
The first USS Colorado, a 3,400-long-ton (3,500 t), three-masted steam screw frigate, was launched on 19 June 1856, by the Norfolk Navy Yard. Named after the Colorado River, she was sponsored by Ms. N. S. Dornin, and commissioned on 13 March 1858, with Captain W. H. Gardner, in command. She was the fifth of the "Franklin-class" frigates, which were all named after US rivers, except for Franklin.

USS Susquehanna, a sidewheel steam frigate, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the Susquehanna River, which rises in Lake Otsego in central New York and flows across Pennsylvania and the northeast corner of Maryland emptying into the Chesapeake Bay.

USS Wabash was a steam screw frigate of the United States Navy that served during the American Civil War. She was based on the same plans as Colorado. Post-war she continued to serve her country in European operations and eventually served as a barracks ship in Boston, Massachusetts, and was sold in 1912.

The first USS Pocahontas, a screw steamer built at Medford, Massachusetts in 1852 as City of Boston, and purchased by the Navy at Boston, Massachusetts on 20 March 1855, was the first United States Navy ship to be named for Pocahontas, the Algonquian wife of Virginia colonist John Rolfe. She was originally commissioned as USS Despatch – the second U.S. Navy ship of that name – on 17 January 1856, with Lieutenant T. M. Crossan in command, and was recommissioned and renamed in 1860, seeing action in the American Civil War. As Pocahontas, one of her junior officers was Alfred Thayer Mahan, who would later achieve international fame as a military writer and theorist of naval power.

USS Albatross was a screw steamer rigged as a three-masted schooner acquired by the Union Navy during the beginning of the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a gunboat with heavy guns and used in the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.
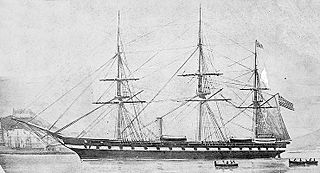
USS Roanoke was a wooden-hulled Merrimack-class screw frigate built for the United States Navy in the mid-1850s. She served as flagship of the Home Squadron in the late 1850s and captured several Confederate ships after the start of the American Civil War in 1861. The ship was converted into an ironclad monitor during 1862–63; the first ship with more than two gun turrets in history. Her conversion was not very successful as she rolled excessively and the weight of her armor and turrets strained her hull. Her deep draft meant that she could not operate off shallow Confederate ports and she was relegated to harbor defense at Hampton Roads, Virginia for the duration of the war. Roanoke was placed in reserve after the war and sold for scrap in 1883.
USS Home was a large steamship purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was placed into service as a hospital ship assigned to support the fleet blockading the ports of the Confederate States of America.
USS Potomska was a wooden screw steamer rigged as a three masted schooner purchased at New York City from H. Haldrege on 25 September 1861. She was commissioned at the New York Navy Yard on 20 December 1861.

USS Aries was an 820-ton iron screw steamer built at Sunderland, England, during 1861–1862, intended for employment as a blockade runner during the American Civil War. She was captured by Union Navy forces during the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America, and was commissioned as a Union gunboat. Aries was named for the constellation.

The USS Cherokee was a 606-ton screw steam gunboat in the US Navy during the American Civil War ship. The ship later served in the Chilean Navy.
USS Western World was a ship acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.

The first USS Emma was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a picket and patrol vessel on Confederate waterways.
USS Augusta Dinsmore was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union naval blockade of Confederate waterways. Because of her relatively large size, she was also sometimes used as a cargo ship.
USS Azalea was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as an armed tugboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.

The first USS Wando was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. In commission from 1864 to 1865, she was used by the United States Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS George W. Rodgers was a schooner captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was initially intended to be used as part of the stone fleet of sunken obstructions; however, she was retained and used as a picket boat and dispatch vessel and, later, as a survey ship, concentrating her efforts in the waterways of the Confederate South.

USS Geranium was a steamship acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War for the purpose of using her as a tugboat in support of Union ships on the blockade of Southern waterways. However, in addition to her tug duties, she also served as a picket ship, dispatch boat, supply runner and other duties assigned to her by the Navy.
USS Glasgow was originally a British cross-Channel sidewheel steamer named Eugenie owned by the South Eastern Railway that was built during the early 1860s. She was sold for blockade-running duties in 1863 and was captured by the Union Navy later that year during the American Civil War. Incorporated into the Navy, she was principally used as a dispatch boat and storeship in support of the Union blockade of the ports of the Confederate States of America. Renamed Glasgow in 1864, she sank after striking an obstacle the following year, but was refloated and repaired. The ship was sold back into commercial service in 1869 and was scrapped 20 years later.

Battery White was an artillery battery constructed by the Confederates during the American Civil War. Built in 1862–63 to defend Winyah Bay on the South Carolina coast, the battery was strongly situated and constructed; however, it was inadequately manned, and was captured without resistance during the final months of the war.
Commodore Jonathan Young was an officer in the United States Navy. He participated in anti-piracy actions and the African Slave Trade Patrol, fought in the Mexican War, Puget Sound War, and American Civil War, and served briefly as commander of the Asiatic Squadron.













