Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampricide. The most common of these are herbicides which account for approximately 80% of all pesticide use. Most pesticides are intended to serve as plant protection products, which in general, protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. As an example, the fungus Alternaria solani is used to combat the aquatic weed Salvinia.
A biocide is defined in the European legislation as a chemical substance or microorganism intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, or exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a slightly different definition for biocides as "a diverse group of poisonous substances including preservatives, insecticides, disinfectants, and pesticides used for the control of organisms that are harmful to human or animal health or that cause damage to natural or manufactured products". When compared, the two definitions roughly imply the same, although the US EPA definition includes plant protection products and some veterinary medicines.
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with formula CH3Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is produced both industrially and biologically. It has a tetrahedral shape and it is a recognized ozone-depleting chemical. It was used extensively as a pesticide until being phased out by most countries in the early 2000s.

Glyphosate is a broad-spectrum systemic herbicide and crop desiccant. It is an organophosphorus compound, specifically a phosphonate, which acts by inhibiting the plant enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase. It is used to kill weeds, especially annual broadleaf weeds and grasses that compete with crops. Its herbicidal effectiveness was discovered by Monsanto chemist John E. Franz in 1970. Monsanto brought it to market for agricultural use in 1974 under the trade name Roundup. Monsanto's last commercially relevant United States patent expired in 2000.

Piperonyl butoxide (PBO) is a pale yellow to light brown liquid organic compound used as a synergist component of pesticide formulations. That is, despite having no pesticidal activity of its own, it enhances the potency of certain pesticides such as carbamates, pyrethrins, pyrethroids, and rotenone. It is a semisynthetic derivative of safrole.

Lindane, also known as gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-HCH), gammaxene, Gammallin and benzene hexachloride (BHC), is an organochlorine chemical and an isomer of hexachlorocyclohexane that has been used both as an agricultural insecticide and as a pharmaceutical treatment for lice and scabies.

The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) is a United States federal law that set up the basic U.S. system of pesticide regulation to protect applicators, consumers, and the environment. It is administered and regulated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the appropriate environmental agencies of the respective states. FIFRA has undergone several important amendments since its inception. A significant revision in 1972 by the Federal Environmental Pesticide Control Act (FEPCA) and several others have expanded EPA's present authority to oversee the sales and use of pesticides with emphasis on the preservation of human health and protection of the environment by "(1) strengthening the registration process by shifting the burden of proof to the chemical manufacturer, (2) enforcing compliance against banned and unregistered products, and (3) promulgating the regulatory framework missing from the original law".
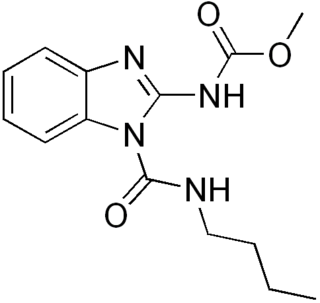
Benomyl is a fungicide introduced in 1968 by DuPont. It is a systemic benzimidazole fungicide that is selectively toxic to microorganisms and invertebrates, especially earthworms, but nontoxic toward mammals.
A Biopesticide is a biological substance or organism that damages, kills, or repels organisms seens as pests. Biological pest management intervention involves predatory, parasitic, or chemical relationships.

Captan is a general use pesticide (GUP) that belongs to the phthalimide class of fungicides. It is a white solid, although commercial samples appear yellow or brownish.

Chlorothalonil (2,4,5,6-tetrachloroisophthalonitrile) is an organic compound mainly used as a broad spectrum, nonsystemic fungicide, with other uses as a wood protectant, pesticide, acaricide, and to control mold, mildew, bacteria, algae. Chlorothalonil-containing products are sold under the names Bravo, Echo, and Daconil. It was first registered for use in the US in 1966. In 1997, the most recent year for which data are available, it was the third most used fungicide in the US, behind only sulfur and copper, with 12 million pounds used in agriculture that year. Including nonagricultural uses, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates, on average, almost 15 million lb (6.8 million kg) were used annually from 1990 to 1996.

Clothianidin is an insecticide developed by Takeda Chemical Industries and Bayer AG. Similar to thiamethoxam and imidacloprid, it is a neonicotinoid. Neonicotinoids are a class of insecticides that are chemically similar to nicotine, which has been used as a pesticide since the late 1700s. Clothianidin and other neonicotinoids act on the central nervous system of insects as an agonist of nAChR, the same receptor as acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter that stimulates and activating post-synaptic acetylcholine receptors but not inhibiting AChE. Clothianidin and other neonicotinoids were developed to last longer than nicotine, which is more toxic and which breaks down too quickly in the environment. However, studies published in 2012 show that neonicotinoid dust released at planting time may persist in nearby fields for several years and be taken up into non-target plants, which are then foraged by bees and other insects.

Pesticides in the United States are used predominantly by the agricultural sector, but approximately a quarter of them are used in houses, yards, parks, golf courses, and swimming pools.
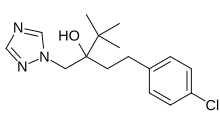
Enilconazole is a fungicide widely used in agriculture, particularly in the growing of citrus fruits. Trade names include Freshgard, Fungaflor, and Nuzone.
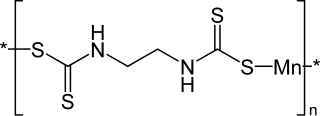
Maneb is a fungicide and a polymeric complex of manganese with the ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate) anionic ligand.

Pesticide regulation in the United States is primarily a responsibility of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). In America, it was not till the 1950s that pesticides were regulated in terms of their safety. The Pesticides Control Amendment (PCA) of 1954 was the first time Congress passed guidance regarding the establishment of safe limits for pesticide residues on food. It authorized the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ban pesticides they determined to be unsafe if they were sprayed directly on food. The Food Additives Amendment, which included the Delaney Clause, prohibited the pesticide residues from any carcinogenic pesticides in processed food. In 1959, pesticides were required to be registered.

Propamocarb is a systemic fungicide used for control of soil, root and leaf disease caused by oomycetes. It is used by watering or spraying. Propamocarb is absorbed and distributed through the plant's tissue.

Fluxapyroxad is a broad-spectrum pyrazole-carboxamide fungicide used on a large variety of commercial crops. It stunts fungus growth by inhibiting the succinate dehydrogenase (SQR) enzyme. Application of fluxapyroxad helps prevent many wilts and other fungal infections from taking hold. As with other systemic pesticides that have a long chemical half-life, there are concerns about keeping fluxapyroxad out of the groundwater, especially when combined with pyraclostrobin. There is also concern that some fungi may develop resistance to fluxapyroxad.

Cyproconazole is an agricultural fungicide of the class of azoles, used on cereal crops, coffee, sugar beet, fruit trees and grapes, on sod farms and golf courses and on wood as a preservative. It was introduced to the market by then Sandoz in 1994.

A pesticide, also called Plant Protection Product (PPP), which is a term used in regulatory documents, consists of several different components. The active ingredient in a pesticide is called “active substance” and these active substances either consist of chemicals or micro-organisms. The aims of these active substances are to specifically take action against organisms that are harmful to plants. In other words, active substances are the active components against pests and plant diseases.