The Heck reaction is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide with an alkene in the presence of a base and a palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. It is named after Tsutomu Mizoroki and Richard F. Heck. Heck was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Ei-ichi Negishi and Akira Suzuki, for the discovery and development of this reaction. This reaction was the first example of a carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction that followed a Pd(0)/Pd(II) catalytic cycle, the same catalytic cycle that is seen in other Pd(0)-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The Heck reaction is a way to substitute alkenes.
The Stille reaction is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis. The reaction involves the coupling of two organic groups, one of which is carried as an organotin compound. A variety of organic electrophiles provide the other coupling partner. The Stille reaction is one of many palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions.
An isocyanide is an organic compound with the functional group –N+≡C−. It is the isomer of the related nitrile (–C≡N), hence the prefix is isocyano. The organic fragment is connected to the isocyanide group through the nitrogen atom, not via the carbon. They are used as building blocks for the synthesis of other compounds.

Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide, discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory.
The Hiyama coupling is a palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction of organosilanes with organic halides used in organic chemistry to form carbon–carbon bonds. This reaction was discovered in 1988 by Tamejiro Hiyama and Yasuo Hatanaka as a method to form carbon-carbon bonds synthetically with chemo- and regioselectivity. The Hiyama coupling has been applied to the synthesis of various natural products.
The Ullmann reaction or Ullmann coupling is a coupling reaction between aryl halides. Traditionally this reaction is effected by copper, but palladium and nickel are also effective catalysts. The reaction is named after Fritz Ullmann.

tert-Butyllithium is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CLi. As an organolithium compound, it has applications in organic synthesis since it is a strong base, capable of deprotonating many carbon molecules, including benzene. tert-Butyllithium is available commercially as hydrocarbon solutions; it is not usually prepared in the laboratory.

A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride Cl−Mg−CH3 and phenylmagnesium bromide (C6H5)−Mg−Br. They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds.
The Negishi coupling is a widely employed transition metal catalyzed cross-coupling reaction. The reaction couples organic halides or triflates with organozinc compounds, forming carbon-carbon bonds (C-C) in the process. A palladium (0) species is generally utilized as the metal catalyst, though nickel is sometimes used. A variety of nickel catalysts in either Ni0 or NiII oxidation state can be employed in Negishi cross couplings such as Ni(PPh3)4, Ni(acac)2, Ni(COD)2 etc.

Organocopper chemistry is the study of the physical properties, reactions, and synthesis of organocopper compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to copper chemical bond. They are reagents in organic chemistry.
Pivalic acid, also known as neovaleric acid, is a carboxylic acid with a molecular formula of (CH3)3CCO2H. This colourless, odiferous organic compound is solid at room temperature. A common abbreviation for the pivalyl or pivaloyl group (t-BuC(O)) is Piv and for pivalic acid (t-BuC(O)OH) is PivOH. It is an isomer of valeric acid, the other two isomers of it are 2-Methylbutanoic acid and 3-Methylbutanoic acid.

Vinyl bromide is a simple vinyl halide. It is a colorless liquid. It is produced from ethylene dibromide. It is mainly used as a comonomer to confer fire retardant properties to acrylate polymers.

Trimethyltin chloride is an organotin compound with the formula (CH3)3SnCl. It is a white solid that is highly toxic and malodorous. It is susceptible to hydrolysis.
Organotellurium chemistry describes the synthesis and properties of organotellurium compounds, chemical compounds containing a carbon-tellurium chemical bond. Organotellurium chemistry is a lightly studied area, in part because of it having few applications.

tert-Butyl peroxybenzoate (TBPB) an organic compound with the formula C6H5CO2CMe3 (Me = CH3). It is the most widely produced perester. It is often used as a radical initiator in polymerization reactions, such as the production of LDPE from ethylene, and for crosslinking, such as for unsaturated polyester resins.

Vinyllithium is an organolithium compound with the formula LiC2H3. A colorless or white solid, it is encountered mainly as a solution in tetrahydrofuran (THF). It is a reagent in synthesis of organic compounds, especially for vinylations.
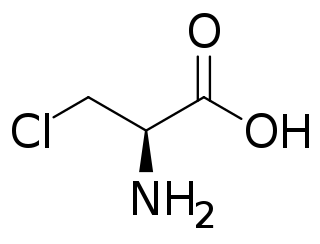
Chloroalanine (3-chloroalanine) is an unnatural amino acid with the formula ClCH2CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a white, water-soluble solid. The compound is usually derived from chlorination of serine. The compound is used in the synthesis of other amino acids by replacement of the chloride. Protected forms of the related iodoalanine are also known.
In cross-coupling reactions, the component reagents are called cross-coupling partners or simply coupling partners. These reagents can be further classified according to their nucleophilic vs electrophilic character:
In organometallic chemistry, metal–halogen exchange is a fundamental reaction that converts an organic halide into an organometallic product. The reaction commonly involves the use of electropositive metals and organochlorides, bromides, and iodides. Particularly well-developed is the use of metal–halogen exchange for the preparation of organolithium compounds.
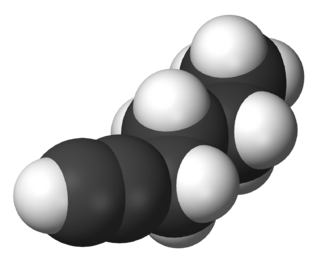
1-Hexyne is a hydrocarbon consisting of a straight six-carbon chain having a terminal alkyne. Its molecular formula is HC2C4H9. A colorless liquid, it is one of three isomers of hexyne. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis.















