
The Energy Policy Act of 2005 is a federal law signed by President George W. Bush on August 8, 2005, at Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The act, described by proponents as an attempt to combat growing energy problems, changed US energy policy by providing tax incentives and loan guarantees for energy production of various types. The most consequential aspect of the law was to greatly increase ethanol production to be blended with gasoline. The law also repealed the Public Utility Holding Company Act of 1935, effective February 2006.
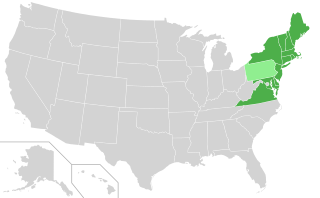
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI, pronounced "Reggie") is the first mandatory market-based program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States. RGGI is a cooperative effort among the states of Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Pennsylvania, Vermont and Virginia to cap and reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the power sector. RGGI compliance obligations apply to fossil-fueled power plants 25 megawatts (MW) and larger within the 12-state region. North Carolina is currently considering joining RGGI.

The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state, and local entities. It addresses issues of energy production, distribution, consumption, and modes of use, such as building codes, mileage standards, and commuting policies. Energy policy may be addressed via legislation, regulation, court decisions, public participation, and other techniques.

The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007, originally named the Clean Energy Act of 2007, is an Act of Congress concerning the energy policy of the United States. As part of the Democratic Party's 100-Hour Plan during the 110th Congress, it was introduced in the United States House of Representatives by Representative Nick Rahall of West Virginia, along with 198 cosponsors. Even though Rahall was 1 of only 4 Democrats to oppose the final bill, it passed in the House without amendment in January 2007. When the Act was introduced in the Senate in June 2007, it was combined with Senate Bill S. 1419: Renewable Fuels, Consumer Protection, and Energy Efficiency Act of 2007. This amended version passed the Senate on June 21, 2007. After further amendments and negotiation between the House and Senate, a revised bill passed both houses on December 18, 2007 and President Bush, a Republican, signed it into law on December 19, 2007, in response to his "Twenty in Ten" challenge to reduce gasoline consumption by 20% in 10 years.
A Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) is a regulation that requires the increased production of energy from renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal, which have been adopted in 38 of 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia. The United States federal RPS is called the Renewable Electricity Standard (RES). Several states have clean energy standards, which also allow for resources that do not produce emissions, such as large hydropower and nuclear power.

Community Choice Aggregation (CCA), also known as Community Choice Energy, municipal aggregation, governmental aggregation, electricity aggregation, and community aggregation, is an alternative to the investor-owned utility energy supply system in which local entities in the United States aggregate the buying power of individual customers within a defined jurisdiction in order to secure alternative energy supply contracts. The CCA chooses the power generation source on behalf of the consumers.

Appalachian Voices is an American environmental organization. Their stated environmental concerns include eliminating air pollution, ending mountaintop removal, cleaning up coal ash pollution and promoting renewable energy and energy efficiency.

Richard Lawrence Saslaw is an American politician serving as Majority Leader of the Senate of Virginia since 2020. A member of the Democratic Party, he served in the Virginia House of Delegates from 1976–80, then was elected to the Senate of Virginia. He currently represents the 35th district, made up of the city of Falls Church and portions of Fairfax County and the city of Alexandria.
New Energy for America was a plan led by Barack Obama and Joe Biden beginning in 2008 to invest in renewable energy sources, reduce reliance on foreign oil, address global warming issues, and create jobs for Americans. The main objective of the New Energy for America plan was to implement clean energy sources in the United States to switch from nonrenewable resources to renewable resources. The plan led by the Obama Administration aimed to implement short-term solutions to provide immediate relief from pain at the pump, and mid- to- long-term solutions to provide a New Energy for America plan. The goals of the clean energy plan hoped to: invest in renewable technologies that will boost domestic manufacturing and increase homegrown energy, invest in training for workers of clean technologies, strengthen the middle class, and help the economy.

California Proposition 7, would have required California utilities to procure half of their power from renewable resources by 2025. In order to make that goal, levels of production of solar, wind and other renewable energy resources would more than quadruple from their current output of 10.9%. It would also require California utilities to increase their purchase of electricity generated from renewable resources by 2% annually to meet Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) requirements of 40% in 2020 and 50% in 2025. Current law AB32 requires an RPS of 20% by 2010.

The American Clean Energy and Security Act of 2009 (ACES) was an energy bill in the 111th United States Congress that would have established a variant of an emissions trading plan similar to the European Union Emission Trading Scheme. The bill was approved by the House of Representatives on June 26, 2009, by a vote of 219–212. With no prospect of overcoming a threatened Republican filibuster, the bill was never brought to the floor of the Senate for discussion or a vote. The House passage of the bill was the "first time either house of Congress had approved a bill meant to curb the heat-trapping gases scientists have linked to climate change."

The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. In total, the United States has emitted over 400 billion metric tons of greenhouse gasses, more than any country in the world.
Modern United States wind energy policy coincided with the beginning of modern wind industry of the United States, which began in the early 1980s with the arrival of utility-scale wind turbines in California at the Altamont Pass wind farm. Since then, the industry has had to endure the financial uncertainties caused by a highly fluctuating tax incentive program. Because these early wind projects were fueled by investment tax credits based on installation rather than performance, they were plagued with issues of low productivity and equipment reliability. Those investment tax credits expired in 1986, which forced investors to focus on improving the reliability and efficiency of their turbines. The 1990s saw rise to a new type of tax credit, the production tax credit, which propelled technological improvements to the wind turbine even further by encouraging investors to focus on electricity output rather than installation.

Christopher Kalani Cushman Lee is an American politician and a Democratic member of the Hawaii Senate. He was the youngest member and only millennial serving in the Hawaii State Legislature when elected in November, 2008. He currently serves as Majority Whip and Chairman of the House Judiciary Committee. He also serves on the boards of several non-profit organizations and commissions.

The Illinois Clean Jobs Bill is a renewable-energy bill that was introduced in the 99th Illinois General Assembly. It was sponsored by Democratic state senator Don Harmon of Oak Park and Democratic state representative Elaine Nekritz of Northbrook. The bill died in committee.

Lashrecse Dianna Aird /ˌlɔ.ʃəˈɹis/ is an American Democratic politician who represented the 63rd District in the Virginia House of Delegates from 2016 to 2022. The district includes Dinwiddie County and the city of Petersburg as well as parts of the counties of Chesterfield and Prince George. Aird served on the General Laws, Health, Welfare and Institutions, and Appropriations committees.
A renewable portfolio standard (RPS) is a regulation that requires the increased production of energy from renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal. Other common names for the same concept include Renewable Electricity Standard (RES) at the United States federal level and Renewables Obligation in the UK.
Arizona House Bill 2005 is state-level legislation introduced in the Arizona State Legislature and signed into law in 2018.
California produces more renewable energy than any other state in the United States except Texas. In 2018, California ranked first in the nation as a producer of electricity from solar, geothermal, and biomass resources and fourth in the nation in conventional hydroelectric power generation. As of 2017, over half of the electricity (52.7%) produced was from renewable sources.

The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA) is a landmark United States federal law which aims to curb inflation by possibly reducing the federal government budget deficit, lowering prescription drug prices, and investing into domestic energy production while promoting clean energy. It was passed by the 117th United States Congress and signed into law by President Joe Biden on August 16, 2022.










