
The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) is a federal public health agency within the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The agency focuses on minimizing human health risks associated with exposure to hazardous substances. It works closely with other federal, state, and local agencies; tribal governments; local communities; and healthcare providers. Its mission is to "Serve the public through responsive public health actions to promote healthy and safe environments and prevent harmful exposures." ATSDR was created as an advisory, nonregulatory agency by the Superfund legislation and was formally organized in 1985.

A safety data sheet (SDS), material safety data sheet (MSDS), or product safety data sheet (PSDS) is a document that lists information relating to occupational safety and health for the use of various substances and products. SDSs are a widely used system for cataloguing information on chemicals, chemical compounds, and chemical mixtures. SDS information may include instructions for the safe use and potential hazards associated with a particular material or product, along with spill-handling procedures. The older MSDS formats could vary from source to source within a country depending on national requirements; however, the newer SDS format is internationally standardized.

VG is a "V-series" nerve agent chemically similar to the better-known VX nerve agent. Tetram is the common Russian name for the substance. Amiton was the trade name for the substance when it was marketed as an insecticide by ICI in the mid-1950s.

Dangerous goods, abbreviated DG, are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials.

The Dangerous Substances Directive was one of the main European Union laws concerning chemical safety, until its full replacement by the new regulation CLP Regulation (2008), starting in 2016. It was made under Article 100 of the Treaty of Rome. By agreement, it is also applicable in the EEA, and compliance with the directive will ensure compliance with the relevant Swiss laws. The Directive ceased to be in force on 31 May 2015 and was repealed by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006.

The Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act of 1986 is a United States federal law passed by the 99th United States Congress located at Title 42, Chapter 116 of the U.S. Code, concerned with emergency response preparedness.

The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labelling schemes previously used around the world. Core elements of the GHS include standardized hazard testing criteria, universal warning pictograms, and harmonized safety data sheets which provide users of dangerous goods with a host of information. The system acts as a complement to the UN Numbered system of regulated hazardous material transport. Implementation is managed through the UN Secretariat. Although adoption has taken time, as of 2017, the system has been enacted to significant extents in most major countries of the world. This includes the European Union, which has implemented the United Nations' GHS into EU law as the CLP Regulation, and United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards.
Hazard statements form part of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). They are intended to form a set of standardized phrases about the hazards of chemical substances and mixtures that can be translated into different languages. As such, they serve the same purpose as the well-known R-phrases, which they are intended to replace.

Azinphos-ethyl was a broad-spectrum organophosphate insecticide.

Methyl thiocyanate is an organic compound with the formula CH3SCN. The simplest member of the organic thiocyanates, it is a colourless liquid with an onion-like odor. It is produced by the methylation of thiocyanate salts. The compound is a precursor to the more useful isomer methyl isothiocyanate (CH3NCS).
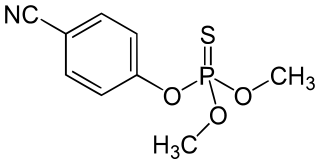
Cyanophos is a cholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide and avicide; for example, against rice stem borers and house flies. It is part of the chemical class of organophosphorus compounds, and is a yellow to reddish-yellow transparent liquid.

Oxamyl is a chemical used as a pesticide that comes in two forms: granulated and liquid. The granulated form has been banned in the United States. It is commonly sold under the trade name Vydate.

Bis(chloromethyl) ketone is a chemical substance with formula C
3H
4Cl
2O. It is a solid, and is used in the making of citric acid. Exposures such as contact or inhalation of bis(chloromethyl) ketone can result in irritation or damage to skin, eyes, throat, lungs, liver and kidneys, as well as headaches and fainting.

Chlormephos (chemical formula: C5H12ClO2PS2) is an organothiophosphate insecticide. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.
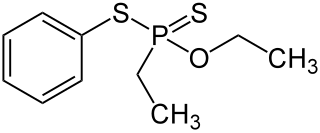
Fonofos is an organothiophosphate insecticide primarily used on corn. It is highly toxic and listed as an extremely hazardous substance.

3,4-Dichlorophenyl isocyanate is a chemical compound used as a chemical intermediate and in organic synthesis. It is a solid, and ranges in colour from white to yellow. It is an irritant for tissues including eyes and mucous membranes, and inhalation of dust from the chemical is poisonous. It can be used industrially in the preparation of triclocarban by reaction with p-chloroaniline.

Demephion is an organothiophosphate insecticide. It is a mixture of two closely related structural isomers demephion-O and demephion-S.
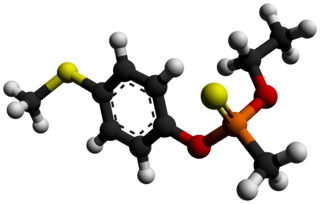
BAY-29952 is a broad spectrum insecticide. It is listed as an extremely hazardous substance according to the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.

Prothoate is an organothiophosphate insecticide also used as an acaricide.






















