
The United Nations General Assembly is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Currently in its 76th session, its powers, composition, functions, and procedures are set out in Chapter IV of the United Nations Charter. The UNGA is responsible for the UN budget, appointing the non-permanent members to the Security Council, appointing the Secretary-General of the United Nations, receiving reports from other parts of the UN system, and making recommendations through resolutions. It also establishes numerous subsidiary organs to advance or assist in its broad mandate. The UNGA is the only UN organ wherein all member states have equal representation.

A United Nations Security Council resolution is a United Nations resolution adopted by the fifteen members of the Security Council (UNSC); the United Nations (UN) body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".

United Nations Security Council Resolution 478, adopted on 20 August 1980, is one of two General Assembly resolutions followed by seven UNSC resolutions condemning Israel's attempted annexation of East Jerusalem. In particular, UNSC res 478 notes Israel's non-compliance with United Nations Security Council Resolution 476 and condemned Israel's 1980 Jerusalem Law which declared Jerusalem to be Israel's "complete and united" capital, as a violation of international law. The resolution states that the council will not recognize this law, and calls on member states to accept the decision of the council. This resolution also calls upon member states to withdraw their diplomatic missions from the city.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1373, adopted unanimously on 28 September 2001, is a counterterrorism measure passed following the 11 September terrorist attacks on the United States. The resolution was adopted under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, and is therefore binding on all UN member states.

United Nations Security Council resolution 497, adopted unanimously on 17 December 1981, declared that the Israeli Golan Heights Law, which effectively annexed the Golan Heights, is "null and void and without international legal effect" and further calls on Israel to rescind its action.

A United Nations resolution is a formal text adopted by a United Nations (UN) body. Although any UN body can issue resolutions, in practice most resolutions are issued by the Security Council or the General Assembly.

The United Nations Security Council veto power is the power of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council to veto any "substantive" resolution. They also happen to be the nuclear-weapon states (NWS) under the terms of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT). However, a permanent member's abstention or absence does not prevent a draft resolution from being adopted. This veto power does not apply to "procedural" votes, as determined by the permanent members themselves. A permanent member can also block the selection of a Secretary-General, although a formal veto is unnecessary since the vote is taken behind closed doors.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 135, adopted on May 27, 1960, after a failed meeting between the Heads of State of France, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, the United Kingdom and the United States, the Council recommended those governments seek solutions of existing international problems by negotiation or other peaceful means as provided in the Charter of the United Nations. The resolution pleaded with them to refrain from the use of threats of force, to seek disarmament in accordance with United Nations General Assembly Resolution 1378, to discontinue all nuclear weapons tests and to avail themselves to the assistance of the Council and any other appropriate UN organs to render these ends.
The Counter-Terrorism Committee is a subsidiary body of the United Nations Security Council.
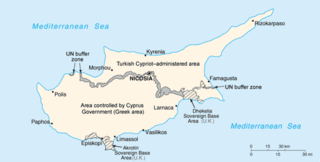
United Nations Security Council Resolution 422, adopted on December 15, 1977, noted a report of the Secretary-General that, due to the existing circumstances, the presence of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus would continue to be essential for a peaceful settlement. The Council expressed its concerns regarding actions which could heighten tensions, and asked the Secretary-General to report back again before May 31, 1978 to follow the implementation of the resolution.

United Nations Security Council resolution 461, adopted on 31 December 1979, after recalling its Resolution 457 (1979), the council noted the increasing tension between Iran and the United States and condemned Iran for continuing to hold American hostages at the U.S. embassy in Tehran. The council also cited the International Court of Justice order to immediately release the hostages without any exceptions.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1197, adopted unanimously on 18 September 1998, after reaffirming its primary responsibility to maintain international peace and security, the Council addressed co-operation efforts with the Organisation of African Unity (OAU).

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1417 extended the mandate of the United Nations Organisation Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 30 June 2003. It was unanimously adopted by the United Nations Security Council on 14 June 2002, at its 4,554th meeting. Resolution 1417 was passed after the security council recalled its previous resolutions regarding the matter, particularly Resolution 1355 (2001).

United Nations Security Council resolution 1625, adopted unanimously at the 2005 World Summit on 14 September 2005, the Council adopted a declaration on the role of the Security Council in conflict prevention, particularly in Africa where many armed conflicts were taking place.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1738, adopted unanimously on December 23, 2006, after reaffirming resolutions 1265 (1999), 1296 (2000), 1502 (2003) and 1674 (2006) on the protection of civilians in armed conflict, the Council condemned attacks against journalists in conflict situations. It was the last resolution adopted by the Security Council in 2006.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1872 was unanimously adopted on 26 May 2009.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1810 was unanimously adopted on 25 April 2008.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1813 was unanimously adopted on 30 April 2008.












