
Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd, or SSTL, is a company involved in the manufacture and operation of small satellites. A spin-off company of the University of Surrey, it is presently wholly owned by Airbus Defence and Space.
CLEO - Cisco router in Low Earth Orbit, is an Internet router from Cisco Systems that was integrated into the UK-DMC Disaster Monitoring Constellation satellite built by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd (SSTL) as a secondary experimental hosted payload, and launched into space with the satellite from Plesetsk on 27 September 2003.
The Disaster Monitoring Constellation for International Imaging (DMCii) or just Disaster Monitoring Constellation (DMC) consists of a number of remote sensing satellites constructed by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd (SSTL) and operated for the Algerian, Nigerian, Turkish, British and Chinese governments by DMC International Imaging. The DMC provides emergency Earth imaging for disaster relief under the International Charter for Space and Major Disasters, which the DMC formally joined in November 2005. Other DMC Earth imagery is used for a variety of civil applications by a variety of governments. Spare available imaging capacity is sold under contract.

An electrically powered spacecraft propulsion system uses electrical, and possibly also magnetic fields, to change the velocity of a spacecraft. Most of these kinds of spacecraft propulsion systems work by electrically expelling propellant at high speed.

The Advanced Research and Global Observation Satellite (ARGOS) was launched on 23 February 1999 carrying nine payloads for research and development missions by nine separate researchers. The mission terminated on 31 July 2003.

Landsat 8 is an American Earth observation satellite launched on 11 February 2013. It is the eighth satellite in the Landsat program; the seventh to reach orbit successfully. Originally called the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM), it is a collaboration between NASA and the United States Geological Survey (USGS). NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, provided development, mission systems engineering, and acquisition of the launch vehicle while the USGS provided for development of the ground systems and will conduct on-going mission operations. It comprises the camera of the Operational Land Imager (OLI) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) which can be used to study Earth surface temperature and is used to study global warming.
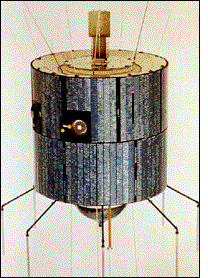
Applications Technology Satellite 3, or ATS-3, was a long-lived American experimental geostationary weather and communications satellite, operated by NASA from 1967 to 2001. It was at one time reputed to be the oldest satellite still in operation. As of 1995, NASA referred to the ATS-3 as "The oldest active communications satellite by a wide margin."
SNAP-1 is a British nanosatellite in low Earth orbit. The satellite was built at the Surrey Space Centre by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd (SSTL) and members of the University of Surrey. It was launched on 28 June 2000 on board a Kosmos-3M rocket from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome in northern Russia. It shared the launch with a Russian Nadezhda search and relay spacecraft and the Chinese Tsinghua-1 microsatellite.
Deimos-1 is a Spanish Earth imaging satellite which is operated by Deimos Imaging who commercializes its imagery directly but also has distribution agreements with other entities like Astrium GEO and DMC International Imaging.
UK-DMC 2 is a British Earth imaging satellite which is operated by DMC International Imaging. It was constructed by Surrey Satellite Technology, based on the SSTL-100 satellite bus. It is part of Britain's contribution to the Disaster Monitoring Constellation, which is coordinated by DMC International Imaging. It is the successor to the UK-DMC satellite.
ALSAT-1 is the first Algerian satellite and it is part of a group of satellites collectively known as the Disaster Monitoring Constellation (DMC). The satellite was built by a group of engineers from Surrey Satellite Technology (SSTL) and Algerian Centre National des Techniques Spatiales (CNTS). It was the first DMC satellite to be launched of the five to seven that are planned. The DMC was the first satellite constellation designed for that objective. The launch took place on 28 November 2002 from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome in northern Russia on a Kosmos-3M launcher in -20 degree Celsius weather. It completed its mission after seven years and nine months in August 2010. The satellite was designed to operate for five years.

Space tethers are long cables which can be used for propulsion, momentum exchange, stabilization and attitude control, or maintaining the relative positions of the components of a large dispersed satellite/spacecraft sensor system. Depending on the mission objectives and altitude, spaceflight using this form of spacecraft propulsion is theorized to be significantly less expensive than spaceflight using rocket engines.
Miranda, also known as X-4, is a British satellite in low Earth orbit. The satellite was launched in March 1974 as an engineering test bed of technologies in orbit.
BILSAT-1 was an earth observation satellite designed and developed by TÜBİTAK Space Technologies Research Institute and produced in Turkey as part of the Disaster Monitoring Constellation (DMC) project in the context of a show-how program led by DMC International Imaging of Surrey Satellite Technology (SSTL).
Sapphire is a Canadian space surveillance satellite which was launched in 2013. Sapphire was commissioned and integrated by MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates (MDA) based on an SSTL-150 bus produced by Surrey Satellite Technology (SSTL) and an optical payload produced by COM DEV International.
PSLV-C28 was the 29th consecutive successful mission of the PSLV program. The PSLV-C28 carried and successfully deployed 5 satellites in the Sun-synchronous orbit. With a launch mass of 320,000 kilograms (710,000 lb) and payload mass of payload mass 1,440 kilograms (3,170 lb), the C28 was the heaviest commercial mission undertaken by the Indian Space Research Organisation and Antrix Corporation. The PSLV-C28 carried three identical optical earth observation satellites, an optical earth observation technology demonstrator microsatellite (CBNT-1), and an experimental nanosatellite (De-orbitSail). All the satellites were built by Surrey Satellite Technology (SSTL). Although built by SSTL, the "De-orbitSail" belonged to the Surrey Space Centre.
Alsat-1B is an Algerian satellite operated by the Agence Spatiale Algerienne for agricultural and disaster monitoring. The contract for the mission was signed in July 2014. The satellite is based on the SSTL-100 bus. The satellite weighs 103 kilograms (227 lb) and carries an earth imaging payload with 12-metre (39 ft) panchromatic imager and 24-metre (79 ft) multispectral cameras.
ArgoMoon is a nanosatellite that will fly on NASA's Artemis 1 mission into a heliocentric orbit in cislunar space on the maiden flight of the Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft, in 2021. The satellite has the dimensions of a shoe box in CubeSat terms, it is a 6U.
EQUULEUS is a nanosatellite of the 6U CubeSat format that will measure the distribution of plasma that surrounds the Earth (plasmasphere) to help scientists understand the radiation environment in that region. It will also demonstrate low-thrust trajectory control techniques, such as multiple lunar flybys, within the Earth-Moon region using water steam as propellant. The spacecraft was designed and developed jointly by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the University of Tokyo.

PSLV-C42 was the 44th mission of the Indian Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) program and its 12th mission in the Core Alone (CA) configuration. PSLV-C42 successfully carried and deployed 2 earth observation satellites in sun-synchronous orbits at an altitude of 588 kilometres (365 mi). It was launched on 16 September 2018 by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) from the first launch pad of the Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. The two international satellites were launched as part of a commercial arrangement between Surrey Satellite Technology Limited (SSTL) and ISRO's commercial arm Antrix Corporation Limited, run under the auspices of the Indian Government's Department of Space.






