The haloalkanes are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes that contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula "RX" where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen.
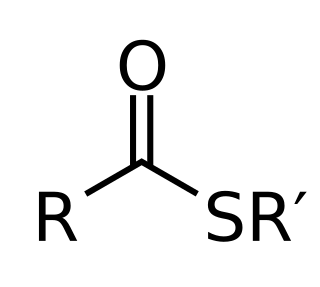
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the molecular structure R−C(=O)−S−R’. They are analogous to carboxylate esters with the sulfur in the thioester replacing oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the thio- prefix. They are the product of esterification of a carboxylic acid with a thiol. In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA. The R and R' represent organyl groups, or H in the case of R.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens. Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for and introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride.
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class includes common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious.

Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides/oxychlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride.
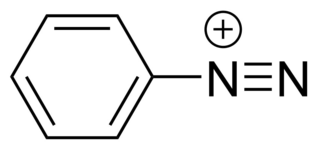
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group [R−N+≡N]X− where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide.
Geminal halide hydrolysis is an organic reaction. The reactants are geminal dihalides with a water molecule or a hydroxide ion. The reaction yields ketones from secondary halides or aldehydes from primary halides.
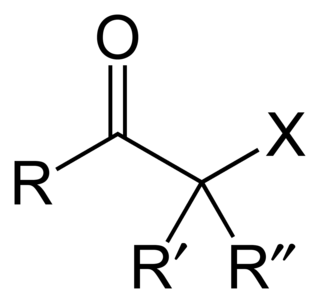
In organic chemistry, an α-halo ketone is a functional group consisting of a ketone group or more generally a carbonyl group with an α-halogen substituent. α-Halo ketones are alkylating agents. Prominent α-halo ketones include phenacyl bromide and chloroacetone.

Thiophosgene is a red liquid with the formula CSCl2. It is a molecule with trigonal planar geometry. There are two reactive C–Cl bonds that allow it to be used in diverse organic syntheses.
In inorganic chemistry, sulfonyl halide groups occur when a sulfonyl functional group is singly bonded to a halogen atom. They have the general formula RSO2X, where X is a halogen. The stability of sulfonyl halides decreases in the order fluorides > chlorides > bromides > iodides, all four types being well known. The sulfonyl chlorides and fluorides are of dominant importance in this series.
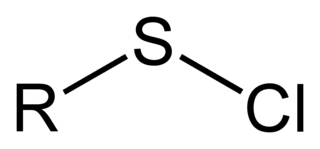
In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfenyl chloride is a functional group with the connectivity R−S−Cl, where R is alkyl or aryl. Sulfenyl chlorides are reactive compounds that behave as sources of RS+. They are used in the formation of RS−N and RS−O bonds. According to IUPAC nomenclature they are named as alkyl thiohypochlorites, i.e. esters of thiohypochlorous acid.
In organic chemistry, thiocarboxylic acids or carbothioic acids are organosulfur compounds related to carboxylic acids by replacement of one of the oxygen atoms with a sulfur atom. Two tautomers are possible: a thione form and a thiol form. These are sometimes also referred to as "carbothioic O-acid" and "carbothioic S-acid" respectively. Of these the thiol form is most common.

Sulfinyl halide have the general formula R−S(O)−X, where X is a halogen. They are intermediate in oxidation level between sulfenyl halides, R−S−X, and sulfonyl halides, R−SO2−X. The best known examples are sulfinyl chlorides, thermolabile, moisture-sensitive compounds, which are useful intermediates for preparation of other sufinyl derivatives such as sulfinamides, sulfinates, sulfoxides, and thiosulfinates. Unlike the sulfur atom in sulfonyl halides and sulfenyl halides, the sulfur atom in sulfinyl halides is chiral, as shown for methanesulfinyl chloride.

Imidoyl chlorides are organic compounds that contain the functional group RC(NR')Cl. A double bond exist between the R'N and the carbon centre. These compounds are analogues of acyl chloride. Imidoyl chlorides tend to be highly reactive and are more commonly found as intermediates in a wide variety of synthetic procedures. Such procedures include Gattermann aldehyde synthesis, Houben-Hoesch ketone synthesis, and the Beckmann rearrangement. Their chemistry is related to that of enamines and their tautomers when the α hydrogen is next to the C=N bond. Many chlorinated N-heterocycles are formally imidoyl chlorides, e.g. 2-chloropyridine, 2, 4, and 6-chloropyrimidines.

Organic thiocyanates are organic compounds containing the functional group RSCN. the organic group is attached to sulfur: R−S−C≡N has a S–C single bond and a C≡N triple bond.
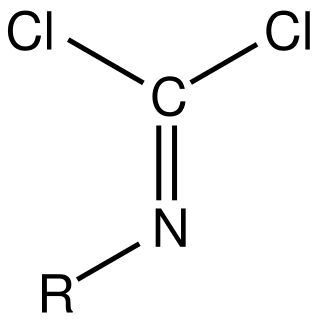
Isocyanide dichlorides are organic compounds containing the RN=CCl2 functional group. Classically they are obtained by chlorination of isocyanides. Phenylcarbylamine chloride is a well-characterized example.
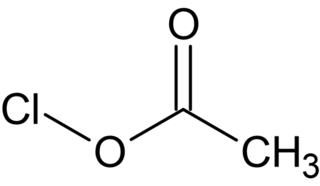
Acetyl hypochlorite, also known as chlorine acetate, is a chemical compound with the formula CH3COOCl. It is a photosensitive colorless liquid that is a short lived intermediate in the Hunsdiecker reaction.













