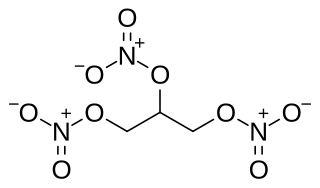
Nitroglycerin (NG), also known as trinitroglycerin (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating glycerol with white fuming nitric acid under conditions appropriate to the formation of the nitric acid ester. Chemically, the substance is an organic nitrate compound rather than a nitro compound, but the traditional name is retained. Discovered in 1847 by Ascanio Sobrero, nitroglycerin has been used as an active ingredient in the manufacture of explosives, namely dynamite, and as such it is employed in the construction, demolition, and mining industries. It is combined with nitrocellulose to form double-based smokeless powder, which has been used as a propellant in artillery and firearms since the 1880s.

Pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN), also known as PENT, pentyl, PENTA, TEN, corpent, or penthrite, is an explosive material. It is the nitrate ester of pentaerythritol, and is structurally very similar to nitroglycerin. Penta refers to the five carbon atoms of the neopentane skeleton. PETN is a very powerful explosive material with a relative effectiveness factor of 1.66. When mixed with a plasticizer, PETN forms a plastic explosive. Along with RDX it is the main ingredient of Semtex and C4.
Monopropellants are propellants consisting of chemicals that release energy through exothermic chemical decomposition. The molecular bond energy of the monopropellant is released usually through use of a catalyst. This can be contrasted with bipropellants that release energy through the chemical reaction between an oxidizer and a fuel. While stable under defined storage conditions, monopropellants decompose very rapidly under certain other conditions to produce a large volume of its own energetic (hot) gases for the performance of mechanical work. Although solid deflagrants such as nitrocellulose, the most commonly used propellant in firearms, could be thought of as monopropellants, the term is usually reserved for liquids in engineering literature.

A plasticizer is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.
ATC code C01Cardiac therapy is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup C01 is part of the anatomical group C Cardiovascular system.

Smokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to black powder. Because of their similar use, both the original black powder formulation and the smokeless propellant which replaced it are commonly described as gunpowder. The combustion products of smokeless powder are mainly gaseous, compared to around 55% solid products for black powder. In addition, smokeless powder does not leave the thick, heavy fouling of hygroscopic material associated with black powder that causes rusting of the barrel.

Otto fuel II is a monopropellant mixture of chiefly propylene glycol dinitrate that is used to drive torpedoes and other weapon systems. It was invented by Otto Reitlinger in 1963. Otto fuel II, sometimes known simply as Otto fuel, is not related to the Otto cycle; it is named after Reitlinger and for being the second iteration of the fuel. It was developed by the US Navy and the first torpedo to use it was the Mark 48 torpedo in the 1960s.

Mannitol hexanitrate is a powerful explosive. Physically, it is a powdery solid at normal temperature ranges, with density of 1.73 g/cm3. The chemical name is hexanitromannitol and it is also known as nitromannite, MHN, and nitromannitol, and by the trademarks Nitranitol and Mannitrin. It is more stable than nitroglycerin, and it is used in detonators.
Triethylene glycol, TEG, or triglycol is a colorless odorless viscous liquid with molecular formula HOCH2CH2OCH2CH2OCH2CH2OH. It is used as a plasticizer for vinyl polymers. It is also used in air sanitizer products, such as "Oust" or "Clean and Pure". When aerosolized it acts as a disinfectant. Glycols are also used as liquid desiccants for natural gas and in air conditioning systems. It is an additive for hydraulic fluids and brake fluids and is used as a base for "smoke machine" fluid in the entertainment industry.

