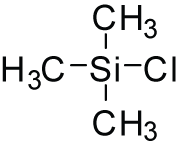Tetrahedrane is a hypothetical platonic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C4H4 and a tetrahedral structure. The molecule would be subject to considerable angle strain and has not been synthesized as of 2023. However, a number of derivatives have been prepared. In a more general sense, the term tetrahedranes is used to describe a class of molecules and ions with related structure, e.g. white phosphorus.

A silabenzene is a heteroaromatic compound containing one or more silicon atoms instead of carbon atoms in benzene. A single substitution gives silabenzene proper; additional substitutions give a disilabenzene, trisilabenzene, etc.

Europium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula EuCl3. The anhydrous compound is a yellow solid. Being hygroscopic it rapidly absorbs water to form a white crystalline hexahydrate, EuCl3·6H2O, which is colourless. The compound is used in research.

A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom [−Si(CH3)3], which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications.
Diphosphene is a type of organophosphorus compound that has a phosphorus–phosphorus double bond, denoted by R-P=P-R'. These compounds are not common but are of theoretical interest. Normally, compounds with the empirical formula RP exist as rings. However, like other multiple bonds between heavy main-group elements, P=P double bonds can be stabilized by a large steric hindrance from the substitutions. The first isolated diphosphene bis(2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenyl)diphosphene was exemplified by Masaaki Yoshifuji and his coworkers in 1981, in which diphosphene is stabilized by two bulky phenyl group.
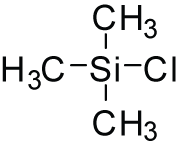
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound, with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry.

Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.
Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide (BSA) is an organosilicon compound with the formula MeC(OSiMe3)NSiMe3 (Me = CH3). It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in diverse organic solvents, but reacts rapidly with moisture and solvents containing OH and NH groups. It is used in analytical chemistry to increase the volatility of analytes, e.g., for gas chromatography. It is also used to introduce the trimethylsilyl protecting group in organic synthesis. A related reagent is N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA).
Silylation is the introduction of one or more (usually) substituted silyl groups (R3Si) to a molecule. Silylations are core methods for production of organosilicon chemistry. Silanization involves similar methods but usually refers to attachment of silyl groups to solids.

Organoindium chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing In-C bonds. The main application of organoindium chemistry is in the preparation of semiconducting components for microelectronic applications. The area is also of some interest in organic synthesis. Most organoindium compounds feature the In(III) oxidation state, akin to its lighter congeners Ga(III) and B(III).

Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetylene (BTMSA) is an organosilicon compound with the formula Me3SiC≡CSiMe3 (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. This compound is used as a surrogate for acetylene.
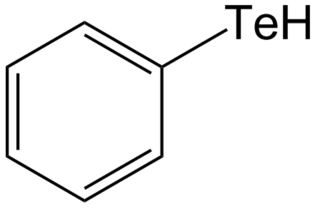
Tellurols are analogues of alcohols and phenols where tellurium replaces oxygen. Tellurols, selenols, and thiols have similar properties, but tellurols are the least stable. Although they are fundamental representatives of organotellurium compounds, tellurols are lightly studied because of their instability. Tellurol derivatives include telluroesters and tellurocyanates (RTeCN).
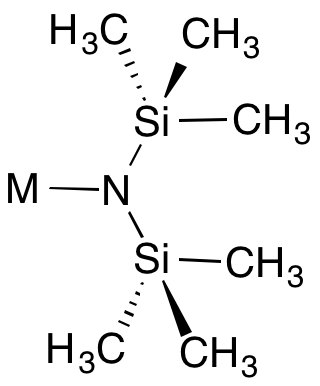
Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides are coordination complexes composed of a cationic metal M with anionic bis(trimethylsilyl)amide ligands (the −N 2 monovalent anion, or −N 2 monovalent group, and are part of a broader category of metal amides.

Trimethylsilyl iodide (iodotrimethylsilane or TMSI) is an organosilicon compound with the chemical formula (CH3)3SiI. It is a colorless, volatile liquid at room temperature.

Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine is the simplest tris(trialkylsilyl)amine which are having the general formula (R3Si)3N, in which all three hydrogen atoms of the ammonia are replaced by trimethylsilyl groups (-Si(CH3)3). Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine has been for years in the center of scientific interest as a stable intermediate in chemical nitrogen fixation (i. e. the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen N2 into organic substrates under normal conditions).
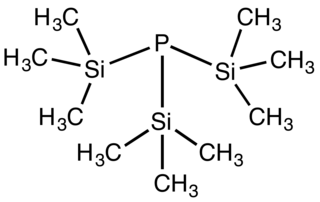
Tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P(SiMe3)3 (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid that ignites in air and hydrolyses readily.

Tris(dimethylamino)methane (TDAM) is the simplest representative of the tris(dialkylamino)methanes of the general formula (R2N)3CH in which three of the four of methane's hydrogen atoms are replaced by dimethylamino groups (−N(CH3)2). Tris(dimethylamino)methane can be regarded as both an amine and an orthoamide.

The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula C
3H+
3. It has attracted attention as the smallest example of an aromatic cation. Its salts have been isolated, and many derivatives have been characterized by X-ray crystallography. The cation and some simple derivatives have been identified in the atmosphere of the Saturnian moon Titan.

Tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)silane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (Me3Si)4Si (where Me = CH3). It is a colorless sublimable solid with a high melting point. The molecule has tetrahedral symmetry. The compound is notable as having silicon bonded to four other silicon atoms, like in elemental silicon.

(Trimethylsilyl)methyllithium is classified both as an organolithium compound and an organosilicon compound. It has the empirical formula LiCH2Si(CH3)3, often abbreviated LiCH2tms. It crystallizes as the hexagonal prismatic hexamer [LiCH2tms]6, akin to some polymorphs of methyllithium. Many adducts have been characterized including the diethyl ether complexed cubane [Li4(μ3-CH2tms)4(Et2O)2] and [Li2(μ-CH2tms)2(tmeda)2].


![Structure of [InC(tms)3]4, an In(I) tetrahedrane (dark gray = In, orange = Si). YUZZOI.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/ec/YUZZOI.svg/222px-YUZZOI.svg.png)