
Mir was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. Mir was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996. It had a greater mass than any previous spacecraft. At the time it was the largest artificial satellite in orbit, succeeded by the International Space Station (ISS) after Mir's orbit decayed. The station served as a microgravity research laboratory in which crews conducted experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and spacecraft systems with a goal of developing technologies required for permanent occupation of space.

The Progress is a Russian expendable cargo spacecraft. Its purpose is to deliver the supplies needed to sustain a human presence in orbit. While it does not carry a crew, it can be boarded by astronauts when docked to a space station, hence it is classified as crewed by its manufacturer. Progress is derived from the crewed Soyuz spacecraft and launches on the same launch vehicle, a Soyuz rocket.

The Automated Transfer Vehicle, originally Ariane Transfer Vehicle or ATV, was an expendable cargo spacecraft developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), used for space cargo transport in 2008–2015. The ATV design was launched to orbit five times, exclusively by the Ariane 5 heavy-lift launch vehicle. It effectively was a larger European counterpart to the Russian Progress cargo spacecraft for carrying upmass to a single destination—the International Space Station (ISS)—but with three times the capacity.

Soyuz TM-21 was a crewed Soyuz spaceflight to Mir. The mission launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome, atop a Soyuz-U2 carrier rocket, at 06:11:34 UTC on March 14, 1995. The flight marked the first time thirteen humans were flying in space simultaneously, with three aboard the Soyuz, three aboard Mir and seven aboard Space Shuttle Endeavour, flying STS-67.
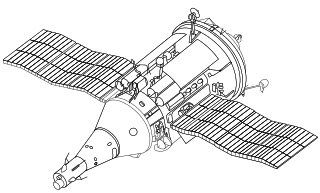
The TKS spacecraft was a Soviet spacecraft conceived in the late 1960s for resupply flights to the military Almaz space station.

The Shuttle–Mir program was a collaborative 11-mission space program between Russia and the United States that involved American Space Shuttles visiting the Russian space station Mir, Russian cosmonauts flying on the Shuttle, and an American astronaut flying aboard a Soyuz spacecraft to engage in long-duration expeditions aboard Mir.
Progress M-5 was a Soviet uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1990 to resupply the Mir space station. The twenty-third of sixty four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 206. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the EO-7 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres. It was the first of ten Progress flights to carry a VBK-Raduga capsule, which was recovered after the flight.
Progress M-7 was a Soviet uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1991 to resupply the Mir space station. The twenty-fifth of sixty four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 208. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the EO-8 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres. It also carried the second VBK-Raduga capsule, intended to return equipment and experiment results to Earth.
Progress M-9 was a Soviet uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1991 to resupply the Mir space station. The twenty-seventh of sixty four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 210. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the EO-9 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres. It was the third Progress spacecraft to carry a VBK-Raduga capsule, which was used to return equipment and experiment results to Earth.
Progress M-10 was a Soviet and subsequently Russian uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1991 to resupply the Mir space station. The 28th of 64 Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 211. It carried supplies including food, water, and oxygen for the EO-10 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres. It carried the fourth VBK-Raduga capsule, which was used to return experiment results and equipment to Earth when the Progress was deorbited.
Progress M-17 was a Russian uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1993 to resupply the Mir space station. The thirty-fifth of sixty-four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 217. In addition to delivering cargo, Progress M-17 was also used to demonstrate extended duration Progress missions; remaining in orbit for almost a year with a docked phase lasting 132 days.
Progress M-18 was a Russian cargo uncrewed spacecraft which was launched in 1993 to resupply the Mir space station. The thirty-sixth of sixty four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 218. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the EO-13 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres.

Progress MS-03, identified by NASA as Progress 64P, was a Progress spaceflight operated by Roscosmos to resupply the International Space Station (ISS). It was the first Progress MS to have an external compartment for releasing satellites.

Kounotori 7 (こうのとり7号機), also known as HTV-7, was the seventh flight of the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV), an uncrewed cargo spacecraft launched on 22 September 2018 to resupply the International Space Station.

Progress M-14, was a Russian uncrewed Progress cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1992 to resupply the Mir space station. The spacecraft was modified to transport the first VDU propulsion unit to Mir. Progress M-14 also carried the sixth VBK-Raduga capsule, which was recovered after the flight.

Progress M-19 was a Russian unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in 1993 to resupply the Mir space station.

Progress M-20 was a Russian unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in 1993 to resupply the Mir space station.

Progress M-23 was a Russian unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in May 1994 to resupply the Mir space station.











