
USS Advance, the second United States Navy ship to be so named, was later known as USS Frolic, and was originally the blockade runner Advance captured by the Union Navy during the latter part of the American Civil War. She was purchased by the Union Navy and outfitted as a gunboat and assigned to the blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America. She also served as dispatch ship and supply vessel when military action eventually slowed.
The CSS Beaufort was an iron-hull gunboat that served in North Carolina and Virginia during the American Civil War. Originally launched as Caledonia at Wilmington, Delaware, in 1854, the ship was owned by James Cathcart Johnston. It saw use as a tugboat on the Dismal Swamp Canal. On July 9, 1861, Beaufort was commissioned into the navy of the state of North Carolina for use in the American Civil War. First serving on the North Carolina coast, Beaufort was present at the battles of Roanoke Island and Elizabeth City in February 1862. Escaping the Confederate defeat at Elizabeth City via the Dismal Swamp Canal, Beaufort reached Norfolk, Virginia, where she joined the James River Squadron.

The third USS Water Witch was a wooden-hulled, sidewheel gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She is best known as the ship fired on by Paraguay in 1855. In 1864 she was captured by the Confederate States Navy, and subsequently was taken into that Navy as CSS Water Witch.
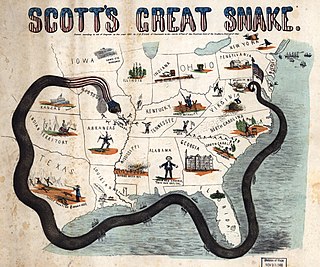
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading.
USS Glide was a sternwheel steamer that served as a tinclad warship during the American Civil War. Built in 1862, the Union Navy purchased her for military service late that year. After being converted to a tinclad and armed with six 24-pounder Dahlgren guns, she entered service with the Mississippi River Squadron in early January 1863. Later that month, she saw action in the Battle of Arkansas Post, firing on Confederate-held Fort Hindman. Sent the next month to Cairo, Illinois, for repairs, Glide was destroyed in a fire of uncertain origin on February 7.
USS Rosalie was a captured Confederate sloop acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.

USS Calhoun was a captured Confederate steamer and blockade runner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.
USS Bloomer was a stern-wheel steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat with orders to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Cowslip was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Mingoe was a large double-ended, side wheel, ironclad steamer gunboat commissioned by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. With heavy guns and a very fast speed of 11 kn, the ship was intended by the Union Navy for use as a bombardment gunboat. They also stationed it as an interceptor gunboat off Confederate waterways to prevent trading with foreign countries.
USS Mobile was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as part of blockade forces to prevent Confederate forces from trading with other countries.
USS Rose was a screw steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Althea was a screw steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. The Union Navy used it as a tugboat, a torpedo boat, and a ship's tender in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS G. W. Blunt was a Sandy Hook pilot boat acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War in 1861. See George W. Blunt (1856) for more details. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat as well as a dispatch boat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Glasgow was originally a British cross-Channel sidewheel steamer named Eugenie owned by the South Eastern Railway that was built during the early 1860s. She was sold for blockade-running duties in 1863 and was captured by the Union Navy later that year during the American Civil War. Incorporated into the Navy, she was principally used as a dispatch boat and storeship in support of the Union blockade of the ports of the Confederate States of America. Renamed Glasgow in 1864, she sank after striking an obstacle the following year, but was refloated and repaired. The ship was sold back into commercial service in 1869 and was scrapped 20 years later.
USS Philippi was a blockade runner captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She served the Union Navy’s struggle against the Confederate States of America as a picket, patrol and dispatch vessel.
USS Tritonia was a 202-ton steamer commissioned by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
The third USS Union was a heavy (1,114-ton) steamer with a powerful 12-inch rifled gun purchased by the United States Navy during the American Civil War.

During the American Civil War, blockade runners were used to get supplies through the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America that extended some 3,500 miles (5,600 km) along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coastlines and the lower Mississippi River. The Confederacy had little industrial capability and could not indigenously produce the quantity of arms and other supplies needed to fight against the Union. To meet this need, numerous blockade runners were constructed in the British Isles and were used to import the guns, ordnance and other supplies that the Confederacy desperately needed, in exchange for cotton that the British textile industry needed greatly. To penetrate the blockade, these relatively lightweight shallow draft ships, mostly built in British shipyards and specially designed for speed, but not suited for transporting large quantities of cotton, had to cruise undetected, usually at night, through the Union blockade. The typical blockade runners were privately owned vessels often operating with a letter of marque issued by the Confederate government. If spotted, the blockade runners would attempt to outmaneuver or simply outrun any Union Navy warships on blockade patrol, often successfully.




