USS Baltimore was a ship of the United States Navy.

The third USS Boston was a 32-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted frigate of the United States Navy. Boston was built by public subscription in Boston under the Act of 30 June 1798. Boston was active during the Quasi-War with France and the First Barbary War. On 12 October 1800, Bostonengaged and captured the French corvette Berceau. Boston was laid up in 1802, and considered not worth repairing at the outbreak of the War of 1812. She was burned at the Washington Naval Yard on 24 August 1814 to prevent her capture by British forces.

USS Constellation was a nominally rated 38-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted frigate of the United States Navy.
The first USS Eagle, a schooner, was built at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1798, and commissioned in the Revenue Cutter Service under the command of Captain H. G. Campbell, USRCS. She placed under control of the Navy in July 1798 for service in the undeclared naval war (Quasi-War) with France.
USS Ganges was a man-of-war in the United States Navy during the Quasi-War with France.
The first USS Montezuma was a merchant ship built in Virginia in 1795. The United States Navy acquired her during the Quasi-War with France and retained her name.
The first USS Norfolk was a brig in the United States Navy during the Quasi-War with France.
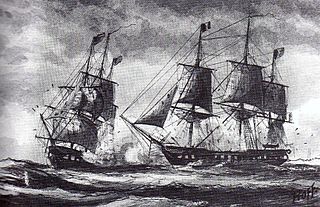
L'Insurgente was a 40-gun Sémillante-class frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1793. During the Quasi War with the United States, the United States Navy frigate USS Constellation, with Captain Thomas Truxtun in command, captured her off the island of Nevis. After her capture she served in the United States Navy as USS Insurgent, patrolling the waters in the West Indies. In September 1800 she was caught up in a severe storm and was presumed lost at sea.

USS Pickering was a brig, the 1st brig built for the UCRC Service, in the United States Revenue Cutter Service and then the United States Navy during the Quasi-War with France. She was named for Timothy Pickering, then the Secretary of State.
The first USS George Washington was a frigate in the United States Navy. She was named after United States Founding Father and President George Washington.
The second USS Delaware was a ship which served in the United States Navy during Quasi-War with France.
USS Merrimack, was a ship launched by an Association of Newburyport Shipwrights and presented to the Navy in 1798. She was the first ship of the Navy to be named for the Merrimack River. She saw action in the Quasi-War.
USS Portsmouth was constructed for the United States Navy in 1798 by master shipbuilder James Hackett to a design of Josiah Fox at what is now Badger's Island in Kittery, Maine, directly across the Piscataqua River from Portsmouth, New Hampshire. She was built with funds contributed by the citizens of Portsmouth.
USS Richmond was a brig purchased for the US Navy in 1798 by the citizens of Richmond, Petersburg, Manchester and Norfolk, Virginia, while being built at Norfolk as Augusta for a Mr. Myers. Renamed Richmond, she was fitted out in the fall of that year and in December stood out from Hampton Roads for the Caribbean with Captain Samuel Barron in command for service in the Quasi-War with France.
USS Herald was a full-rigged ship of about 270 tons burthen built in 1797 at Newburyport, Massachusetts. The US Navy purchased her on 15 June 1798, and sold her in 1801. She became the French 20-gun privateer corvette Africaine. In 1804 a British privateer seized her on 4 May 1804 off the coast, near Charleston, South Carolina. The seizure gave rise to a case in the U.S. courts that defined the limits of U.S. territorial waters. The U.S. courts ruled that the privateer had seized Africaine outside U.S. jurisdiction. Africaine then became a Liverpool-based slave ship that made two voyages carrying slaves from West Africa to the West Indies. After the abolition of the slave trade in 1807 she became a West Indiaman that two French privateers captured in late 1807 or early 1808.
USRC Virginia was a schooner built in 1797 for the United States Revenue Cutter Service at Portsmouth, Virginia. At the outset of the Quasi-War in 1798, the only ships available to the Navy were the 10 ships of the Revenue cutter service, the largest of which was the Virginia. She was transferred to the Navy in 1798 and served in the Quasi War until 1800, when she was returned to the Revenue Cutter Service, recommissioned in 1802 and sold in 1807.
HMS Pheasant was an 18-gun Merlin class sloop of the Royal Navy.

Diligente was a French Navy Naïade-class corvette, launched in 1794 as a brig. HMS Crescent captured her in the Antilles in 1800. The British took her into service as a 14-gun transport and sold her in 1814.

Experiment was a 50-gun ship of the line of the British Royal Navy. Captured by Sagittaire during the War of American Independence, she was recommissioned in the French Navy, where she served into the 1800s.

HMS Aeolus (1758) was a 32-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. In 1800, she renamed as HMS Guernsey.






