The rib cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrate animals that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels. The circumferential enclosure formed by left and right rib cages, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi-rigid bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdles to form the core part of the axial skeleton.

A sclerite is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instead it refers most commonly to the hardened parts of arthropod exoskeletons and the internal spicules of invertebrates such as certain sponges and soft corals. In paleontology, a scleritome is the complete set of sclerites of an organism, often all that is known from fossil invertebrates.
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments.

In human anatomy, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), also known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurcation as the superior epigastric and musculophrenic arteries.
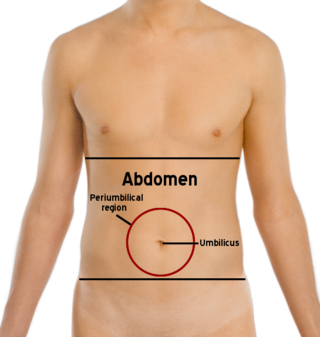
The abdomen is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax.
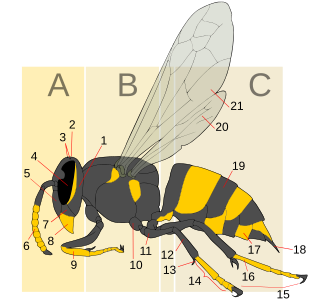
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, tarsus, ischium, metatarsus, carpus, dactylus, patella.

Insect wings are adult outgrowths of the insect exoskeleton that enable insects to fly. They are found on the second and third thoracic segments, and the two pairs are often referred to as the forewings and hindwings, respectively, though a few insects lack hindwings, even rudiments. The wings are strengthened by a number of longitudinal veins, which often have cross-connections that form closed "cells" in the membrane. The patterns resulting from the fusion and cross-connection of the wing veins are often diagnostic for different evolutionary lineages and can be used for identification to the family or even genus level in many orders of insects.

This glossary of entomology describes terms used in the formal study of insect species by entomologists.

The sternum is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen.

The mesothorax is the middle of the three segments of the thorax of hexapods, and bears the second pair of legs. Its principal sclerites are the mesonotum (dorsal), the mesosternum (ventral), and the mesopleuron (lateral) on each side. The mesothorax is the segment that bears the forewings in all winged insects, though sometimes these may be reduced or modified, as in beetles (Coleoptera) or Dermaptera, in which they are sclerotized to form the elytra, and the Strepsiptera, in which they are reduced to form halteres that attach to the mesonotum. All adult insects possess legs on the mesothorax. In some groups of insects, the mesonotum is hypertrophied, such as in Diptera, Hymenoptera, and Lepidoptera), in which the anterior portion of the mesonotum forms most of the dorsal surface of the thorax. In these orders, there is also typically a small sclerite attached to the mesonotum that covers the wing base, called the tegula. In one group of insects, the Hemiptera, the dorsal surface of the thorax is typically formed primarily of the prothorax, but also in part by the enlarged posterior portion of the mesonotum, called the scutellum; in the Coleoptera, the scutellum may or may not be visible, usually as a small triangular plate between the elytral bases, thus similar in position to the Hemipteran scutellum. In Diptera and Hymenoptera the mesothoracic scutellum is also distinct, but much smaller than the mesoscutum.

Fuxianhuia is a genus of Lower Cambrian fossil arthropod known from the Chengjiang fauna in China. Its purportedly primitive features have led to its playing a pivotal role in discussions about the euarthropod stem group. Nevertheless, despite being known from many specimens, disputes about its morphology, in particular its head appendages, have made it one of the most controversial of the Chengjiang taxa, and it has been discussed extensively in the context of the arthropod head problem.

Arthropods are covered with a tough, resilient integument, cuticle or exoskeleton of chitin. Generally the exoskeleton will have thickened areas in which the chitin is reinforced or stiffened by materials such as minerals or hardened proteins. This happens in parts of the body where there is a need for rigidity or elasticity. Typically the mineral crystals, mainly calcium carbonate, are deposited among the chitin and protein molecules in a process called biomineralization. The crystals and fibres interpenetrate and reinforce each other, the minerals supplying the hardness and resistance to compression, while the chitin supplies the tensile strength. Biomineralization occurs mainly in crustaceans. In insects and arachnids, the main reinforcing materials are various proteins hardened by linking the fibres in processes called sclerotisation and the hardened proteins are called sclerotin. The dorsal tergum, ventral sternum, and the lateral pleura form the hardened plates or sclerites of a typical body segment.

