
A personal digital assistant (PDA), also known as a handheld PC, is a multi-purpose mobile device which functions as a personal information manager. PDAs have been mostly displaced by the widespread adoption of highly capable smartphones, in particular those based on iOS and Android, and thus saw a rapid decline in use after 2007.
Windows Media Audio (WMA) is a series of audio codecs and their corresponding audio coding formats developed by Microsoft. It is a proprietary technology that forms part of the Windows Media framework. WMA consists of four distinct codecs. The original WMA codec, known simply as WMA, was conceived as a competitor to the popular MP3 and RealAudio codecs. WMA Pro, a newer and more advanced codec, supports multichannel and high resolution audio. A lossless codec, WMA Lossless, compresses audio data without loss of audio fidelity. WMA Voice, targeted at voice content, applies compression using a range of low bit rates. Microsoft has also developed a digital container format called Advanced Systems Format to store audio encoded by WMA.

A Pocket PC is a class of personal digital assistant (PDA) that runs the Windows Mobile or Windows Embedded Compact operating system that has some of the abilities of modern desktop PCs. The name was introduced by Microsoft in 2000 as a rebranding of the Palm-size PC category. Some of these devices also had integrated phone and data capabilities, which were called Pocket PC Phone Edition. Windows "Smartphone" is another Windows CE based platform for non-touch flip phones or dumber phones.

Palm is a line of personal digital assistants (PDAs) and mobile phones developed by California-based Palm, Inc., originally called Palm Computing, Inc. Palm devices are often remembered as "the first wildly popular handheld computers," responsible for ushering in the smartphone era.
Windows Media Video (WMV) is a series of video codecs and their corresponding video coding formats developed by Microsoft. It is part of the Windows Media framework. WMV consists of three distinct codecs: The original video compression technology known as WMV, was originally designed for Internet streaming applications, as a competitor to RealVideo. The other compression technologies, WMV Screen and WMV Image, cater for specialized content. After standardization by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE), WMV version 9 was adapted for physical-delivery formats such as HD DVD and Blu-ray Disc and became known as VC-1. Microsoft also developed a digital container format called Advanced Systems Format to store video encoded by Windows Media Video.
Windows Embedded Compact, formerly Windows Embedded CE, Windows Powered and Windows CE, is a discontinued operating system developed by Microsoft for mobile and embedded devices. It was part of the Windows Embedded family and served as the foundation of several classes of devices including the Handheld PC, Pocket PC, Auto PC, Windows Mobile, Windows Phone 7 and others.
Qt Extended is an application platform for embedded Linux-based mobile computing devices such as personal digital assistants, video projectors and mobile phones. It was initially developed by The Qt Company, at the time known as Qt Software and a subsidiary of Nokia. When they cancelled the project the free software portion of it was forked by the community and given the name Qt Extended Improved. The QtMoko Debian-based distribution is the natural successor to these projects as continued by the efforts of the Openmoko community.

RealPlayer, formerly RealAudio Player, RealOne Player and RealPlayer G2, is a cross-platform media player app, developed by RealNetworks. The media player is compatible with numerous container file formats of the multimedia realm, including MP3, MP4, QuickTime File Format, Windows Media format, and the proprietary RealAudio and RealVideo formats. RealPlayer is also available for other operating systems; Linux, Unix, Palm OS, Windows Mobile, and Symbian versions have been released.
Musepack or MPC is an open source lossy audio codec, specifically optimized for transparent compression of stereo audio at bitrates of 160–180 kbit/s. It was formerly known as MPEGplus, MPEG+ or MP+.
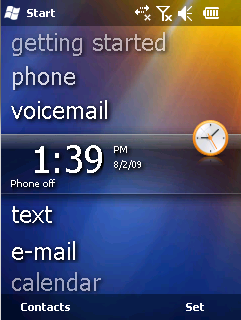
Windows Mobile is a discontinued mobile operating system developed by Microsoft for smartphones and personal digital assistants.

