National Register of Historic Places listing
It was listed on the NRHP Orleans Parish, Louisiana on February 1, 2016. [5] There are nine contributing resources. Of those, three original warehouses were used as storage for military supplies and munitions from 1918 through 1945. In between wars, the storage space was rented out to commercial entities. [5] The other six contributing resources are the recreation pavilion/service station, switching building, cargo ramp, and three water tanks. [6] The fence, main switchgear and electric substation are non-contributing objects. Additional non-contributing structures include a gazebo, canopy, hazardous waste container, transformer house, and several pedestrian bridges. Non-contributing buildings include a corrugated metal shed, parking access ramp, racquetball facility, gas station, pass and tag building, and several sentry buildings and gates. [7]

Fort Sam Houston is a U.S. Army post in San Antonio, Texas. Known colloquially as "Fort Sam," it is named for the U.S. Senator from Texas, U.S. Representative from Tennessee, Tennessee and Texas governor, and first president of the Republic of Texas, Sam Houston.

Fort Myer is the previous name used for a U.S. Army post next to Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington County, Virginia, and across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. Founded during the American Civil War as Fort Cass and Fort Whipple, the post merged in 2005 with the neighboring Marine Corps installation, Henderson Hall, and is today named Joint Base Myer–Henderson Hall.

Fort Scott National Historic Site is a historical area under the control of the United States National Park Service in Bourbon County, Kansas, United States. Named after General Winfield Scott, who achieved renown during the Mexican–American War, during the middle of the 19th century the fort served as a military base for US Army action in what was the edge of settlement in 1850. For the next quarter century, it was used as a supply base and to provide security in turbulent areas during the opening of the West to settlement, a period which included Bleeding Kansas and the American Civil War.

Fort D. A. Russell, also known as Fort Francis E. Warren, Francis E. Warren Air Force Base and Fort David A. Russell, was a post and base of operations for the United States Army, and later the Air Force, located in Cheyenne, Wyoming. The fort had been established in 1867 to protect workers for the Union Pacific Railroad. It was named in honor of David Allen Russell, a Civil War general killed at the Battle of Opequon. In 1930, the fort's name was changed to Fort Francis E. Warren. In 1949, it became Francis E. Warren Air Force Base.

Jean Lafitte National Historical Park and Preserve protects the natural and cultural resources of Louisiana's Mississippi River Delta region. It is named after French pirate Jean Lafitte and consists of six separate sites and a park headquarters.

Fort Ethan Allen was a United States Army installation in Vermont, named for American Revolutionary War figure Ethan Allen. Established as a cavalry post in 1894 and closed in 1944, today it is the center of a designated national historic district straddling the town line between Colchester and Essex. Locally, it is known simply as "The Fort", and now houses a Vermont National Guard installation a variety of businesses, academic institutions, and residential areas.

Fort Mason, in San Francisco, California originated as a coastal defense site during the American Civil War. The nucleus of the property was owned by John C. Frémont and disputes over compensation by the United States continued into 1968. In 1882 the defenses were named for Richard Barnes Mason, a military governor before statehood. Fort Mason became the headquarters for an Army command that included California and the Hawaiian Islands from 1904 to 1907. In 1912 the Army began building a port facility with piers and warehouses to be a home base for ships of the Army Transport Service serving Alaska, Hawaii, the Philippines and other Pacific Army posts and focus of Army supply for the Pacific.

Louisiana National Guard Training Center Pineville is a Louisiana National Guard installation located northeast of Pineville, Louisiana, primarily in Rapides Parish, but also extending northward into Grant Parish. It is operated and owned by the Louisiana National Guard as one of their main training areas.

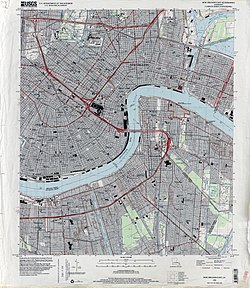
Fort Pike State Historic Site is a decommissioned 19th-century United States fort, named after Brigadier General Zebulon Pike. It was built following the War of 1812 to guard the Rigolets pass in Louisiana, a strait from the Gulf of Mexico, via Lake Borgne, to Lake Pontchartrain bordering New Orleans. It was located near the community of Petite Coquille, now within the city limits of New Orleans.

