
USS Susan B. Anthony (AP-72) was a turbo-electric ocean liner, Santa Clara, of the Grace Steamship Company that was built in 1930. Santa Clara was turned over to the War Shipping Administration (WSA) on 28 February 1942 and operated by Grace Lines as agent for WSA as a troop ship making voyages to the South Pacific. The ship was chartered to the Navy on 7 August 1942 for operation as a United States Navy transport ship. The ship was sunk 7 June 1944 off Normandy by a mine while cruising through a swept channel with all 2,689 people aboard being saved.
USS Gemini may refer to the following U.S. Navy ships:

USS Arthur Middleton (AP-55/APA-25) was the lead ship of the Arthur Middleton-class attack transports and was in service with the United States Navy from 1942 to 1946. She was named for Founding Father Arthur Middleton and was scrapped in 1973.

USS Edison (DD-439), a Gleaves-class destroyer, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for Thomas Alva Edison, an inventor and businessman who developed many important devices and received the Navy Distinguished Service Medal for his contributions to the Navy during World War I. Edison was one of the few U.S. Navy ships to be named for a civilian.

USS Aries (AK-51) (1918–1952) was a United States Navy cargo ship built as Lake Geneva under a United States Shipping Board (USSB) contract in 1918 at Duluth, Minnesota, by the McDougall Duluth Shipbuilding Company, to augment American logistics capability during World War I. The freighter was delivered to the Navy at Montreal, Quebec, Canada, on 21 September 1918 and was placed in commission the following day for service in the Naval Overseas Transportation Service. Aries was named for the constellation.

USS Algorab (AKA-8) was laid down as Mormacwren, one of the earliest Maritime Commission-type C2 ships, on 10 August 1938 by the Sun Shipbuilding & Drydock Co., Chester, Pennsylvania as hull 177 for Moore-McCormack. Mormacwren was acquired by the United States Navy 6 June 1941, commissioned 15 June 1941 as USS Algorab (AK-25) and was redesignated an attack transport on 1 February 1943 with the hull number chanted to AKA-8. Algorab decommissioned on 3 December 1945 and was delivered to the Maritime Commission on 30 June 1946 for disposal, purchased by Wallem & Co. on 4 April 1947 for commercial service.

USS Alcyone (AKA-7) was an Arcturus-class attack cargo ship named after Alcyone, the brightest star in the star cluster Pleiades. She served as a commissioned ship for five years and one month.

USS Alchiba (AKA-6) was an Arcturus-class attack cargo ship of the United States Navy, named after Alchiba, a star in the constellation Corvus. She served as a commissioned ship for 4 years and 7 months.

USS Thomas Jefferson (APA-30), serving from 1 May 1942 until 18 July 1955, was a transport and then reclassified on 1 February 1943 as a President Jackson-class attack transport. She was laid down under Maritime Commission contract as President Garfield on 5 February 1940 at Newport News, Virginia, by the Newport News Shipbuilding & Drydock Company for the American President Lines. The ship was launched on 20 November 1940, sponsored by Miss Eugenia Merrill. President Garfield was completed 26 March 1941 and acquired by the War Shipping Administration (WSA) 29 November 1941 with American President Lines, the WSA agent, operating the ship as a troop transport. On 1 May 1942 the United States Navy purchased the ship and commissioned her USS Thomas Jefferson, named for Founding Father Thomas Jefferson, on 31 August 1942.

USS Stratford (AK-45/AP-41) was a Stratford-class transport commissioned by the U.S. Navy for service in World War II. She was responsible for delivering military personnel and equipment to ships and stations in the war zone.

USS Triangulum (AK-102) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. Triangulum was named after the constellation Triangulum. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater.

USS Ara (AK-136) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. Ara is named after the constellation Ara. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater.

USS Custer (AP-85/APA-40) was a Bayfield-class attack transport in service with the United States Navy from 1943 to 1946. She was sold into commercial service in 1948 and was scrapped in 1973.

USS Leonard Wood (APA-12) was built by Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corporation and launched 17 September 1921 at Sparrows Point, Maryland as Nutmeg State, an Emergency Fleet Corporation Design 1029 ship intended as a World War I troop transport, but redesigned upon the armistice as a passenger and cargo ship and completed as Western World for delivery to the United States Shipping Board. The ship's acceptance on 5 May 1922 and delivery on 9 May 1922 marked the completion of the wartime shipbuilding program of the Emergency Fleet Corporation and the Shipping Board.
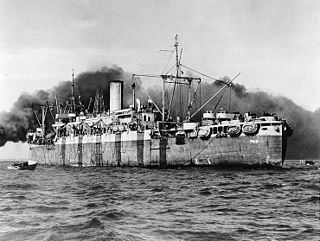
SS President Roosevelt was an ocean liner in service in the 1920s and 1930s. Originally built as a Harris-class attack transport towards the end of World War I, she entered commercial service after her completion. Having been built as Peninsula State, she was soon renamed President Pierce and then President Roosevelt. Requisitioned for service as a troopship with the US Navy during World War II, she was renamed USS Joseph T. Dickman (APA-13) and served in the Atlantic and Pacific theaters, being scrapped postwar in 1948.

USS General J. C. Breckinridge (AP-176) was a troopship that served with the United States Navy in World War II, the Korean War and the Vietnam War. In October 1949 she was redesignated T-AP-176 but retained her Navy crew. Her namesake was United States Marine Corps Lieutenant General James Carson Breckinridge (1877-1942), who was the grandson of John Cabell Breckinridge, who served as Vice President of the United States from 1857 to 1861.

USS Mount Vernon (AP-22) was a troop transport that served with the United States Navy during World War II. Prior to her military service, she was a luxury ocean liner named SS Washington.

USS Republic (AP-33) was a troop transport that served with the US Navy during World War II. In World War I she served with the Navy as USS President Grant (ID-3014) before being turned over to the Army and named Republic. The ship was renamed the President Buchanan in 1921 before reverting to Republic in 1924.

The Stratford class transport was a class of transport ship that served with the United States Navy during World War II. Their purpose was to transport soldiers to overseas service.

USS Livingston (AP-163/AK-222) was a Crater-class cargo ship built for the US Navy during World War II. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater.


















