Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-10-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles, and no trailing wheels. This arrangement was often named Decapod, especially in the United States, although this name was sometimes applied to locomotives of 0-10-0 "Ten-Coupled" arrangement, particularly in the United Kingdom. Notable German locomotives of this type include the war locomotives of Class 52.

The Norfolk and Western Railway, commonly called the N&W, was a US class I railroad, formed by more than 200 railroad mergers between 1838 and 1982. It was headquartered in Roanoke, Virginia, for most of its existence. Its motto was "Precision Transportation"; it had a variety of nicknames, including "King Coal" and "British Railway of America". In 1986, N&W merged with Southern Railway to form today's Norfolk Southern Railway.
A 2-8-8-2, in the Whyte notation for describing steam locomotive wheel arrangements, is an articulated locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a two-wheel trailing truck. The equivalent UIC classification is, refined to Mallet locomotives, (1'D)D1'. These locomotives usually employ the Mallet principles of articulation—with the rear engine rigidly attached to the boiler and the front engine free to rotate—and compounding. The 2-8-8-2 was a design largely limited to American locomotive builders. The last 2-8-8-2 was retired in 1962 from the N&W's roster, two years past the ending of steam though steam was still used on steel mill lines and other railroads until 1983.
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a 2-6-6-2 is a locomotive with one pair of unpowered leading wheels, followed by two sets of three pairs of powered driving wheels and one pair of trailing wheels. The wheel arrangement was principally used on Mallet-type articulated locomotives, although some tank locomotive examples were also built. A Garratt locomotive or Golwé locomotive with the same wheel arrangement is designated 2-6-0+0-6-2 since both engine units are pivoting.

The USRA 0-6-0 was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. This was the standard light switcher locomotive of the USRA types, and was of 0-6-0 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or "C" in UIC classification.
The USRA 0-8-0 was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. This was the standard heavy switcher locomotive of the USRA types, and was of 0-8-0 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or "D" in UIC classification.

The USRA Light Mikado was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. This was the standard light freight locomotive of the USRA types, and was of 2-8-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 1′D1′ in UIC classification.

The USRA Heavy Mikado was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration (USRA), the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. These locomotives were of 2-8-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 1′D1′ in UIC classification. A total of 233 locomotives were built to this plan for the USRA; postwar, it became a de facto standard design, which was built to the total of 957 locomotives including the USRA originals and all subsequent copies.

The USRA Heavy Santa Fe was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. These locomotives were of 2-10-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 1′E1′ in UIC classification; this arrangement was commonly named "Santa Fe" in the United States. At the time, the Santa Fe was the largest non-articulated type in common use, primarily in slow drag freight duty in ore or coal service.
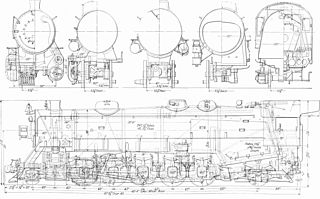
The USRA Light Santa Fe was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. These locomotives were of 2-10-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 1′E1′ in UIC classification; this arrangement was commonly named "Santa Fe" in the United States. At the time, the Santa Fe was the largest non-articulated type in common use, primarily in slow drag freight duty in ore or coal service.

Norfolk and Western 475 is a 4-8-0 "Mastodon" type steam locomotive built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in June 1906 as part of the Norfolk and Western Railway's (N&W) first order of M class numbered 375–499. It was first assigned to haul freight trains on the N&W mainline before being reassigned to branch line duties on the Blacksburg Branch in the 1920s.

Southern Railway 1401 is a 4-6-2 steam locomotive built in July 1926 by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) of Richmond, Virginia, for the Southern Railway (SOU) as a member of the Ps-4 class, which was based on the United States Railroad Administration (USRA) Heavy Pacific design with some minor differences. It was assigned to haul the SOU's Crescent Limited passenger train between Washington, D.C., and Atlanta, Georgia.

The USRA Light Pacific was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. It was the standard light passenger locomotive of the USRA types, with a 4-6-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 2′C1′ in UIC classification.

Atlanta and West Point 290 is a P-74 steam locomotive built in March 1926 by the Lima Locomotive Works (LLW) in Lima, Ohio for the Atlanta and West Point Railroad. It is a 4-6-2 heavy "Pacific" type steam locomotive, which was remarkably similar to the Southern Railway's Ps-4 class. With sister locomotive No. 190 built for the Western Railway of Alabama (WRA), No. 290 ferried the Southern Railway's Crescent passenger train from Atlanta, Georgia to Montgomery, Alabama until its retirement from revenue service in 1954.

The Southern Railway Ps-4 was a class of 4-6-2 steam locomotives built for the Southern Railway, as well as its subsidiaries, the Alabama Great Southern Railroad and the Cincinnati, New Orleans and Texas Pacific Railway. The locomotives were notable for their green with gold trim liveries, and have been regarded by Smithsonian curator John H. White Jr. as being "among the most celebrated passenger locomotives operated in the United States...."
The USRA Heavy Pacific was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. This was the standard heavy passenger locomotive of the USRA types, and was 4-6-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 2′C1′ in UIC classification.
The USRA Light Mountain was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. This was the standard light freight locomotive of the USRA types, and was of 4-8-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 2′D1′ in UIC classification.
The USRA Heavy Mountain was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. This was the standard light freight locomotive of the USRA types, and was of 4-8-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 2′D1′ in UIC classification.

Norfolk and Western 2050 is a class "Y3a" 2-8-8-2 Mallet steam locomotive built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) at their own Richmond Works for the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1923.












