A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is a, plural aes. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter Alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type.

The Cyrillic script, Slavonic script or simply Slavic script is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia, and used by many other minority languages.
Gamma is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop IPA:[ɡ]. In Modern Greek, this letter normally represents a voiced velar fricative IPA:[ɣ], except before either of the two front vowels, where it represents a voiced palatal fricative IPA:[ʝ]; while /g/ in foreign words is instead commonly transcribed as γκ).

Type design is the art and process of designing typefaces. This involves drawing each letterform using a consistent style. The basic concepts and design variables are described below.
A cedilla, or cedille, is a hook or tail added under certain letters as a diacritical mark to modify their pronunciation. In Catalan, French, and Portuguese it is used only under the letter c, and the entire letter is called, respectively, c trencada, c cédille, and c cedilhado. It is used to mark vowel nasalization in many languages of sub-Saharan Africa, including Vute from Cameroon.
Beta is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive IPA:[b]. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative IPA:[v] while IPA:[b] in borrowed words is instead commonly transcribed as μπ. Letters that arose from beta include the Roman letter ⟨B⟩ and the Cyrillic letters ⟨Б⟩ and ⟨В⟩.

The letter F with hook is a letter of the Latin script, based on the italic form of f; or on its regular form with a descender hook added. A very similar-looking letter, ⟨ʄ⟩, is used in the IPA for a voiced palatal implosive.

Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals and smaller lowercase in the written representation of certain languages. The writing systems that distinguish between the upper- and lowercase have two parallel sets of letters: each in the majuscule set has a counterpart in the minuscule set. Some counterpart letters have the same shape, and differ only in size, but for others the shapes are different. The two case variants are alternative representations of the same letter: they have the same name and pronunciation and are typically treated identically when sorting in alphabetical order.

The Ol Chiki script, also known as Ol Chemetʼ, Ol Ciki, Ol, and sometimes as the Santali alphabet invented by Pandit Raghunath Murmu in the year 1925, is the official writing system for Santali, an Austroasiatic language recognized as an official regional language in India. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. It has 30 letters, the design of which is intended to evoke natural shapes. The script is written from left to right, and has two styles. Unicode does not maintain a distinction between these two, as is typical for print and cursive variants of a script. In both styles, the script is unicameral.
The shapes of the letters are not arbitrary, but reflect the names for the letters, which are words, usually the names of objects or actions representing conventionalized form in the pictorial shape of the characters.

The ʻokina, also called by several other names, is a unicameral consonant letter used within the Latin script to mark the phonemic glottal stop in many Polynesian languages.

Esh is a character used in phonology to represent the voiceless postalveolar fricative.
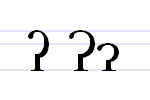
The character ⟨ʔ⟩ called glottal stop, is an alphabetic letter in some Latin alphabets, most notably in several languages of Canada where it indicates a glottal stop sound. Such usage derives from phonetic transcription, for example the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), that use this letter for the glottal stop sound. The letter derives graphically from use of the apostrophe ⟨ʼ⟩ or the symbol ʾ for glottal stop.

Ou is a ligature of the Greek letters ο and υ which was frequently used in Byzantine manuscripts. This omicron-upsilon ligature is still seen today on icon artwork in Greek Orthodox churches, and sometimes in graffiti or other forms of informal or decorative writing.

Latin alpha or script a is a letter of the Latin alphabet based on one lowercase form of a, or on the Greek lowercase alpha (α).
A letter is a segmental symbol of a phonemic writing system. The inventory of all letters forms an alphabet. Letters broadly correspond to phonemes in the spoken form of the language, although there is rarely a consistent and exact correspondence between letters and phonemes.

Đ, known as crossed D or dyet, is a letter formed from the base character D/d overlaid with a crossbar. Crossing was used to create eth (ð), but eth has an uncial as its base whereas đ is based on the straight-backed roman d, like in Sámi Languages and Vietnamese. Crossed d is a letter in the alphabets of several languages and is used in linguistics as a voiced dental fricative.

Q with hook tail is a letter of the extended Latin alphabet. It was introduced by Lutheran missionaries in Papua New Guinea for use in the Numanggang language in the 1930s or 1940s. In 2002, it was decided to discontinue using the letter. It is still used in the Kâte language to represent a voiced labial-velar plosive.

The Latin script is the most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world. It is the standard script of the English language and is often referred to simply as "the alphabet" in English. It is a true alphabet which originated in the 7th century BC in Italy and has changed continually over the last 2,500 years. It has roots in the Semitic alphabet and its offshoot alphabets, the Phoenician, Greek, and Etruscan. The phonetic values of some letters changed, some letters were lost and gained, and several writing styles ("hands") developed. Two such styles, the minuscule and majuscule hands, were combined into one script with alternate forms for the lower and upper case letters. Modern uppercase letters differ only slightly from their classical counterparts, and there are few regional variants.
Greek orthography has used a variety of diacritics starting in the Hellenistic period. The more complex polytonic orthography, which includes five diacritics, notates Ancient Greek phonology. The simpler monotonic orthography, introduced in 1982, corresponds to Modern Greek phonology, and requires only two diacritics.
The letter Ƭ, called T with hook, is a letter of the Latin alphabet based on the letter t. It is used in the Serer language.











