif Gaynanov and Bayaman Erkinbayev developed this style together, and then the ways separated. Two different styles appeared named "Alysh" and "Kurash" belt wrestling. Since then, the sport has been included in the 2013 Summer Universiade program, recognized by the Asian Olympic Council, and contested at the Asian Games and Asian Indoor Games. The sport's executives struggle to promote it to the level of an official Olympic sport.

The International Esports Federation (IESF) is a global organisation based in South Korea whose mission it is to have esports recognized as a legitimate sport.
The International Military Sports Council (IMSC) or Conseil International du Sport Militaire (CISM), is an international sports association, established in 1948 and headquartered in Brussels. It is the world's second-largest multi-discipline sports organisation, after the International Olympic Committee, holding more than 20 competitions annually. Under its auspices, soldiers who may previously have met on the battlefield compete on the sports playing field. CISM organises various sporting events, including the Military World Games and World Military Championships, for the armed forces of 140 member countries. The aim of CISM is to promote sport activity and physical education between armed forces as a means to foster world peace. The motto of CISM is "Friendship through Sport" and is based on three pillars of sport, education and solidarity.

Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, through casual or organized participation, improve participants' physical health. Hundreds of sports exist, from those between single contestants, through to those with hundreds of simultaneous participants, either in teams or competing as individuals. In certain sports such as racing, many contestants may compete, simultaneously or consecutively, with one winner; in others, the contest is between two sides, each attempting to exceed the other. Some sports allow a "tie" or "draw", in which there is no single winner; others provide tie-breaking methods to ensure one winner and one loser. A number of contests may be arranged in a tournament producing a champion. Many sports leagues make an annual champion by arranging games in a regular sports season, followed in some cases by playoffs.

Ethnosport is a set of traditional styles of physical activity, methods of their preservation, and their development, as described in the ethnosport theory of Russian cultural anthropologist Alexey Kylasov.

The CSIT – International Workers and Amateurs in Sports Confederation is an international multi-sports organization. It was established as the successor to Socialist Workers' Sport International and as such celebrated its centenary in 2013. The core principles of contributing to physical activity and sports have stayed in its action policy: it is a right of men and women to do sports no matter what are their professionalism levels. The key concept of the CSIT's sport policy has always been "Sports for all". The policy stems from the historic ideas of the international worker sport movement.

The International Federation of Muaythai Associations, or IFMA, called the International Federation of Muaythai Amateur until 27 July 2019, is the sole recognised sport governing body of amateur and professional Muay Thai and Muay boran consisting of 140 member countries worldwide with 5 continental federations after unification of International Federation of Muaythai Amateur and World Muaythai Council. IFMA is officially recognised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC), the Global Association of International Sports Federations (GAISF), the Association of IOC Recognised International Sports Federations (ARISF), the Olympic Council of Asia (OCA), World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) International World Games Association (IWGA), and Trim and Fitness International Sport for All Association (TAFISA). Muaythai has been included in many official sport programs such as the World Games, World Combat Games, Arafura Games, TAFISA Games, SEA Games, Asian Indoor and Martial Arts Games, Asian Beach Games, Demonstration Sport in the Asian Games.













