
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel and an oxidizing agent into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied.

A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell, is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or primary battery, which is supplied fully charged and discarded after use. It is composed of one or more electrochemical cells. The term "accumulator" is used as it accumulates and stores energy through a reversible electrochemical reaction. Rechargeable batteries are produced in many different shapes and sizes, ranging from button cells to megawatt systems connected to stabilize an electrical distribution network. Several different combinations of electrode materials and electrolytes are used, including lead–acid, zinc–air, nickel–
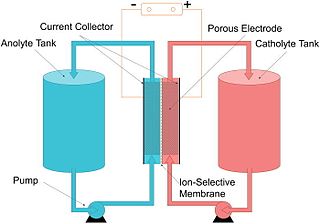
The vanadium redox battery (VRB), also known as the vanadium flow battery (VFB) or vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB), is a type of rechargeable flow battery. It employs vanadium ions as charge carriers. The battery uses vanadium's ability to exist in a solution in four different oxidation states to make a battery with a single electroactive element instead of two. For several reasons, including their relative bulkiness, vanadium batteries are typically used for grid energy storage, i.e., attached to power plants/electrical grids.

A flow battery, or redox flow battery, is a type of electrochemical cell where chemical energy is provided by two chemical components dissolved in liquids that are pumped through the system on separate sides of a membrane. Ion transfer inside the cell occurs through the membrane while both liquids circulate in their own respective space. Cell voltage is chemically determined by the Nernst equation and ranges, in practical applications, from 1.0 to 2.43 volts. The energy capacity is a function of the electrolyte volume and the power is a function of the surface area of the electrodes.
Energy Conversion Devices (ECD) was an American photovoltaics manufacturer of thin-film solar cells made of amorphous silicon used in flexible laminates and in building-integrated photovoltaics. The company was also a manufacturer of rechargeable batteries and other renewable energy related products. ECD was headquartered in Rochester Hills, Michigan.
A zinc-bromine battery is a rechargeable battery system that uses the reaction between zinc metal and bromine to produce electric current, with an electrolyte composed of an aqueous solution of zinc bromide. It is being developed as an alternative to lithium-ion batteries for stationary power applications from domestic through to grid-scale. The water-based electrolyte makes the battery system less prone to overheating and fire compared with lithium-ion battery systems.
Konarka Technologies, Inc. was a solar energy company based in Lowell, Massachusetts, founded in 2001 as a spin-off from University of Massachusetts Lowell. In late May 2012, the company filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy protection and laid off its approximately 80-member staff. The company’s operations have ceased and a trustee is tasked with liquidating the company’s assets for the benefit of creditors.

A123 Systems, LLC, a subsidiary of the Chinese Wanxiang Group Holdings, is a developer and manufacturer of lithium iron phosphate batteries and energy storage systems.

An electric vehicle battery is a rechargeable battery used to power the electric motors of a battery electric vehicle (BEV) or hybrid electric vehicle (HEV). Typically lithium-ion batteries, they are specifically designed for high electric charge capacity.

The renewable-energy industry is the part of the energy industry focusing on new and appropriate renewable energy technologies. Investors worldwide have paid greater attention to this emerging industry in recent years. In many cases, this has translated into rapid renewable energy commercialization and considerable industry expansion. The wind power, solar power and hydroelectric power industries provide good examples of this.

An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices.
A solid-state battery is a battery technology that uses solid electrodes and a solid electrolyte, instead of the liquid or polymer gel electrolytes found in lithium-ion or lithium polymer batteries.

CODA Automotive Inc. was a privately held American company headquartered in Los Angeles, California. The company designed and assembled lithium-iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery systems for automotive and power storage utility applications, and electric cars. Miles Automotive partnered with Hafei and Qingyuan Electric Vehicle to establish Coda Automotive as an affiliate company. The name CODA comes from the musical term for the concluding passage of a piece of music. CODA Automotive has said that it chose the name because its electric vehicle technology represents an end for combustion engine vehicles, and the start of the electric vehicle era.
Form Energy is an American energy storage company focused on developing a new class of cost-effective, multi-day energy storage systems that will enable a reliable and fully-renewable electric grid year-round. Form Energy's first commercial product is a rechargeable iron-air battery capable of storing electricity for 100 hours at system costs competitive with legacy power plants.
Aquion Energy was a Bethlehem, Pennsylvania and Washington, D.C.-based company that manufactured sodium ion batteries and electricity storage systems.
Aluminium-ion batteries are a class of rechargeable battery in which aluminium ions serve as charge carriers. Aluminium can exchange three electrons per ion. This means that insertion of one Al3+ is equivalent to three Li+ ions. Thus, since the ionic radii of Al3+ (0.54 Å) and Li+ (0.76 Å) are similar, significantly higher numbers of electrons and Al3+ ions can be accepted by cathodes with little damage. Al has 50 times (23.5 megawatt-hours m-3) the energy density of Li and is even higher than coal.
Research in lithium-ion batteries has produced many proposed refinements of lithium-ion batteries. Areas of research interest have focused on improving energy density, safety, rate capability, cycle durability, flexibility, and cost.
nanoFlowcell Holdings plc is a Swiss flow cell battery research and development company.
The Iron Redox Flow Battery (IRFB), also known as Iron Salt Battery (ISB), stores and releases energy through the electrochemical reaction of iron salt. This type of battery belongs to the class of redox-flow batteries (RFB), which are alternative solutions to Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIB) for stationary applications. The IRFB can achieve up to 70% energy efficiency. In comparison, other long duration storage technologies provide lower efficiencies.
Tinci Materials, simply known as Tinci, is a Chinese cosmetics materials manufacturer founded by Xu Jinfu in 2000. The company primarily involves in the R&D and production of new fine chemical materials, especially specializing in the producing of electrolytes. Additionally, the company also makes battery materials and specialty chemicals.








