
Summer time in Europe is the variation of standard clock time that is applied in most European countries in the period between spring and autumn, during which clocks are advanced by one hour from the time observed in the rest of the year, with a view to making the most efficient use of seasonal daylight. It corresponds to the notion and practice of daylight saving time (DST) to be found in some other parts of the world.

The United Kingdom uses Greenwich Mean Time and British Summer Time (UTC+01:00).
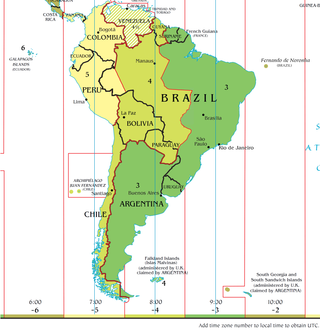
Argentina is located at a longitude that would naturally put it in the UTC−04:00 or UTC−05:00 time zone; however, it actually uses the UTC−03:00 time zone. Argentina determines whether to change clocks in observation of daylight saving time on a year-by-year basis, and individual provinces may opt out of the federal decision. At present, Argentina does not change clocks.

The time zone in Germany is Central European Time and Central European Summer Time. Daylight saving time is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. The doubled hour during the switch back to standard time is named 2A and 2B.

Pakistan uses one time zone, which is Pakistan Standard Time (PST). This is UTC+05:00 — that is, five hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time.

Time in Ukraine is defined as UTC+02:00 and in summer as UTC+03:00. Part of Eastern European Time, it is locally referred to as Kyiv Time. The change for the summer time takes place in the last Sunday of March at 03:00 when the time is changed by an hour ahead, and the last Sunday of October at 04:00, when the time changes an hour back. In this way, the clocks in Ukraine are always one hour ahead of those in central Europe.

Portugal has two time zones and observes daylight saving time. Continental Portugal and Madeira use UTC+00:00, while the Azores use UTC–01:00. Daylight saving time is observed nationwide from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October, when continental Portugal and Madeira advance one hour to UTC+01:00, and the Azores advances one hour to UTC+00:00.
Hungary is in the Central European Time zone, which is one hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The country observes Daylight Saving Time (DST). DST was first introduced in Hungary in 1916 and was observed until 1919. It was also in use between 1941–1949 and 1954–1957. DST has been in use again since 1980.
Switzerland uses Central European Time (CET) during the winter as standard time, which is one hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC+01:00), and Central European Summer Time (CEST) during the summer as daylight saving time, which is two hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC+02:00).

Spain has two time zones and observes daylight saving time. Spain mainly uses CET (UTC+01:00) and CEST (UTC+02:00) in Peninsular Spain, Ceuta, Melilla and the plazas de soberanía. In the Canary Islands, the time zone is WET (UTC±00:00) and WEST (UTC+01:00). DST is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October throughout Spain.

Denmark, including its dependencies of Faroe Islands and Greenland, uses six time zones.
Time in the Kingdom of the Netherlands is denoted by Central European Time during the winter as standard time in the Netherlands, which is one hour ahead of coordinated universal time (UTC+01:00), and Central European Summer Time (CEST) during the summer as daylight saving time, which is two hours ahead of coordinated universal time (UTC+02:00). The Caribbean Netherlands – which consist of the islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba – all observe Atlantic Standard Time (AST) year-round, which is four hours behind coordinated universal time (UTC−04:00).

Time in Poland is given by Central European Time. Daylight saving time, which moves an hour ahead, is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. This is shared with several other EU member states.
In Slovenia, the standard time is Central European Time. Daylight saving time is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. This is shared with several other EU member states.
In North Macedonia, the standard time is Central European Time. Daylight saving time is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. This is shared with several other EU member states.

Svalbard, an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean belonging to the Kingdom of Norway, uses Central European Time (CET) during the winter as standard time, which is one hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC+01:00), and Central European Summer Time (CEST) during the summer as daylight saving time, which is two hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC+02:00). This is shared with the rest of Norway, as is Svalbard's use of daylight saving time, which the territory observes annually by advancing the clock forward on the last Sunday in March and back again on the last Sunday in October. However, as Svalbard experiences midnight sun during the summer due to being located north of the Arctic Circle, it gives daylight saving time no utility, and is only observed in order to make communicating with Norway Proper more convenient. At the 74th parallel north, the midnight sun lasts 99 days and polar night 84 days, while the respective figures at the 81st parallel north are 141 and 128 days.

Time in Transnistria, a breakaway state internationally recognised as being part of Moldova, is given by Eastern European Time. Daylight saving time, which moves one hour ahead to UTC+03:00 is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October.

Time in Latvia is given by Eastern European Time. Daylight saving time, which moves one hour ahead to UTC+03:00 is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October.

Time in Lithuania is given by Eastern European Time. Daylight saving time, which moves one hour ahead to UTC+03:00 is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. Latvia adopted EET in 1920.

Time in Libya is given by a single time zone, officially denoted as Eastern European Time. The zone is also known as Central Africa Time (CAT). Libya has observed EET since 5 November 2012, after it was announced in 2013 that Libya would be on permanent daylight saving time. Libya previously observed several different time zones as standard time and daylight saving time. For residents of western Libya, including Tripoli, solar time is usually one hour behind standard time.






