USS Baltimore was a ship of the United States Navy.

The third USS Boston was a 32-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted frigate of the United States Navy. Boston was built by public subscription in Boston under the Act of 30 June 1798. Boston was active during the Quasi-War with France and the First Barbary War. On 12 October 1800, Bostonengaged and captured the French corvette Berceau. Boston was laid up in 1802, and considered not worth repairing at the outbreak of the War of 1812. She was burned at the Washington Naval Yard on 24 August 1814 to prevent her capture by British forces.

USS Adams was a 28-gun (rated) sailing frigate of the United States Navy. She was laid down in 1797 at New York City by John Jackson and William Sheffield and launched on 8 June 1799. Captain Richard Valentine Morris took command of the ship.
The first USS Eagle, a schooner, was built at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1798, and commissioned in the Revenue Cutter Service under the command of Captain H. G. Campbell, USRCS.
USS Ganges was a man-of-war in the United States Navy during the Quasi-War with France.
The first USS Montezuma was a merchant ship built in Virginia in 1795. The United States Navy acquired her during the Quasi-War with France and retained her name.
The first USS Norfolk was a brig in the United States Navy during the Quasi-War with France.
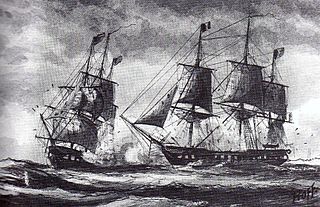
L'Insurgente was a 40-gun Sémillante-class frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1793. During the Quasi War with the United States, the United States Navy frigate USS Constellation, with Captain Thomas Truxtun in command, captured her off the island of Nevis. After her capture she served in the United States Navy as USS Insurgent, patrolling the waters in the West Indies. In September 1800 she was caught up in a severe storm and was presumed lost at sea.
USS Retaliation was the French privateer Croyable, built in Maryland, that then operated out of Santo Domingo. Delaware captured her on 7 July 1798 off New Jersey. She then served in the United States Navy during Quasi-War with France. Two French frigates recaptured her on 20 November 1798. The French Navy took her into service as Magicienne. However, Merrimack captured her on 28 June 1799. She served in the US Navy in the Caribbean briefly, before arriving in Philadelphia in August. She was paid off (decommissioned) there and sold on 29 November.

USS Pickering was a brig, the 1st brig built for the UCRC Service, in the United States Revenue Cutter Service and then the United States Navy during the Quasi-War with France. She was named for Timothy Pickering, then the Secretary of State.
The first USS George Washington was a frigate in the United States Navy. She was named after United States Founding Father and President George Washington.
The second USS Delaware was a ship which served in the United States Navy during Quasi-War with France.
The second USS General Greene was a frigate in the United States Navy during the Quasi-War with France.
USS Augusta was a brig purchased by the US Navy on 30 June 1799 at Norfolk, Virginia. She mistakenly went to Trenton, New Jersey arriving on 13 September, she was then ordered to Marcus Hook, Pennsylvania for inspection by naval constructor Joshua Humphreys to see if the transport would be suitable for use as a warship. Capt. Bird was replaced by Lieutenant Archibald McElroy on the 13th. Humphreys approved and fitting out began in September. She was placed in commission for service in the Quasi-War with France sometime late in 1799.
USS Richmond was a brig purchased for the US Navy in 1798 by the citizens of Richmond, Petersburg, Manchester and Norfolk, Virginia, while being built at Norfolk as Augusta for a Mr. Myers. Renamed Richmond, she was fitted out in the fall of that year and in December stood out from Hampton Roads for the Caribbean with Captain Samuel Barron in command for service in the Quasi-War with France.
USS Herald was a full-rigged ship of about 270 tons burthen built in 1797 at Newburyport, Massachusetts. The US Navy purchased her on 15 June 1798, and sold her in 1801. She became the French 20-gun privateer corvette Africaine. In 1804 a British privateer seized her on 4 May 1804 off the coast, near Charleston, South Carolina. The seizure gave rise to a case in the U.S. courts that defined the limits of U.S. territorial waters. The U.S. courts ruled that the privateer had seized Africaine outside U.S. jurisdiction. Africaine then became a Liverpool-based slave ship that made two voyages carrying slaves from West Africa to the West Indies. After the abolition of the slave trade in 1807 she became a West Indiaman that two French privateers captured in late 1807 or early 1808.
The first USS Patapsco was a sloop in the United States Navy.
USRC Virginia was a schooner built in 1797 for the United States Revenue Cutter Service at Portsmouth, Virginia. At the outset of the Quasi-War in 1798, the only ships available to the Navy were the 10 ships of the Revenue cutter service, the largest of which was the Virginia. She was transferred to the Navy in 1798 and served in the Quasi War until 1800, when she was returned to the Revenue Cutter Service, recommissioned in 1802 and sold in 1807.
HMS Pheasant was an 18-gun Merlin class sloop of the Royal Navy.
The Connecticut was a sailing frigate built by Seth Overton at Chatham, Conn. and launched 6 June 1799 at Middletown, Conn. During outfitting, probably on or just before 7 July she foundered. She was refloated. She sailed 15 Oct. 1799 under the command of Captain Moses Tryon for the Guadaloupe Station, arriving off Puerto Rico on 28 October. She cruised in the West Indies for a year during the Quasi-War with France, protecting American commerce from French privateers. Connecticut's successful career was highlighted by the capture of four privateers and the recapture of seven American merchantmen. On 7 November, 1799 she recaptured a schooner captured 15 days earlier. On 6 December she recaptured brig "Penelope" captured by French privateer "Fleur de Mair" on 3 December. On 29 December she captured off Point Petre French privateer brig "Conqueror of Italy", the most successful privateer operating out of Guadeloupe having captured 200 American merchant ships. Arriving at New London, Conn., 18 Oct. 1800. Connecticut was sold at New York in 1801 for $19,300.



