
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior responsible for administering federal lands. Headquartered in Washington, D.C., and with oversight over 247.3 million acres (1,001,000 km2), it governs one eighth of the country's landmass.
In the United States, a territory is any extent of region under the sovereign jurisdiction of the federal government of the United States, including all waters. The United States asserts sovereign rights for exploring, exploiting, conserving, and managing its territory. This extent of territory is all the area belonging to, and under the dominion of, the United States federal government for administrative and other purposes. The United States total territory includes a subset of political divisions.
In all modern states, a portion of land is held by central or local governments. This is called public land, state land, or Crown land. The system of tenure of public land, and the terminology used, varies between countries. The following examples illustrate some of the range.

The General Land Office (GLO) was an independent agency of the United States government responsible for public domain lands in the United States. It was created in 1812 to take over functions previously conducted by the United States Department of the Treasury. Starting with the enactment of the Land Ordinance of 1785, which created the Public Land Survey System, the Treasury Department had already overseen the survey of the Northwest Territory, including what is now the state of Ohio.

The Sagebrush Rebellion was a movement in the Western United States in the 1970s and the 1980s that sought major changes to federal land control, use, and disposal policy in 13 western states in which federal land holdings include between 20% and 85% of a state's area. Supporters of the movement wanted more state and local control over the lands, if not outright transfer of them to state and local authorities and/or privatization. As much of the land in question is sagebrush steppe, supporters adopted the name "Sagebrush Rebellion."
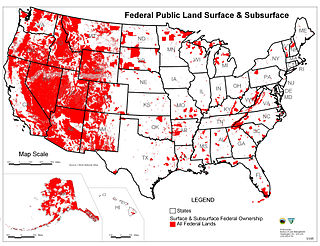
Federal lands are lands in the United States owned by the federal government. Pursuant to the Property Clause of the United States Constitution, Congress has the power to retain, buy, sell, and regulate federal lands, such as by limiting cattle grazing on them. These powers have been recognized in a long line of United States Supreme Court decisions.

The Upper Missouri River Breaks National Monument is a national monument in the western United States, protecting the Missouri Breaks of north central Montana. Managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), it is a series of badland areas characterized by rock outcroppings, steep bluffs, and grassy plains; a topography referred to as "The Breaks" by locals.

The Taylor Grazing Act of 1934 is a United States federal law that provides for the regulation of grazing on the public lands to improve rangeland conditions and regulate their use.

The Federal Land Policy and Management Act (FLPMA) is a United States federal law that governs the way in which the public lands administered by the Bureau of Land Management are managed. The law was enacted in 1976 by the 94th Congress and is found in the United States Code under Title 43. The Federal Land Policy and Management Act phased out homesteading in the United States by repealing the pre-existing Homestead Acts.

Grazing rights is the right of a user to allow their livestock to feed (graze) in a given area.
Kleppe v. New Mexico, 426 U.S. 529 (1976), was a United States Supreme Court decision that unanimously held the Wild and Free-Roaming Horses and Burros Act of 1971, passed in 1971 by the United States Congress to protect these animals from "capture, branding, harassment, or death", to be a constitutional exercise of congressional power. In February 1974, the New Mexico Livestock Board rounded up and sold 19 unbranded burros from Bureau of Land Management (BLM) land. When the BLM demanded the animals' return, the state filed suit claiming that the Wild Free-Roaming Horses and Burros Act was unconstitutional, claiming the federal government did not have the power to control animals in federal lands unless they were items in interstate commerce or causing damage to the public lands.
In U.S. Law, Section 15 lands are public lands that lie outside a grazing district administered by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) under Section 15 of the Taylor Grazing Act of 1934. The BLM authorizes livestock grazing on these lands by issuing leases to private parties.
The Pryor Mountains Wild Horse Range is a refuge for a historically significant herd of free-roaming mustangs, the Pryor Mountain mustang, feral horses colloquially called "wild horses", located in the Pryor Mountains of Montana and Wyoming in the United States. The range has an area of 39,650 acres (160.5 km2) and was established in 1968 along the Montana–Wyoming border as the first protected refuge dedicated exclusively for mustangs. It was the second feral horse refuge in the United States. About a quarter of the refuge lies within the Bighorn Canyon National Recreation Area. A group of federal agencies, led by the Bureau of Land Management, administers the range.

The Wild and Free-Roaming Horses and Burros Act of 1971 (WFRHBA), is an Act of Congress, signed into law by President Richard M. Nixon on December 18, 1971. The act covered the management, protection and study of "unbranded and unclaimed horses and burros on public lands in the United States."

Management of free-roaming feral and semi-feral horses, on various public or tribal lands in North America is accomplished under the authority of law, either by the government of jurisdiction or efforts of private groups. In western Canada, management is a provincial matter, with several associations and societies helping to manage wild horses in British Columbia and Alberta. In Nova Scotia, and various locations in the United States, management is under the jurisdiction of various federal agencies. The largest population of free-roaming horses is found in the Western United States. Here, most of them are protected under the Wild and Free-Roaming Horses and Burros Act of 1971 (WFRH&BA), and their management is primarily undertaken by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), but also by the U. S. Forest Service (USFS)

The Federal Lands Jobs and Energy Security Act is a bill that would require the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) to establish certain fees for activities related to the development of oil and gas on federal lands. A portion of those amounts along with a portion of fees from renewable energy projects on federal lands would be available to the agency, subject to appropriation, to cover the costs of activities aimed at increasing energy development on federal lands. The bill also would exempt lawsuits related to energy production on federal lands from the Equal Access to Justice Act (EAJA). In addition, the legislation would require the BLM to offer for sale at least 25 percent of onshore federal lands nominated by firms for oil and gas leasing. It was introduced in the United States House of Representatives during the 113th United States Congress. President Barack Obama threatened to veto the bill on November 19, 2013.
The 2014 Bundy standoff was an armed confrontation between supporters of cattle rancher Cliven Bundy and law enforcement following a 21-year legal dispute in which the United States Bureau of Land Management (BLM) obtained court orders directing Bundy to pay over $1 million in withheld grazing fees for Bundy's use of federally owned land adjacent to Bundy's ranch in southeastern Nevada.
Grazing rights in Nevada covers a number of rangeland Federal and state laws and regulations applicable to the state of Nevada. Rangelands are distinguished from pasture lands because they grow primarily native vegetation, rather than plants established by humans. Ranchers may lease or obtain permits to use portions of this public rangeland and pay a fee based on the number and type of livestock and the period for which they are on the land.

The Lowering Gasoline Prices to Fuel an America That Works Act of 2014 is a bill that would revise existing laws and policies regarding the development of oil and gas resources on the Outer Continental Shelf. The bill is intended to increase domestic energy production and lower gas prices.
In the United States, land owned and managed by governmental organizations is referred to as public land. As of 2020, the federal government owns roughly 640 million acres of land, the majority of which is concentrated in the Western US and Alaska. Privatization of public land involves the selling or auctioning of public lands to the private sector. The private sector can refer to private individuals, industry, or corporations.








