
Arthur LeRoy Bristol, Jr. was a vice admiral in the United States Navy, who held important commands during World War I and World War II, and was an early aircraft carrier commander.
USS Allen (DD-66) was a Sampson-class destroyer of the United States Navy launched in 1916. She was the second Navy ship named for Lieutenant William Henry Allen (1784–1813), a naval officer during the War of 1812. She was the longest-serving destroyer on the Naval Vessel Register when she was sold in 1946 and was one of the few US Navy ships completed during World War I to serve in World War II.

USS Crowninshield (DD–134) was a Wickes-class destroyer in the United States Navy between World War I and World War II. She was named for Benjamin Williams Crowninshield. In World War II she was transferred to the Royal Navy where she was named HMS Chelsea, and subsequently to the Soviet Navy where she was named Derzky.

USS Eberle (DD-430) was a Gleaves-class destroyer of the United States Navy. The ship is named for Rear Admiral Edward Walter Eberle, who commanded the Atlantic and Pacific Fleets and was Chief of Naval Operations from 1923 to 1927. The destroyer entered service in 1940 and spent the majority of her career in the Atlantic Ocean. Placed in reserve following the war, the ship was transferred to the Hellenic Navy in 1951. Renamed Niki, the destroyer remained in service until 1972 when she was scrapped.
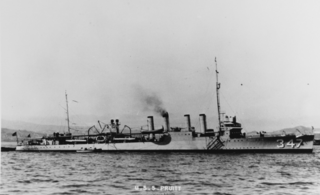
USS Pruitt (DD-347/DM-22/AG-101) was a United States Navy Clemson-class destroyer in commission from 1920 to 1945. She saw service during World War II. She was named for United States Marine Corps Corporal John H. Pruitt, a World War I Medal of Honor recipient who was killed in action Western Front on 4 October 1918 during the Battle of Blanc Mont Ridge.

USS Winchester (SP-156) was an armed yacht that served in the United States Navy as a patrol vessel from 1917 to 1919. Prior to and following World War I, Winchester was a private yacht, later renamed Renard. In World War II, Renard was requisitioned for use in the Royal Canadian Navy as a patrol vessel, keeping her name. She was returned to her owners in 1944.

USS Isabel (SP-521), later PY-10, was a yacht in commission in the United States Navy as a destroyer from 1917 to 1920 and as a patrol yacht from 1921 to 1946.

The American motor yacht Haida was built in Germany in 1929 for Max C. Fleischmann and later saw service in the United States Navy during World War II as patrol yacht USS Argus (PY-14) and USC&GS Pioneer. In 1946 she returned to her role as a private yacht under a sequence of names and owners, and after a further refit in 2016 is now Haida 1929.

USS Hilo (AGP-2) was a converted yacht that saw service as a motor torpedo boat tender in the United States Navy during World War II. It was originally the yacht Caroline built for Eldridge R. Johnson and launched 18 July 1931. Caroline was at the time the second largest yacht and largest American built Diesel yacht. It was built with a laboratory as well as palatial quarters and was loaned and equipped by Johnson for the Johnson-Smithsonian Deep-Sea Expedition of 1933 that explored the Puerto Rico Trench. The yacht was sold in 1938 to William B. Leeds and renamed Moana replacing an earlier Leeds yacht of the same name.
USS Goldfinch (AM-77) was a minesweeper acquired by the U.S. Navy for the dangerous task of removing mines from minefields laid in the water to prevent ships from passing.

USS Oceanographer (AGS-3) was a survey ship of the United States Navy during World War II that produced charts chiefly of passages in the Solomon Islands area of the Pacific Ocean. Upon transfer to the Navy, she had initially briefly been named and classed as gunboat USS Natchez (PG-85). Before her World War II Navy service, she had been USC&GS Oceanographer (OSS-26), a survey ship with the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey from 1930.

USS Mizpah (PY-29) was a United States Navy patrol yacht. Constructed in 1926, the vessel was constructed as the pleasure yacht Savarona. In 1929 it was renamed Allegro and then Mizpah for use on the Great Lakes. The vessel was acquired by the United States Navy in 1942 and converted to a warship and commissioned the same year. Mizpah served as a convoy escort along the United States East Coast before becoming a school ship in 1944. Following the end of the war, the vessel returned to private operation in 1946 until 1967 when Mizpah was laid up with a broken crankshaft at Tampa, Florida. An attempt to save the ship proved futile and Mizpah was scuttled off the coast of Florida as an artificial reef in 1968. The wreck is now a popular dive site.

USS Crystal (PY-25), built in 1929 as the yacht Cambriona for Walter O. Briggs of Detroit, Michigan, was a patrol yacht in the United States Navy. The Navy acquired the yacht in January 1942 as Vida commissioning the vessel as Crystal in February. Naval service was in Hawaii until November 1945. After sale in November 1947 the vessel operated commercially in Central and South America.

USS Zircon (PY-16) was the private yacht Nakhoda acquired by the United States Navy in 1940 serving as an armed yacht from 1941 to 1946. The yacht Nakhoda was built for automobile executive Frederick J. Fisher by Pusey and Jones Corporation, Wilmington, Delaware delivered in 1930. After the war the yacht was sold and reverted to the original name until sold in 1951 to the United New York Sandy Hook Pilots Association and renamed New York.

Aphrodite was a yacht built to requirements by owner Colonel Oliver H. Payne of New York City as an ocean going steam yacht with barque rig and capable of good speed under sail alone. The yacht was launched 1 December 1898 and completed in 1899 to be the largest American built steam yacht at the time. The yacht served in the United States Navy as the patrol vessel USS Aphrodite from May 1917 to July 1919. The yacht was given the designation SP-135 for Section patrol and was, unlike the majority of section patrol vessels, sent overseas rather than acting in that capacity in home waters. The yacht was returned to private service after the war.
Maryann, sometimes seen as Maryanne or Mary Anne, was a yacht requisitioned and converted by the United States Navy during the defense of the Philippines in World War II and destroyed 5 May 1942 at Corregidor to prevent capture. The yacht was "in service" and not commissioned.

USS Siren (PY-13), briefly CMc-1, was built by Pusey and Jones, Wilmington, Delaware and launched 15 November 1929 as the yacht Lotosland. The yacht was acquired by the United States Navy in October 1940 and placed in commission as a Patrol Yacht from 1940 to 1946.

USS Turquoise (PY-18), was a yacht in commission in the United States Navy as a Patrol Yacht from 1940 to 1943.

USS Tourmaline (PY-20) was a converted yacht that patrolled with the United States Navy in World War II.

USS Ruby (PY-21) was a converted yacht that patrolled with the United States Navy in World War II.

















