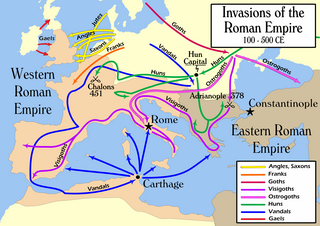
The Migration Period, also known as the Barbarian Invasions, was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman kingdoms. The term refers to the important role played by the migration, invasion, and settlement of various tribes, notably the Franks, Goths, Alemanni, Alans, Huns, early Slavs, Pannonian Avars, Magyars, and Bulgars within or into the former Western Empire and Eastern Europe. The period is traditionally taken to have begun in AD 375 and ended in 568. Various factors contributed to this phenomenon of migration and invasion, and their role and significance are still widely discussed.
The Vistula Veneti were an Indo-European people that inhabited the region of central Europe east of the Vistula River and the areas around the Bay of Gdańsk. The name first appeared in the 1st century AD in the writings of ancient Romans who differentiated a group of peoples whose manner and language differed from that of the Germanic and Sarmatian tribes. In the 6th century AD, Byzantine sources described the Veneti as the ancestors of the Slavs, who during the second phase of the Migration Period moved south across the northern frontier of the Byzantine Empire.

Dervan or Derwan was an early duke of the Sorbs.
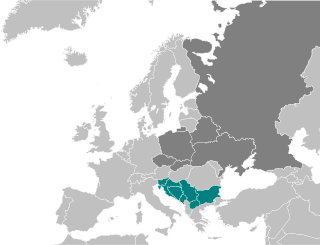
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes.

Aladzha Monastery is a medieval Orthodox Christian cave monastery complex in northeastern Bulgaria, 17 km north of central Varna and 3 km west of Golden Sands beach resort, in a protected forest area adjacent to the Golden Sands Nature Park.

The Sclaveni or Sklabenoi were early Slavic tribes that raided, invaded and settled the Balkans in the Early Middle Ages and eventually became the progenitors of modern South Slavs. They were mentioned by early Byzantine chroniclers as barbarians having appeared at the Byzantine borders along with the Antes, another Slavic group. The Sclaveni were differentiated from the Antes and Wends ; however, they were described as kin. Eventually, most South Slavic tribes accepted Byzantine or Frankish suzerainty, and came under their cultural influences and Chalcedonian Christianity. The term was widely used as general catch-all term until the emergence of separate tribal names by the 10th century.

The Antes, or Antae, were an early East Slavic tribal polity of the 6th century CE. They lived on the lower Danube River, in the northwestern Black Sea region, and in the regions around the Don River. Scholars commonly associate the Antes with the archaeological Penkovka culture.

Much of the territory of the modern state of Serbia was part of the Roman Empire and later the Eastern Roman Empire. In particular, the region of Central Serbia was under Roman rule for about 800 years, starting from the 1st century BC, interrupted by the arrival of the Slavs into the Balkans during the 6th century, but continued after fall of the First Bulgarian Empire in the early 11th century and permanently ended with the rise of the Second Bulgarian Empire in the late 12th century. The territories were administratively divided into the provinces of Moesia, Pannonia and Dardania. Moesia Superior roughly corresponds to modern Serbia proper; Pannonia Inferior included the eastern part of Serbia proper; Dardania included the western part of Serbia proper. After its reconquest from the Bulgarians by Emperor Basil II in 1018, it was reorganized into the Theme of Bulgaria.

The early Slavs were an Indo-European peoples who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages in Central and Eastern Europe and established the foundations for the Slavic nations through the Slavic states of the High Middle Ages. The Slavs' original homeland is still a matter of debate due to a lack of historical records; however, scholars believe that it was in Eastern Europe, with Polesia being the most commonly accepted location.

The Penkovka culture is an archaeological culture in Ukraine, Moldova and reaching into Romania. Its western boundary is usually taken to at the middle Prut and Dniester rivers, where contact with the Korchak culture occurs. Its bearers are commonly identified as the Antes people of 6th-century Byzantine historiography.
Florin Curta is a Romanian-born American archaeologist and historian who is a professor of medieval history and archaeology at the University of Florida.
The Chronicle of Monemvasia is a medieval text of which four versions, all written in medieval Greek, are extant. The author of the account is currently unknown. The Chronicle, specifically the version from the Iberikon monastery, narrates the events that depict the Avaro-Slavic conquest and colonization of mainland Greece, covering a period from 587 to 805 AD. Despite its compelling narrative, the Chronicle is not an actual chronicle. The text represents a compilation of sources involving Avars and Slavs and focuses on the foundation of the metropolitan see of Patras. It is possible that the Chronicle was actually used in negotiations with the metropolitan of Corinth over the status of the metropolitan of Patras.
Boz was the king of the Antes, an early Slavic people that lived in parts of present-day Ukraine. His story is mentioned by Jordanes in the Getica (550–551); in the preceding years, the Ostrogoths under Ermanaric had conquered a large number of tribes in Central Europe, including the Antes. Some years after the Ostrogothic defeat by the invading Huns, a king named Vinitharius, Ermanaric's great-nephew, marched against the Antes of Boz and defeated them. Vinitharius condemned Boz, his sons, and seventy of his nobles, to crucifixion, in order to terrorize the Antes. These conflicts constitute the only pre-6th century contacts between Germanics and Slavs documented in written sources.
The Drougoubitai, also Drogobitai or Dragobitai, variously anglicized as Drugubites, Drogubites, Druguvites, Draguvites etc., were a South Slavic group (Sclaveni) who settled in the Balkans in the 7th century. Two distinct branches are mentioned in the sources, one living in medieval Macedonia to the north and east of Thessalonica and around Veroia.
The Belegezites were a South Slavic (Sklavenoi) tribe that lived in the area of Thessaly in the Early Middle Ages. They are one of the tribes listed in the Miracles of Saint Demetrius.

Archbishopric of Justiniana Prima was an Eastern Christian autonomous Archbishopric with see in the city of Justiniana Prima and jurisdiction over the Late Roman Diocese of Dacia in central parts of the Southeastern Europe.
Strymonites or Strymonian Slavs were a tribe of Sclaveni who settled in the region of the river Strymon (Struma) in eastern parts of the historical region of Macedonia.
The Baiounitai or Vayunites were a Sclavene tribe which settled the region of Macedonia at the end of 6th century. The Baiounitai initially settled in the region west of Thessalonica. They belonged to a group of Slavic tribes that unsuccessfully tried to capture the city at the beginning of the 7th century, after which they are believed to have migrated to the region of northern Epirus, between Ioannina in Greece and Himara in modern Albania.

Samo's Empire is the historiographical name for the West Slavic tribal union established by King ("Rex") Samo, which existed between 623/631 and 658 in Central Europe. The extension of Samo's power, before and after 631 is disputable.
This is a select bibliography of post-World War II English-language books and journal articles about the Early Slavs and Rus' and its borderlands until the Mongol invasions beginning in 1223. Book entries may have references to reviews published in academic journals or major newspapers when these could be considered helpful.









