
The USS Albireo (AK-90) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of the US Navy in World War II and manned by a US Coast Guard crew. She was the only ship of the Navy to have borne this name. She is named after Albireo, a star in the constellation of Cygnus.

USS Alkes (AK-110) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II, named after Alkes, a star in the Crater constellation. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.

USS Rutilicus (AK-113) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater.
USS Alkaid (AK-114) was a Crater-class cargo ship, converted from a Liberty Ship, commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. She was first named after William G. Sumner, a classical liberal American social scientist. She was renamed and commissioned after Alkaid, a star in the Big Dipper asterism or constellation Ursa Major. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.
USS Alderamin (AK-116) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the U.S. Navy for service in World War II, named after Alderamin, the alpha star in constellation Cepheus. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.
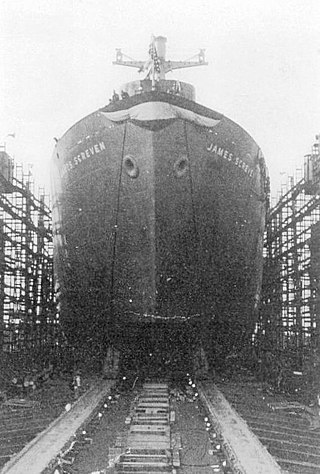
USS Shaula (AK-118) was a Crater-class cargo ship, converted from a Liberty Ship, commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. She was first named after James Screven, an American general during the American Revolutionary War. She was renamed and commissioned after Shaula, the second-brightest star system in the constellation of Scorpius. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.
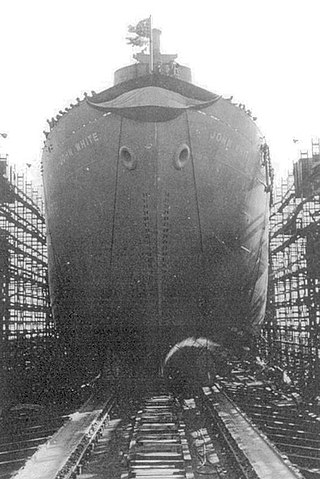
USS Menkar (AK-123) was a Crater-class cargo ship, converted from a Liberty Ship, commissioned by the U.S. Navy for service in World War II. She was first named after John White, a settler among those who sailed with Richard Grenville, to present-day North Carolina, in 1585, to found the Roanoke Colony. White acted as artist and mapmaker to the expedition. He became the governor, in 1587, of the colony, and his granddaughter, Virginia Dare, was the first English child born in the Americas. She was renamed and commissioned after Menkar, the second-brightest star in the constellation of Cetus. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.

USS Azimech (AK-124) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II, named after the Azimech, the other name of Spica, the brightest star in constellation Virgo. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.

USS Melucta (AK-131) was a Crater-class cargo ship, converted from a Liberty Ship, commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. She was first named after Thomas A. McGinley, the president of the Duff-Norton Manufacturing Co., and inventor of an improved high-speed screw jack and lifting machinery. She was renamed and commissioned after Melucta, a star in the constellation Gemini. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.
USS Syrma (AK-134) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the U.S. Navy for service in World War II. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.

USS Ara (AK-136) was a Crater-class cargo ship commissioned by the US Navy for service in World War II. Ara is named after the constellation Ara. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater.

USS Beaverhead (AK-161) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship commissioned by the U.S. Navy for service in World War II. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.
USS Blount (AK-163) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship commissioned by the U.S. Navy for service in World War II. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.

USS Bullock (AK-165) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship commissioned by the U.S. Navy for service in World War II. She was responsible for delivering troops, goods and equipment to locations in the war zone.

USS Pontotoc (AK-206/AG-94/AVS-7) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship acquired by the US Navy shortly before the end of World War II. She was converted into a Gwinnett-class aviation stores issue ship to carry aviation parts and spares, and to issue them to the US Pacific Fleet and activities as needed.

USS Poinsett (AK-205) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship acquired by the US Navy just prior to the end of World War II. She carried supplies and ammunition to the Pacific Ocean battle areas and was awarded one battle star for her operations in the Borneo area.
USS Kenosha (AK-190) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship that served the US Navy during the clean-up phase of World War II. When her service was no longer required in 1946, she was decommissioned and returned to the U.S. Maritime Commission where she was sold to the Kingdom of Norway in 1947.
USS Muskingum (AK-198/T-AK-198) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship that was constructed for the US Navy under a US Maritime Commission (MARCOM) contract during the closing period of World War II. She supported the end-of-war Navy effort. On 7 March 1946 Muskingum was placed in service under bareboat charter with the US Army under the Shipping Control Authority for the Japanese Merchant Marine with a Japanese crew. In 1950, she was reactivated and placed into service with the Military Sea Transportation Service as USNS Muskingum (T-AK-198) until being struck from the Navy list in 1973. She was ultimately transferred to the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) and the Republic of Palau.
USS Schuyler (AK-209) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship that was constructed for the US Navy during the closing period of World War II. She served with distinction in the Pacific Ocean theatre of operations and returned home in 1946 to be placed into the reserve "mothball" fleet where she silently remained until she was scrapped in 1971.

USS Screven (AK-210) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship that was constructed for the US Navy during the closing period of World War II. She served in the Pacific Ocean theatre of operations and returned home in 1946 to be placed into the "mothball fleet" where she remained until sold in 1947 for commercial maritime service.