Internet Explorer Mobile was a mobile version of Internet Explorer developed by Microsoft, based on versions of the MSHTML (Trident) layout engine. IE Mobile comes loaded by default with Windows Phone and Windows CE. Later versions of Internet Explorer Mobile are based on the desktop version of Internet Explorer. Older versions however, called Pocket Internet Explorer, are not based on the same layout engine.
The Palm Treo 700w is a Windows Mobile-powered smartphone that was officially announced on September 26, 2005. As Palm's first Windows Mobile-powered Treo, the 700w offered an alternative for users who want or need to use Microsoft software. It was offered by Verizon Wireless, and other CDMA carriers. A newer version of this phone has been released, the Treo 700wx.
CoreAVC was a proprietary codec for decoding the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video format.

Opera Mobile is a mobile web browser for smartphones, tablets and PDAs developed by Opera.

Zune is a discontinued software program that was developed by Microsoft for Windows that functions as a full media player, library, media streaming server, mobile device management, and interface for the discontinued Zune Marketplace. The software is used to sync with all devices with Zune functionality including the Zune 4, 8, 16, 30, 80, 120, Zune HD, Windows Phone 7, and Microsoft Kin. Zune devices work exclusively with the Zune software, which applies many design principles of Microsoft's Metro design language.

The Palm Foleo was a planned subnotebook computer that was announced by mobile device manufacturer Palm Inc. on May 30, 2007, and canceled three months later. It intended to serve as a companion for smartphones including Palm's own Treo line. The device ran on the Linux operating system and featured 256 MB of flash memory and an immediate boot-up feature.
A mobile operating system is an operating system for smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, smartglasses, or other non-laptop personal mobile computing devices. While computers such as typical/mobile laptops are "mobile", the operating systems used on them are generally not considered mobile ones, as they were originally designed for desktop computers that historically did not have or need specific mobile features. This line distinguishing mobile and other forms has become blurred in recent years, due to the fact that newer devices have become smaller and more mobile unlike hardware of the past. Key notabilities blurring this line are the introduction of tablet computers and light-weight laptops and the hybridization of the two in 2-in-1 PCs.

The Zune HD is a portable media player in the Zune product family released on September 15, 2009, by Microsoft. It was a direct competitor with Apple's iPod Touch series of mobile devices. It was initially released in 16 and 32 GB capacities. A 64 GB version was released on April 9, 2010. It has a touchscreen interface for navigation and included Wi-Fi for synchronization, access to the Zune Marketplace and Web browsing.

Symbian is a discontinued mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for smartphones. It was originally developed as a proprietary software OS for personal digital assistants in 1998 by the Symbian Ltd. consortium. Symbian OS is a descendant of Psion's EPOC, and was released exclusively on ARM processors, although an unreleased x86 port existed. Symbian was used by many major mobile phone brands, like Samsung, Motorola, Sony Ericsson, and above all by Nokia. It was also prevalent in Japan by brands including Fujitsu, Sharp and Mitsubishi. As a pioneer that established the smartphone industry, it was the most popular smartphone OS on a worldwide average until the end of 2010, at a time when smartphones were in limited use, when it was overtaken by iOS and Android. It was notably less popular in North America.
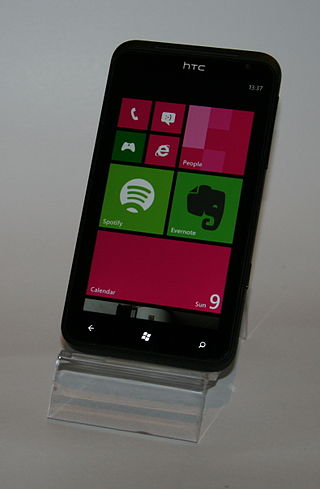
Windows Phone 7 is the first release of the Windows Phone mobile client operating system, released worldwide on October 21, 2010, and in the United States on November 8, 2010. It runs on the Windows CE 6.0 kernel.