The Van Wyck Homestead Museum or Van Wyck-Wharton House is an early 18th-century Dutch colonial house in the Town of Fishkill, New York, United States of America. It served as a headquarters to a major military supply depot during the American Revolutionary War and has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places since April 13, 1972; the adjoining Fishkill Supply Depot Site has been listed on the NRHP since January 21, 1974. It is located on US 9 just south of Interstate 84. Excavations during the construction of a nearby gas station and the Dutchess Mall in the early 1970s unearthed many artifacts at the site, particularly materiel.
Fort Holabird was a United States Army post in the city of Baltimore, Maryland, active from 1918 to 1973.

Fort Yuma was a fort in California located in Imperial County, across the Colorado River from Yuma, Arizona. It was Established in 1848. It served as a stop on the Butterfield Overland Mail route from 1858 until 1861. The fort was retired from active military service on May 16, 1883, and transferred to the Department of the Interior. The Fort Yuma Indian School and the Saint Thomas Yuma Indian Mission now occupy the site. It is one of the "associated sites" listed as Yuma Crossing and Associated Sites on the National Register of Historic Places in the Yuma Crossing National Heritage Area. In addition, it is registered as California Historical Landmark #806.

Marine Corps Logistics Base Barstow is a United States Marine Corps supply and maintenance installation located in the Mojave Desert east of Barstow, in San Bernardino County, Southern California.

Naval Support Activity New Orleans was a United States Navy installation until September 2011. During its time in operation, it was the largest military installation in greater New Orleans. It hosts activities for other branches of service and federal agencies.

Fort Omaha, originally known as Sherman Barracks and then Omaha Barracks, is an Indian War-era United States Army supply installation. Located at 5730 North 30th Street, with the entrance at North 30th and Fort Streets in modern-day North Omaha, Nebraska, the facility is primarily occupied by the Metropolitan Community College. A Navy Operational Support Center and Marine Corps Reserve unit, along with an Army Reserve unit occupy the periphery of the 82.5 acres (33.4 ha) fort. The government deeded all but four parcels of the land to the Metropolitan Community College in 1974.

The Omaha Quartermaster Depot Historic District, including several brick structures built in Italianate and other styles, was built for the U.S. Army between 1881 and 1894. Located in South Omaha between Hickory and 22nd Streets, Woolworth Avenue and the Union Pacific Railroad main line in Omaha, Nebraska, the depot was listed on the National Register of Historic Places as a historic district in 1979. The depot previously operated as United States Army Reserve facility. The facility is considered surplus by the GSA and was put up for auction in the fall of 2013.

The Philadelphia Quartermaster Depot, now known as the Defense Logistics Agency Troop Support, was founded as the Schuylkill Arsenal in 1799.

The United States Army Transport Service (ATS) was established as a sea-going transport service that was independent of the Navy Department. ATS operated army transport ships for both troop transport and cargo service between United States ports and overseas posts. This service is often confused with the Army Transportation Service, created in France in 1917 to manage American Expeditionary Forces transport. ATS was a branch of the Quartermaster Corps responsible for land and water transport, becoming a separate United States Army Transportation Corps on July 31, 1942.

Naval Station Pearl Harbor is a United States naval base on the island of Oahu, Hawaii. In 2010, as part of the recommendations of the Base Realignment and Closure (BRAC) commission, the naval station was consolidated with the United States Air Force's Hickam Air Force Base to form Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam. Since 1940, Pearl Harbor has been the headquarters of the United States Pacific Fleet.
New Orleans Military Ocean Terminal (NOMOT) was a large military ocean terminal at New Orleans, Louisiana. It served as a transfer point between rail, trucks, and ships for the import and export of weapons, ammunition, explosives and military equipment for the United States Army. It was located at 4400 Dauphine Street New Orleans, Louisiana 70145 on the Mississippi River and Inner Harbor Navigation Canal, also called the Industrial Canal, the entrance to the Turning Basin in Bywater, New Orleans. New Orleans Military Ocean Terminal had three large warehouses at Dauphine Street and Poland Ave on the 25-acre site. New Orleans Military Ocean Terminal has 1.5 million square feet of floor space and a 5 story parking garage. The terminal was closed in September 2011 and ownership was transferred to the City of New Orleans in 2014.