
USS Culgoa (AF-3) was a refrigerated supply ship in the United States Navy.

USS Langley (CV-1/AV-3) was the United States Navy's first aircraft carrier, converted in 1920 from the collier USS Jupiter, and also the US Navy's first turbo-electric-powered ship. Conversion of another collier was planned but canceled when the Washington Naval Treaty required the cancellation of the partially-built Lexington-class battlecruisers Lexington and Saratoga, freeing up their hulls for conversion to the aircraft carriers Lexington and Saratoga. Langley was named after Samuel Pierpont Langley, an American aviation pioneer. Following another conversion to a seaplane tender, Langley fought in World War II. On 27 February 1942, while ferrying a cargo of USAAF P-40s to Java, she was attacked by nine twin-engine Japanese bombers of the Japanese 21st and 23rd naval air flotillas and so badly damaged that she had to be scuttled by her escorts.

USS New Orleans was a United States Navy protected cruiser of the New Orleans class.
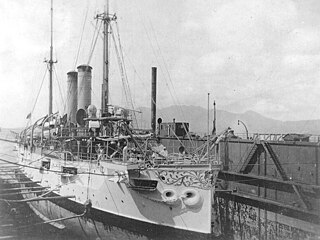
USS Cleveland (C-19/PG-33/CL-21) was a United States Navy Denver-class protected cruiser.

The third USS Albany was a United States Navy protected cruiser of the New Orleans class. She saw service in the Philippine–American War and World War I.

The first USS Astoria (SP-2005/AK-8) was a steel-hulled, coal-burning steam cargo ship of the United States Navy.

The second USS Sacramento (PG-19) was a gunboat in the United States Navy.

USS Sara Thompson (SP-3148/AO-8) was a tanker in the United States Navy. She was purchased at the start of World War I by the U.S. Navy and served as a tanker supporting American troops in Europe. Post-war she operated in the Pacific Ocean, supporting Navy operations in the Guam, China, and the Philippines. Because of her age and deteriorating condition, she spent her final days in the US Navy as a receiving hulk in the Philippines.

The first USS Saturn (AG-4) was an iron collier in the United States Navy.

USS Isabel (SP-521), later PY-10, was a yacht in commission in the United States Navy as a destroyer from 1917 to 1920 and as a patrol yacht from 1921 to 1946.

USS Fulton (AS-1) was constructed as a submarine tender in 1914, but later was converted into a gunboat and redesignated PG-49.

USS Brutus, formerly the steamer Peter Jebsen, was a collier in the United States Navy. She was built in 1894 at South Shields-on-Tyne, England, by John Readhead & Sons and was acquired by the U.S. Navy early in 1898 from L. F. Chapman & Company. She was renamed Brutus and commissioned at the Mare Island Navy Yard on 27 May 1898, with Lieutenant Vincendon L. Cottman, commanding officer and Lieutenant Randolph H. Miner, executive officer.

USS Celtic (AF-2) was a Celtic-class stores ship acquired by the U.S. Navy for use in the Spanish–American War. She served again during World War I in the dangerous North Atlantic Ocean, delivering general goods and ammunition to American Expeditionary Force troops in Europe.

USS Glacier (AF-4) was a Glacier-class stores ship acquired by the U.S. Navy for use in the Spanish–American War. She served again during World War I in the dangerous North Atlantic Ocean, delivering general goods and ammunition to American Expeditionary Force troops in Europe.

USS Houston (AK-1) was a cargo ship that was acquired by the U.S. Navy for service in World War I. During World War II, she served as a commercial cargo ship under charter to the United States Lines by the War Shipping Administration.

USS Beaufort (AK-6) was a cargo ship acquired by the U.S. Navy for service in World War I.

USS Quincy (AK-10) was a cargo ship acquired by the U.S. Navy for service in World War I.

USS Gold Star (AK-12) was a U.S. Navy cargo ship that saw service before and during World War II. She was responsible for delivering necessary goods and equipment to ships and stations in the war zone.

USS Triangulum (AK-102) was an Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. Triangulum was named after the constellation Triangulum. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater.

USS Phobos (AK-129) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the U.S. Navy for service in World War II. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.




















