Service history
Lyra departed San Francisco 28 August 1943, with 8,000 tons of lend-lease cargo for New Zealand. En route she towed one unit of a sectional dock to Espiritu Santo, New Hebrides, and arrived Wellington, New Zealand, 19 October. The cargo ship returned to San Francisco 24 November. On 17 December she began a three-day experimental run to help perfect towing techniques.
Two days after Christmas, she again departed for Espiritu Santo towing Auxiliary Repair Dry Dock ARD-12. The ship then proceeded to Tulagi and Munda, Solomon Islands, embarking 200 troops from the latter for transport to Guadalcanal, which she reached 29 February 1944. Lyra returned to Tulagi and Guadalcanal, and was back in San Francisco 2 April after steaming 13,567 miles (21,834 km). From 29 April to 30 June, she made two short voyages between the west coast and Pearl Harbor.
The cargo ship's next assignment was a towing operation to Manus, Admiralty Islands, between 21 August and 15 January 1945. On 26 February she voyaged to Samar, Philippine Islands, and returned to home port 1 June. Her seventh voyage, 17 June to 24 August, took her to Honolulu and Saipan. She sailed from San Francisco 26 September to Samar for her last assignment before decommissioning in Norfolk 3 May 1946. Lyra was redelivered to War Shipping Administration (WSA) 5 days later. She was sold 7 January 1947, to A. G. Pappadakis and operated out of Piraeus, Greece, as Virginia.

USS Arided (AK-73), a Crater-class cargo ship, is the only ship of the US Navy to have this name. She was named after Arided, the other name of Deneb, the alpha star of constellation Cygnus.
USS Hyperion (AK-107) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the US Navy in World War II. Named after Saturn's moon Hyperion, she is the only ship of the Navy to bear this name.

USS Carina (AK-74) was a Crater-class cargo ship, and the only ship of the US Navy to have this name. She was named for the southern constellation Carina, with most of her sister ships being named for constellations or stars.

USS Cassiopeia (AK-75) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the US Navy in World War II. She was the only ship of to bear this name. She is named after the Northern Hemisphere constellation Cassiopeia.
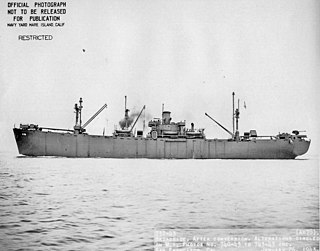
USS Deimos (AK-78) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of US Navy in World War II. It was the first ship of the Navy to have borne the name Deimos, after one of the moons of Mars.

The USS Albireo (AK-90) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the US Navy in World War II and manned by a US Coast Guard crew. She was the only ship of the Navy to have borne this name. She is named after Albireo, a star in the constellation of Cygnus.
USS Venus (AK-135) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the United States Navy in World War II. Originally liberty ship SS William Williams, named after William Williams, a signer of the Declaration of Independence, it was taken over by the Navy after being damaged in a torpedo attack and renamed after the planet Venus. It was the only ship of the Navy to bear this name.

USS Crater (AK-70) was the lead ship of her class of converted liberty ship cargo ships in the service of the US Navy in World War II. She was first named after John James Audubon, an American ornithologist, naturalist, and painter. She was renamed and commissioned after the constellation Crater, she was the only ship of the Navy to bear this name.

USS Adhara (AK-71) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the US Navy in the Pacific theater in World War II. Named after the star Adhara in the constellation Canis Major, it was the only ship of the Navy to bear this name.

USS Aludra (AK-72) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the US Navy in World War II. Named after the star Aludra in the constellation Canis Major, it was the first ship of the Navy to bear this name.

USS Celeno (AK-76) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the US Navy in World War II. Named with a variant spelling of the star Celaeno in the constellation Pleiades, it was the only ship of the Navy to bear this name.

USS Cetus (AK-77) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the US Navy in World War II. Named after the equatorial constellation Cetus, it was the only ship of the Navy to bear this name.

The USS Alnitah (AK-127) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the US Navy in World War II. Named a spelling variation of the star Alnitak in the constellation Orion, it was the only ship of the Navy to bear this name.

USS Draco (AK-79) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. Named after the constellation Draco. She was responsible for delivering goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.

USS Cor Caroli (AK-91) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II and manned by a US Coast Guard crew. She was named after Cor Caroli, the brightest star in constellation Canes Venatici. She was responsible for delivering goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.

USS Sculptor (AK-103) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. Sculptor was named after the constellation Sculptor. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater.

USS Ganymede (AK-104) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone. Named after the largest of the moons of Jupiter, Ganymede was the only ship of the Navy to bear this name.
USS Alderamin (AK-116) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the U.S. Navy for service in World War II, named after Alderamin, the alpha star in constellation Cepheus. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.
USS Wateree (ATA-174), the third ship named USS Wateree, was a Sotoyomo-class auxiliary fleet tug in the service of the United States Navy during World War II. She later served with the Military Sea Transportation Service and the Peruvian Navy as a diving support ship. In Peruvian naval service she was renamed BAP Unanue (ATA-136).

USS Sibley (APA-206) was a Haskell-class attack transport in service with the United States Navy from 1944 to 1946. She was scrapped in 1975.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
















