Related Research Articles
A network operating system (NOS) is a specialized operating system for a network device such as a router, switch or firewall.
Linksys is an American brand of data networking hardware products mainly sold to home users and small businesses. It was founded in 1988 by the couple Victor and Janie Tsao, both Taiwanese immigrants to the United States. Linksys products include WiFi routers, mesh WiFi systems, Wifi extenders, access points, network switches, WiFi networking and smart home automation products. It is headquartered in Irvine, California.
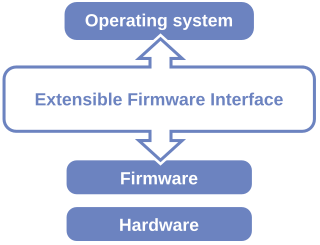
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware. UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface originally present in all IBM PC-compatible personal computers, with most UEFI firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services. UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even with no operating system installed.

The Linksys WRT54G Wi-Fi series is a series of Wi-Fi–capable residential gateways marketed by Linksys, a subsidiary of Cisco from 2003 until acquired by Belkin in 2013. A residential gateway connects a local area network to a wide area network.

A wireless router is a device that performs the functions of a router and also includes the functions of a wireless access point. It is used to provide access to the Internet or a private computer network. Depending on the manufacturer and model, it can function in a wired local area network, in a wireless-only LAN, or in a mixed wired and wireless network.

Ralink Technology, Corp. was a Wi-Fi chipset manufacturer mainly known for their IEEE 802.11 chipsets. Ralink was founded in 2001 in Cupertino, California, then moved its headquarters to Hsinchu, Taiwan.
In a computer, the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) provides an open standard that operating systems can use to discover and configure computer hardware components, to perform power management e.g. putting unused hardware components to sleep, to perform auto configuration e.g. Plug and Play and hot swapping, and to perform status monitoring. First released in December 1996, ACPI aims to replace Advanced Power Management (APM), the MultiProcessor Specification, the PCI BIOS specification, and the Plug and Play BIOS (PnP) Specification. ACPI brings the power management under the control of the operating system, as opposed to the previous BIOS-centric system that relied on platform-specific firmware to determine power management and configuration policies. The specification is central to the Operating System-directed configuration and Power Management (OSPM) system. ACPI defines a hardware abstraction interface between the system firmware, the computer hardware components, and the operating systems.

DD-WRT is Linux-based firmware for wireless routers and access points. Originally designed for the Linksys WRT54G series, it now runs on a wide variety of models. DD-WRT is one of a handful of third-party firmware projects designed to replace manufacturer's original firmware with custom firmware offering additional features or functionality.
The NSLU2 is a network-attached storage (NAS) device made by Linksys introduced in 2004 and discontinued in 2008. It makes USB flash memory and hard disks accessible over a network using the SMB protocol. It was superseded mainly by the NAS200 and in another sense by the WRT600N and WRT300N/350N which both combine a Wi-Fi router with a storage link.
A proprietary device driver is a closed-source device driver published only in binary code. In the context of free and open-source software, a closed-source device driver is referred to as a blob or binary blob. The term usually refers to a closed-source kernel module loaded into the kernel of an open-source operating system, and is sometimes also applied to code running outside the kernel, such as system firmware images, microcode updates, or userland programs. The term blob was first used in database management systems to describe a collection of binary data stored as a single entity.

Tomato is a family of community-developed, custom firmware for consumer-grade computer networking routers and gateways powered by Broadcom chipsets. The firmware has been continually forked and modded by multiple individuals and organizations, with the most up-to-date fork provided by the FreshTomato project.
ipkg, or the Itsy Package Management System, is a discontinued lightweight package management system designed for embedded devices that resembles Debian's dpkg. It was used in the Unslung operating system for the Linksys NSLU2 (Optware), in OpenWrt, Openmoko, webOS, Gumstix, the iPAQ, QNAP NAS appliances and elsewhere; as of early 2017 it can still be used for the Synology NAS appliances and in the LuneOS operating system.

The Texas Instruments AR7 or TI-AR7 is a fully integrated single-chip ADSL CPE access router solution. The AR7 combines a MIPS32 processor, a DSP-based digital transceiver, and an ADSL analog front end.
SlugOS is common source base for a group of firmware distributions for the Linksys NSLU2.
The NAS200 is a network-attached storage appliance intended for the consumer market. It was originally marketed by the Linksys division of Cisco Systems in 2007.
Linksys WAG300N is a Draft-N wireless gateway with two large captive antennae and 4 Ethernet ports. It was the smallest such device tested by MacUser, but the web interface was deemed "infuriating" and transfer rates to a MacBook "untenably slow". WAG300N is based on a Broadcom BCM63xx SoC, and runs a Linux-based firmware.
Last most recent official released firmware:
Product Versions: /(Annex B)
Classification: Firmware Release History
Release Date: 23 May 2008
Firmware-Version: 1.01.07 (ETSI)
Linksys manufactures a series of network routers. Many models are shipped with Linux-based firmware and can run third-party firmware. The first model to support third-party firmware was the very popular Linksys WRT54G series.
OpenWrt is an open-source project for embedded operating systems based on Linux, primarily used on embedded devices to route network traffic. The main components are Linux, util-linux, musl, and BusyBox. All components have been optimized to be small enough to fit into the limited storage and memory available in home routers.
DebWrt is a discontinued, niche Linux distribution mainly installed on embedded systems. It was built on top of an OpenWrt base which was used to load a fully functional version of Debian from the RootFS stored on the attached USB storage device. For easy installation and deinstallation of packages it relied on the dpkg Package management system. DebWrt used the command-line interface of Bash. There was no web-based GUI interface.