
Irredentism is one state's desire to annex the territory of another state. This desire can be motivated by ethnic reasons because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent state. Historical reasons may also be responsible, i.e., that the territory previously formed part of the parent state. However, difficulties in applying the concept to concrete cases have given rise to academic debates about its precise definition. Disagreements concern whether either or both ethnic and historical reasons have to be present and whether non-state actors can also engage in irredentism. A further dispute is whether attempts to absorb a full neighboring state are also included. There are various types of irredentism. For typical forms of irredentism, the parent state already exists before the territorial conflict with a neighboring state arises. However, there are also forms of irredentism in which the parent state is newly created by uniting an ethnic group spread across several countries. Another distinction concerns whether the country to which the disputed territory currently belongs is a regular state, a former colony, or a collapsed state.

A nation-state is a political unit where the state, a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory, and the nation, a community based on a common identity, are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant national or ethnic group.

Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate authority over other people in order to establish a law or change existing laws. In political theory, sovereignty is a substantive term designating supreme legitimate authority over some polity. In international law, sovereignty is the exercise of power by a state. De jure sovereignty refers to the legal right to do so; de facto sovereignty refers to the factual ability to do so. This can become an issue of special concern upon the failure of the usual expectation that de jure and de facto sovereignty exist at the place and time of concern, and reside within the same organization.

Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 242 (S/RES/242) was adopted unanimously by the UN Security Council on November 22, 1967, in the aftermath of the Six-Day War. It was adopted under Chapter VI of the UN Charter. The resolution was sponsored by British ambassador Lord Caradon and was one of five drafts under consideration.

A territorial dispute or boundary dispute is a disagreement over the possession or control of land between two or more political entities.
The right of conquest was historically a right of ownership to land after immediate possession via force of arms. It was recognized as a principle of international law that gradually deteriorated in significance until its proscription in the aftermath of World War II following the concept of crimes against peace introduced in the Nuremberg Principles. The interdiction of territorial conquests was confirmed and broadened by the UN Charter, which provides in article 2, paragraph 4, that "All Members shall refrain in their international relations from the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state, or in any other manner inconsistent with the purposes of the United Nations." Although civil wars continued, wars between established states have been rare since 1945. Nations that have resorted to the use of force since the Charter came into effect have typically invoked self-defense or the right of collective defense.

A war of aggression, sometimes also war of conquest, is a military conflict waged without the justification of self-defense, usually for territorial gain and subjugation.

Gibraltar, a British Overseas Territory, located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, is the subject of a territorial claim by Spain. It was captured in 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–1714). The Spanish Crown formally ceded the territory in perpetuity to the British Crown in 1713, under Article X of the Treaty of Utrecht. Spain later attempted to recapture the territory during the thirteenth siege (1727) and the Great Siege (1779–1783). British sovereignty over Gibraltar was confirmed in later treaties signed in Seville (1729) and the Treaty of Paris (1783).
Pan-Iranism is an ideology that advocates solidarity and reunification of Iranian peoples living in the Iranian plateau and other regions that have significant Iranian cultural influence.
The International law bearing on issues of Arab–Israeli conflict, which became a major arena of regional and international tension since the birth of Israel in 1948, resulting in several disputes between a number of Arab countries and Israel.
The Westphalian system, also known as Westphalian sovereignty, is a principle in international law that each state has exclusive sovereignty over its territory. The principle developed in Europe after the Peace of Westphalia in 1648, based on the state theory of Jean Bodin and the natural law teachings of Hugo Grotius. It underlies the modern international system of sovereign states and is enshrined in the United Nations Charter, which states that "nothing ... shall authorize the United Nations to intervene in matters which are essentially within the domestic jurisdiction of any state."
Civic nationalism, otherwise known as democratic nationalism, is a form of nationalism that adheres to traditional liberal values of freedom, tolerance, equality, and individual rights, and is not based on ethnocentrism. Civic nationalists often defend the value of national identity by saying that individuals need it as a partial shared aspect of their identity in order to lead meaningful, autonomous lives and that democratic polities need a national identity to function properly. Liberal nationalism is used in the same sense as 'civic nationalism', but liberal ethnic nationalism also exists, and "state nationalism" is a branch of civic nationalism, but it can also be illiberal.
The partition of Quebec refers to the secession of regions of the province of Quebec, rather than to partitions in a strict political sense. It is usually discussed as a possibility in the event of Quebec secession from Canada. It was not a key issue in either the 1980 Referendum on Quebec Sovereignty or the 1995 Referendum on Quebec Sovereignty, but dominated the politics of national unity for about two years in the aftermath of the second referendum. Since then, the issue has occasionally resurfaced.
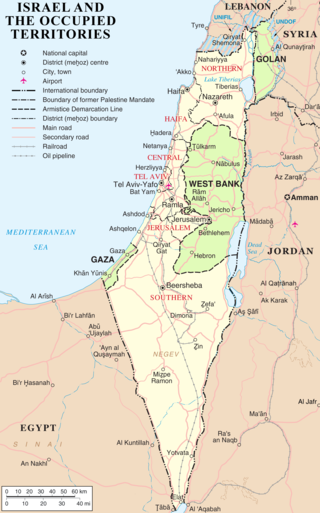
The modern borders of Israel exist as the result both of past wars and of diplomatic agreements between the State of Israel and its neighbours, as well as an effect of the agreements among colonial powers ruling in the region before Israel's creation. Only two of Israel's five total potential land borders are internationally recognized and uncontested, while the other three remain disputed; the majority of its border disputes are rooted in territorial changes that came about as a result of the 1967 Arab–Israeli War, which saw Israel occupy large swathes of territory from its rivals. Israel's two formally recognized and confirmed borders exist with Egypt and Jordan since the 1979 Egypt–Israel peace treaty and the 1994 Israel–Jordan peace treaty, while its borders with Syria, Lebanon and the Palestinian territories remain internationally defined as contested.
A sovereign state is a state that has the highest authority over a territory.

A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of Earth's water surface areas using physiographical or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources, encompassing maritime features, limits and zones. Generally, a maritime boundary is delineated at a particular distance from a jurisdiction's coastline. Although in some countries the term maritime boundary represents borders of a maritime nation that are recognized by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, maritime borders usually serve to identify the edge of international waters.

International reactions to the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation have largely been condemnatory of Russia's actions, supportive of Ukraine's sovereignty and territorial integrity, and supportive of finding a quick end to the crisis. The United States and the European Union responded by enacting sanctions against Russia for its role in the crisis, and urged Russia to withdraw. Russia has accused the United States and the EU of funding and directing the revolution and retaliated to the sanctions by imposing its own.

A quasi-state is a political entity that does not represent a fully autonomous sovereign state with its own institutions.

The Golan Heights are a rocky plateau in the Levant region of Western Asia that was captured by Israel from Syria in the 1967 Six-Day War. The international community, with the exception of Israel and the United States, generally regards the Golan Heights to be Syrian territory held by Israel under military occupation. Following the war, Syria dismissed any negotiations with Israel as part of the Khartoum Resolution.