Ethylene glycol dinitrate, abbreviated EGDN and NGC, also known as Nitroglycol, is a colorless, oily, explosive liquid obtained by nitrating ethylene glycol. It is similar to nitroglycerine in both manufacture and properties, though it is more volatile and less viscous. Unlike nitroglycerine, the chemical has a perfect oxygen balance, meaning that its ideal exothermic decomposition would completely convert it to low energy carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen gas, with no excess unreacted substances, without needing to react with anything else.
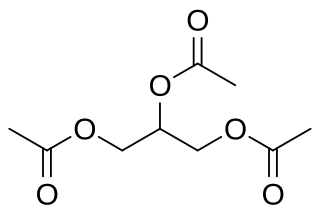
Triacetin is the organic compound with the formula C3H5(OCOCH3)3. It is classified as a triglyceride, i.e., the triester of glycerol with acetic acid. It is a colorless, viscous, and odorless liquid with a high boiling point and a low melting point. It has a mild, sweet taste in concentrations lower than 500 ppm, but may appear bitter at higher concentrations. It is one of the glycerine acetate compounds.

Nitroglycerin, also known as glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), is a vasodilator used for heart failure, high blood pressure (hypertension), anal fissures, painful periods, and to treat and prevent chest pain caused by decreased blood flow to the heart (angina) or due to the recreational use of cocaine. This includes chest pain from a heart attack. It is taken by mouth, under the tongue, applied to the skin, or by injection into a vein.

Propylene glycol dinitrate (PGDN, 1,2-propylene glycol dinitrate, or 1,2-propanediol dinitrate) is an organic chemical, an ester of nitric acid and propylene glycol. It is structurally similar to nitroglycerin, except that it has one fewer nitrate group. It is a characteristically and unpleasantly smelling colorless liquid, which decomposes at 121 °C, below its boiling point. It is flammable and explosive. It is shock-sensitive and burns with a clean flame producing water vapor, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen gas.

2-Nitrodiphenylamine is an organic chemical with the formula C6H5NHC6H4NO2. It is a nitrated derivative of diphenylamine. It is a red solid, usually found in form of flakes or powder. It is polar but hydrophobic.
A pyrotechnic composition is a substance or mixture of substances designed to produce an effect by heat, light, sound, gas/smoke or a combination of these, as a result of non-detonative self-sustaining exothermic chemical reactions. Pyrotechnic substances do not rely on oxygen from external sources to sustain the reaction.

1,2,4-Butanetriol trinitrate (BTTN), also called butanetriol trinitrate, is an important military propellant. It is a colorless to brown explosive liquid.

Diethylene glycol dinitrate (DEGDN) is an explosive nitrated alcohol ester with the formula C4H8N2O7. While chemically similar to numerous other high explosives, pure diethylene glycol dinitrate is difficult to ignite or detonate. Ignition typically requires localized heating to the decomposition point unless the DEGDN is first atomized.

A nitrovasodilator is a pharmaceutical agent that causes vasodilation by donation of nitric oxide (NO), and is mostly used for the treatment and prevention of angina pectoris.
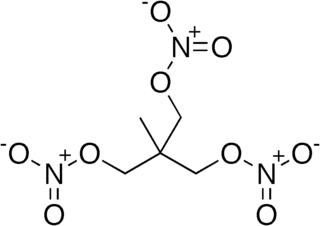
Trimethylolethane trinitrate (TMETN), also known as metriol trinitrate or nitropentaglycerin, is a nitrate ester. It is a high explosive similar to nitroglycerin. It is a transparent oily liquid, colorless to light brown. It is odorless. It is used in some solid propellants and smokeless powders as a plasticizer. Its chemical formula is CH3−C(CH2−O−NO2)3.
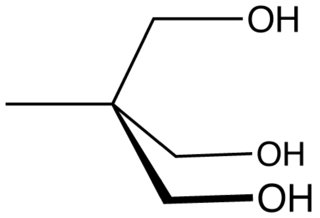
Trimethylolethane (TME) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(CH2OH)3. This colorless solid is a triol, as it contains three hydroxy functional groups. More specifically, it features three primary alcohol groups in a compact neopentyl structure. Its esters are known for their resistance to heat, light, hydrolysis, and oxidation. More important than TME and closely related is trimethylolpropane (TMP).