Radiodonta is an extinct order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. They may be referred to as radiodonts, radiodontans, radiodontids, anomalocarids, or anomalocaridids, although the last two originally refer to the family Anomalocarididae, which previously included all species of this order but is now restricted to only a few species. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa Anomalocaris canadensis, Hurdia victoria, Peytoia nathorsti, Titanokorys gainessii, Cambroraster falcatus and Amplectobelua symbrachiata, the Ordovician Aegirocassis benmoulai and the Devonian Schinderhannes bartelsi.

Insect morphology is the study and description of the physical form of insects. The terminology used to describe insects is similar to that used for other arthropods due to their shared evolutionary history. Three physical features separate insects from other arthropods: they have a body divided into three regions, three pairs of legs, and mouthparts located outside of the head capsule. This position of the mouthparts divides them from their closest relatives, the non-insect hexapods, which include Protura, Diplura, and Collembola.
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids.

The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word sternum originates from Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon) 'chest'.
Most insects reproduce oviparously, i.e. by laying eggs. The eggs are produced by the female in a pair of ovaries. Sperm, produced by the male in one testicle or more commonly two, is transmitted to the female during mating by means of external genitalia. The sperm is stored within the female in one or more spermathecae. At the time of fertilization, the eggs travel along oviducts to be fertilized by the sperm and are then expelled from the body ("laid"), in most cases via an ovipositor.

Megachile campanulae, known as the bellflower resin bee, is a species of bee in the family Megachilidae. Described in 1903, these solitary bees are native to eastern North America. Studies in 2013 placed them among the first insect species to use synthetic materials for making nests. They are considered mason bees, which is a common descriptor of bees in several families, including Megachilidae. Within the genus Megachile, frequently also referred to as leafcutter bees, M. campanulae is a member of the subgenus Chelostomoides, which do not construct nests from cut leaves, but rather from plant resins and other materials. Females lay eggs in nests constructed with individual cell compartments for each egg. Once hatched, the eggs progress through larval stages and subsequently will overwinter as pupae. The bees are susceptible to parasitism from several other bee species, which act as brood parasites. They are medium-sized bees and the female adults are typically larger than the males. They are important pollinators of numerous native plant species throughout their range.

Fuxianhuiida is an extinct clade of arthropods from the Cambrian of China. All currently known species are from Cambrian Series 2 aged deposits in Yunnan Province, including the Chengjiang biota. Although historically suggested to be members of the arthropod stem group recent research has suggested that they may be closely related to mandibulates. Many specimens are known with exceptional soft tissue preservation, including preserved guts and neural tissue, which given their basal phylogenetic position makes them important in understanding the evolution of Arthropoda as a whole. They reach a size of up to 15 cm, and are interpreted as benthic predators and scavengers. The Fuxianhuiid exoskeleton is unmineralised, and the number of tergites ranges from 15 to over 40. The cephalon is covered by a head shield and contains stalked eyes connected by the anterior sclerite, antennae, a butterfly shaped hyposome and a posterior facing mouth. Fuxianhuiids possess specialized post-antennal appendages with serrated edges used for food processing. The presence of gnathobases in members of Chengjiangocardidae suggests that they were capable of durophagy. In most Fuxianhuiids, the thorax tergites narrow posteriorly, terminating in either a swimming paddle or paired flukes with a tail spine. In members of Fuxianhuiidae the thorax is divided into two sections, the anterior wide opisthothorax and the posterior narrow limbless tail-like abdomen.

Perothops is a genus of false click beetles in the family Eucnemidae containing 3 species. They are known as beech-tree beetles or perothopid beetles. They are small as they are only 10–18 millimeters long. It is the only genus in the monotypic subfamily Perothopinae. They are dark-colored beetles that are found across the United States, generally in forests. The genus was discovered by Johann Friedrich von Eschscholtz in 1836. It used to be considered a family not part of Eucnemidae. The genus's name is from Greek, translating to "maimed/crippled eye" or "eye of little necklaces/bands", referring to the placement of perothopid eyes.