
Flaviviridae is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors. The family gets its name from the yellow fever virus; flavus is Latin for "yellow", and yellow fever in turn was named because of its propensity to cause jaundice in victims. There are 89 species in the family divided among four genera. Diseases associated with the group include: hepatitis (hepaciviruses), hemorrhagic syndromes, fatal mucosal disease (pestiviruses), hemorrhagic fever, encephalitis, and the birth defect microcephaly (flaviviruses).
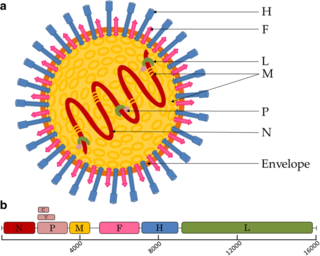
Paramyxoviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include measles, mumps, and respiratory tract infections. The family has four subfamilies, 17 genera, and 78 species, three genera of which are unassigned to a subfamily.

Morbillivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Mononegavirales, in the family Paramyxoviridae. Humans, dogs, cats, cattle, seals, and cetaceans serve as natural hosts. This genus includes seven species. Diseases in humans associated with viruses classified in this genus include measles: fever, and rash; in animals, they include acute febrile respiratory tract infection.

Indian Standard time (IST) is the time zone observed throughout India, with a time offset of UTC+05:30. India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. In military and aviation time IST is designated E* ("Echo-Star"). It is indicated as Asia/Kolkata in the IANA time zone database.
Roseolovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. There are currently six species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: HHV-6: sixth disease ; HHV-7: symptoms analog to the 'sixth disease'.
Rhadinovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae. Humans and other mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 12 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: Kaposi's sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma and multicentric Castleman's disease, caused by Human gammaherpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), also known as Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV). The term rhadino comes from the Latin fragile, referring to the tendency of the viral genome to break apart when it is isolated.

Parapoxvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Poxviridae, in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae. Like all members of the family Poxviridae, they are oval, relatively large, double-stranded DNA viruses. Parapoxviruses have a unique spiral coat that distinguishes them from other poxviruses. Parapoxviruses infect vertebrates, including a wide selection of mammals, and humans.
Mardivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae. Chickens, turkeys, and quail serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: Marek's disease, which causes asymmetric paralysis of one or more limbs, neurological symptoms, and development of multiple lymphomas that manifest as solid tumors. Gallid herpesvirus 2 is the only one of these viruses known to be pathogenic and due to the antigenic similarity between the three viruses the other two have been used to vaccinate against Marek's disease. These viruses have double stranded DNA genomes with no RNA intermediate.
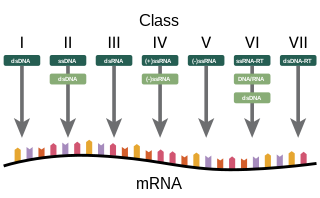
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Seven Baltimore groups are described that take into consideration whether the viral genome is made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA), whether the genome is single- or double-stranded, and whether the sense of a single-stranded RNA genome is positive or negative.

Gallid alphaherpesvirus 1 (GaHV-1) is a species of virus in the order Herpesvirales, family Herpesviridae, subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae, and genus Iltovirus. Originally recognised in chickens in the United States in 1926, this virus causes avian infectious laryngotracheitis, a potentially fatal, economically deleterious disease, widely recognised as one of the most contagious diseases in the poultry industry. The virus and its associated disease also occur in pheasants.
Varicellovirus (var′i-sel′ō-vi′rŭs) is a genus of viruses belonging to subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae, a member of family Herpesviridae. Humans and mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 19 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: HHV-3—chickenpox (varicella) and shingles; BoHV-1—infectious bovine rhinotracheitis/infectious pustular vulvovaginitis (IPV); SuHV-1 —Aujesky's disease characterized by central nervous system signs, high mortality rates in young animals, and respiratory illness in older pigs.

Iridoviridae is a family of viruses with double-stranded DNA genomes. Amphibians, fish, and invertebrates such as arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 22 species in this family, divided among two subfamilies and seven genera.

A viral disease occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.

Rubulavirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the family Paramyxoviridae. Humans, apes, pigs, and dogs serve as natural hosts. There are currently 18 species in the two genera Orthorubulavirus and Pararubulavirus. Diseases associated with this genus include mumps. Members of the subfamily are collectively called rubulaviruses. The subfamily was previously a genus named Rubulavirus but was elevated to subfamily in 2018. Viruses of this subfamily appear to be most closely related to members of Avulavirinae.
Yatapoxvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Poxviridae, in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae. Monkeys and baboons serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: histiocytomas, tumor-like mass of mononuclear cells.

Ampullaviridae is a family of viruses that infect archaea of the genus Acidianus. Only one genus in this family has been described, Bottigliavirus, which contains three species. The name of the family and genus is derived from the Latin word for bottle, ampulla, due to the virions having the shape of a bottle. The family was first described during an investigation of the microbial flora of hot springs in Italy.

Mitovirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses, in the family Mitoviridae. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There are five species in the genus.
Phasmaviridae is a family of viruses with negative stranded RNA genomes associated with insect hosts. They are a member of the order Bunyavirales. Phasmaviruses were first discovered in phantom midges of the genus Chaoborus in 2014.

Orthornavirae is a kingdom of viruses that have genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and which encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The RdRp is used to transcribe the viral RNA genome into messenger RNA (mRNA) and to replicate the genome. Viruses in this kingdom also share a number of characteristics involving evolution, including high rates of genetic mutations, recombinations, and reassortments.
Tolivirales is an order of RNA viruses which infect insects and plants. Member viruses have a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome. The virions are non-enveloped, spherical, and have an icosahedral capsid. The name of the group is a syllabic abbreviation of "tombusvirus-like" with the suffix -virales indicating a virus order.












