The General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) is an academic qualification in a particular subject, taken in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. State schools in Scotland use the Scottish Qualifications Certificate instead. Private schools in Scotland may choose to use GCSEs from England.
The General Certificate of Education (GCE) is a subject-specific family of academic qualifications used in awarding bodies in England, Wales, Northern Ireland, Crown dependencies and a few Commonwealth countries. For some time, the Scottish education system has been different from those in the other countries of the United Kingdom.
National Vocational Qualifications (NVQs) are practical work-based awards in England, Wales and Northern Ireland that are achieved through assessment and training. The regulatory framework supporting NVQs was withdrawn in 2015 and replaced by the Regulated Qualifications Framework (RQF), although the term "NVQ" may be used in RQF qualifications if they "are based on recognised occupational standards, work-based and/or simulated work-based assessment and where they confer occupational competence".

The British undergraduate degree classification system is a grading structure for undergraduate degrees or bachelor's degrees and integrated master's degrees in the United Kingdom. The system has been applied in other countries and regions.
In the Scottish secondary education system, the Higher is one of the national school-leaving certificate exams and university entrance qualifications of the Scottish Qualifications Certificate (SQC) offered by the Scottish Qualifications Authority. It superseded the old Higher Grade on the Scottish Certificate of Education (SCE). Both are normally referred to simply as "Highers".
Vocational Certificate of Education, usually shortened to VCE or Vocational A-Level or AVCE, was a vocational qualification that used to be available in further education colleges and sixth forms in the United Kingdom.
The Advanced Higher is an optional qualification which forms part of the Scottish secondary education system brought in to replace the Certificate of Sixth Year Studies (CSYS). The first certification of Advanced Higher was in 2001. It is normally taken by students aged around 16–18 years of age after they have completed Highers, which are the main university entrance qualification in Scotland.
The Welsh Baccalaureate, or Welsh Bacc, is an educational qualification delivered in secondary schools and colleges across Wales. The Welsh Government says that it gives broader experiences than traditional learning programmes, developing transferable skills useful for education and employment. The Welsh Bacc is offered at Advanced, National Foundation and National/Foundation level, and is studied alongside a range of academic and vocational qualifications.
The Scottish Certificate of Education was a Scottish secondary education certificate, used in schools and sixth form institutions, from 1962 until 1999. It replaced the older Junior Secondary Certificate (JSC) and the Scottish Leaving Certificate (SLC), and it was the Scottish equivalent of the General Certificate of Education, used in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. One primary distinction between the Scottish Leaving Certificate and the Scottish Certificate of Education was that the latter had less strict regulations in terms of compulsory subjects and workload of the individual curricula.
The Scottish Qualifications Certificate (SQC) is the successor to the Scottish Certificate of Education and the Record of Education and Training, and is the main educational qualification awarded to students in secondary, further, and vocational education. The SQC is awarded by the Scottish Qualifications Authority. It forms part of the wider array of qualifications available in the Scottish education system, including Scottish Vocational Qualifications, Higher National Certificates and Higher National Diplomas. Each level is fully integrated with the Scottish Credit and Qualifications Framework and the three upper levels are awarded UCAS Tariff Points.
The BTEC Level 3 diploma is a Further Education qualification and vocational qualification taken in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The qualification is organised and awarded by Pearson within the BTEC brand and it is equivalent to A-Levels. It is equivalent to the GCE A Levels, more specifically to three A2 awards and the AVCE.

The A Level is a subject-based qualification conferred as part of the General Certificate of Education, as well as a school leaving qualification offered by the educational bodies in the United Kingdom and the educational authorities of British Crown dependencies to students completing secondary or pre-university education. They were introduced in England and Wales in 1951 to replace the Higher School Certificate.
The General Certificate of Education (GCE) Advanced Level, or A Level, is a main school leaving qualification in England, Wales, Northern Ireland, the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man. It is available as an alternative qualification in other countries.
An Extended Project Qualification (EPQ) is a qualification taken by some students in England and Wales, which is equivalent to 50% of an A level. They are part of level three of the National Qualifications Framework. It is currently graded A*-E.
The BTEC Foundation Diploma in Art and Design is a vocational qualification taken in England and Wales and Northern Ireland by young people aged 18 and over and by adults. The qualification is organised and awarded by the Edexcel Foundation within the BTEC brand.
Alternative pathways in education are alternative means of obtaining educational qualifications, other than the traditional means of gaining access to or completing the required study to obtain the educational qualifications.
A high school diploma or high school degree is a North American academic school leaving qualification awarded upon high school graduation. The high school diploma is typically obtained after a course of study lasting four years, from grade 9 to grade 12. The diploma is awarded by the school in accordance with the requirements of the local state or provincial government. Requirements for earning the diploma vary by jurisdiction, and there may be different requirements for different streams or levels of high school graduation. Typically they include a combination of selected coursework meeting specified criteria for a particular stream and acceptable passing grades earned on the state exit examination.
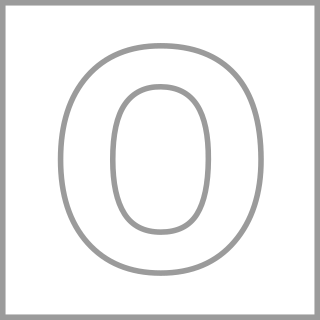
The General Certificate of Education (GCE) Ordinary Level, also called the O-level or O level, was a subject-based academic qualification. Introduced in 1951 as a replacement for the 16+ School Certificate (SC), the O-level would act as a pathway to the new, more in-depth and academically rigorous A-level, in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. Later the complementary and more vocational Certificate of Secondary Education (CSE) was added to broaden the subjects available and offer qualifications in non-academic subjects.
In the United Kingdom, the Technical Level, or more commonly, the Tech Level, is a school leaving qualification offered by educational bodies to students completing secondary or pre-university education. Tech-Levels are the vocational equivalent of the A-levels and is generally required for university entrance. Tech-Levels are generally worked towards over two years and split into a number of parts, with one part studied in each year. The first part is known as the Certificate Level. The second part is known as the Diploma Level and is more in-depth and rigorous than the Certificate Level. The Certificate Level is a qualification in its own right, and the Certificate Units combined with the Diploma units forms the complete Technical Level qualification. T Levels will offer students a mixture of classroom learning and ‘on-the-job’ experience during an industry placement of at least 315 hours.



