
USS Parsons (DD-949/DDG-33) began her career as a Forrest Sherman-class destroyer of the United States Navy. She was named in honor of Rear Admiral William S. Parsons (1901–1953), who worked on the Manhattan Project during World War II.

USS Whipple (DE-1062/FF-1062) was a Knox-class frigate commissioned in the United States Navy from 1970 to 1995. In 2002, Whipple was donated to the Mexican Navy and renamed ARM Mina (F-214).

USS Crommelin (FFG-37), twenty-eighth ship of the Oliver Hazard Perry-class of guided-missile frigates, was named for five brothers: Rear Admiral John G. Crommelin (1902–1996), Vice Admiral Henry Crommelin (1904–1971), Commander Charles L. Crommelin (1909–1945), Lieutenant Commander Richard Crommelin (1917–1945), and Captain Quentin C. Crommelin (1919–1997). The Crommelin brothers were the only group of five siblings ever to graduate from the United States Naval Academy. Four of them became pilots, and Time magazine dubbed them "The Indestructibles." The brothers saw action in more than ten campaigns in the Pacific Theater. Henry, the second-oldest, became a Surface Warfare Officer while Richard and Charles died in combat as naval aviators in 1945. Individually and as a fighting family, they gained fame in World War II, attaining outstanding combat records and multiple decorations. Crommelin (FFG-37) is the first ship of that name in the United States Navy.
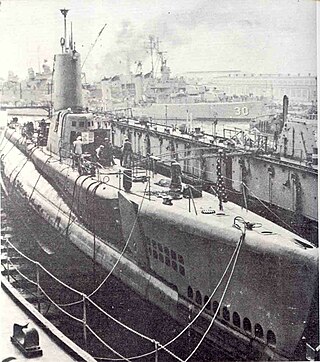
USS Medregal (SS-480/AGSS-480), a Tench-class submarine, was the only ship of the United States Navy to be named for the medregal, a streamlined, fast-swimming, bluish-colored fish of the jack family which abounds in waters of the West Indies and in the Atlantic as far north as the Carolinas.

USS McGinty (DE-365) was a John C. Butler-class destroyer escort of the United States Navy.

USS Nicholas (DD/DDE-449) was a Fletcher-class destroyer of the United States Navy, serving for a total of 27 years, including through most of World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War. She was the second Navy ship to be named for Major Samuel Nicholas.

USS O'Bannon (DD/DDE-450), a Fletcher-class destroyer, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named after Lieutenant Presley O'Bannon (1784–1850), the Marine Corps's "hero of Derna".

USS Acree (DE-167) was a Cannon-class destroyer escort in service the United States Navy from 1943 to 1946. She was scrapped in 1973.

USS Putnam (DD-757), an Allen M. Sumner-class destroyer, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named for Charles Putnam. She was built and saw action in the Pacific during World War II. She was laid down on 11 July 1943 by Bethlehem Steel Co., Shipbuilding Division, San Francisco, California and launched on 26 March 1944; sponsored by Mrs. Doana Putnam Wheeler. The ship was commissioned on 12 October 1944. Cdr. Frederick V. H. Hilles was in command.

USS O'Brien (DD-725), an Allen M. Sumner-class destroyer, was the fourth ship of the United States Navy to be named after Captain Jeremiah O'Brien and his five brothers, Gideon, John, William, Dennis and Joseph, who captured HMS Margaretta on 12 June 1775 during the American Revolution.

USS Watts (DD-567) was a Fletcher-class destroyer of the United States Navy.

USS John Rodgers (DD-574) was a Fletcher-class destroyer of the United States Navy commissioned during World War II and the second ship to bear the name. She was named after three members of the Rodgers family who served in the Navy from the War of 1812 through World War I. John Rodgers served in several wartime actions in the Pacific, receiving 12 battle stars.

USS Walton (DE-361) was a John C. Butler-class destroyer escort in the United States Navy. It was named after Merrit Cecil Walton, a Marine Corps platoon sergeant with the U.S. 1st Marine Division, who died on Gavutu during the Battle of Guadalcanal and was posthumously awarded the Navy Cross for "extraordinary heroism".

USS Badger (FF-1071) was a Knox-class frigate in service in the United States Navy from 1970 to 1991. She was sunk as a target in 1998.

USS Bauer (DE-1025) was a Dealey-class destroyer escort in the United States Navy. She was named for Lieutenant Colonel Harold William Bauer, naval aviator and recipient of the Medal of Honor for extraordinary heroism and conspicuous courage as Commander of Marine Fighting Squadron 212 in the South Pacific between 10 May and 14 November 1942.

USS Amick (DE-168) was a Cannon-class destroyer escort built for the United States Navy during World War II. She served in the Atlantic Ocean and then the Pacific Ocean and provided escort service against submarine and air attack for Navy vessels and convoys.

USS Blair (DE-147) was an Edsall-class destroyer escort in service with the United States Navy from 1943 to 1946 and from 1951 to 1960. She was scrapped in 1974. Blair was named in honor of Chief Machinist's Mate Eugene Blair, who was awarded the Silver Star posthumously for his brave actions when his ship was attacked and bombed by Japanese planes near Port Darwin, Australia, in mid-February 1942.

USS Alvin C. Cockrell (DE-366) was a John C. Butler-class destroyer escort in service with the United States Navy from 1944 to 1946 and from 1951 to 1968. She was finally sunk as a target in 1969.

USS Vance (DE-387) was an Edsall-class destroyer escort, named after Joseph Williams Vance, Jr.

USS Wiseman (DE-667) was a Buckley-class destroyer escort in service with the United States Navy for several periods between 1944 and 1973. She was scrapped in 1974.




















