
SPARC is a reduced instruction set computing (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) originally developed by Sun Microsystems. Its design was strongly influenced by the experimental Berkeley RISC system developed in the early 1980s. First developed in 1986 and released in 1987, SPARC was one of the most successful early commercial RISC systems, and its success led to the introduction of similar RISC designs from a number of vendors through the 1980s and 90s.
The IBM RS64 is a family of microprocessors that were used in the late 1990s in IBM's RS/6000 and AS/400 servers.
Simultaneous multithreading (SMT) is a technique for improving the overall efficiency of superscalar CPUs with hardware multithreading. SMT permits multiple independent threads of execution to better utilize the resources provided by modern processor architectures.
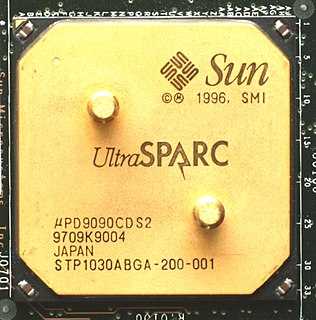
The UltraSPARC is a microprocessor developed by Sun Microsystems and fabricated by Texas Instruments, introduced in mid-1995. It is the first microprocessor from Sun to implement the 64-bit SPARC V9 instruction set architecture (ISA). Marc Tremblay was a co-microarchitect.

The POWER5 is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by IBM. It is an improved version of the POWER4. The principal improvements are support for simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and an on-die memory controller. The POWER5 is a dual-core microprocessor, with each core supporting one physical thread and two logical threads, for a total of two physical threads and four logical threads.
SPARC64 is a microprocessor developed by HAL Computer Systems and fabricated by Fujitsu. It implements the SPARC V9 instruction set architecture (ISA), the first microprocessor to do so. SPARC64 was HAL's first microprocessor and was the first in the SPARC64 brand. It operates at 101 and 118 MHz. The SPARC64 was used exclusively by Fujitsu in their systems; the first systems, the Fujitsu HALstation Model 330 and Model 350 workstations, were formally announced in September 1995 and were introduced in October 1995, two years late. It was succeeded by the SPARC64 II in 1996.

Sun Microsystems' UltraSPARC T1 microprocessor, known until its 14 November 2005 announcement by its development codename "Niagara", is a multithreading, multicore CPU. Designed to lower the energy consumption of server computers, the CPU typically uses 72 W of power at 1.4 GHz.

Rock was a multithreading, multicore, SPARC microprocessor under development at Sun Microsystems. Canceled in 2010, it was a separate project from the SPARC T-Series (CoolThreads/Niagara) family of processors.

Sun Microsystems' UltraSPARC T2 microprocessor is a multithreading, multi-core CPU. It is a member of the SPARC family, and the successor to the UltraSPARC T1. The chip is sometimes referred to by its codename, Niagara 2. Sun started selling servers with the T2 processor in October 2007.
The SPARC Enterprise series is a range of UNIX server computers based on the SPARC V9 architecture. It was co-developed by Sun Microsystems and Fujitsu, and introduced in 2007. They were marketed and sold by Sun Microsystems, Fujitsu, and Fujitsu Siemens Computers under the common brand of "SPARC Enterprise", superseding Sun's Sun Fire and Fujitsu's PRIMEPOWER server product lines.
The SPARC64 V (Zeus) is a SPARC V9 microprocessor designed by Fujitsu. The SPARC64 V was the basis for a series of successive processors designed for servers, and later, supercomputers.
The hyperSPARC, code-named "Pinnacle", is a microprocessor that implements the SPARC Version 8 instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Ross Technology for Cypress Semiconductor.

The UltraSPARC III, code-named "Cheetah", is a microprocessor that implements the SPARC V9 instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Sun Microsystems and fabricated by Texas Instruments. It was introduced in 2001 and operates at 600 to 900 MHz. It was succeeded by the UltraSPARC IV in 2004. Gary Lauterbach was the chief architect.

The UltraSPARC II, code-named "Blackbird", is a microprocessor implementation of the SPARC V9 instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Sun Microsystems. Marc Tremblay was the chief architect. Introduced in 1997, it was further development of the UltraSPARC operating at higher clock frequencies of 250 MHz, eventually reaching 650 MHz.

The microSPARC is a microprocessor implementing the SPARC V8 instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Sun Microsystems. It was a low-end microprocessor intended for low-end workstations and embedded systems. The microprocessor was developed by Sun, but the floating-point unit (FPU) was licensed from Meiko Scientific. It contained 800,000 transistors.

The SPARC T3 microprocessor is a multithreading, multi-core CPU produced by Oracle Corporation. Officially launched on 20 September 2010, it is a member of the SPARC family, and the successor to the UltraSPARC T2.
The IBM A2 is an open source massively multicore capable and multithreaded 64-bit Power ISA processor core designed by IBM using the Power ISA v.2.06 specification. Versions of processors based on the A2 core range from a 2.3 GHz version with 16 cores consuming 65 W to a less powerful, four core version, consuming 20 W at 1.4 GHz.

The SPARC T4 is a SPARC multicore microprocessor introduced in 2011 by Oracle Corporation. The processor is designed to offer high multithreaded performance, as well as high single threaded performance from the same chip. The chip is the 4th generation processor in the T-Series family. Sun Microsystems brought the first T-Series processor to market in 2005.
The MCST R1000 is a 64-bit microprocessor developed by Moscow Center of SPARC Technologies (MCST) and fabricated by TSMC.
The SPARC T-series family of RISC processors and server computers, based on the SPARC V9 architecture, was originally developed by Sun Microsystems, and later by Oracle Corporation after its acquisition of Sun. Its distinguishing feature from earlier SPARC iterations is the introduction of chip multithreading (CMT) technology, a multithreading, multicore design intended to drive greater processor utilization at lower power consumption.










