
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications may include bone fractures, muscle spasms, an abnormally curved spine, or intellectual disability.

Vitamin A is a group of unsaturated nutritional organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal, and several provitamin A carotenoids. Vitamin A has multiple functions: it is important for growth and development, for the maintenance of the immune system, and for good vision. Vitamin A is needed by the retina of the eye in the form of retinal, which combines with protein opsin to form rhodopsin, the light-absorbing molecule necessary for both low-light and color vision. Vitamin A also functions in a very different role as retinoic acid, which is an important hormone-like growth factor for epithelial and other cells.

Retinol, also known as vitamin A1-alcohol, is a vitamin in the vitamin A family found in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is ingested to treat and prevent vitamin A deficiency, especially that which results in xerophthalmia. In regions where deficiency is common, a single large dose is recommended to those at high risk a couple of times a year. It is also used to reduce the risk of complications in those who have measles. It is used by mouth or injection into a muscle.
Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) in (via the gut) and out (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and between body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and bone. Bone acts as a calcium storage center for deposits and withdrawals as needed by the blood via continual bone remodeling.

Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 and colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D which is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is also found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement. It is used to treat and prevent vitamin D deficiency and associated diseases, including rickets. It is also used for familial hypophosphatemia, hypoparathyroidism that is causing low blood calcium, and Fanconi syndrome. Vitamin-D supplements may not be effective in people with severe kidney disease. It is usually taken by mouth.

Ergocalciferol, also known as vitamin D2 and calciferol, is a type of vitamin D found in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to prevent and treat vitamin D deficiency. This includes vitamin D deficiency due to poor absorption by the intestines or liver disease. It may also be used for low blood calcium due to hypoparathyroidism. It is used by mouth or injection into a muscle.
A hormone receptor is a receptor molecule that binds to a specific hormone. Hormone receptors are a wide family of proteins made up of receptors for thyroid and steroid hormones, retinoids and Vitamin D, and a variety of other receptors for various ligands, such as fatty acids and prostaglandins. There are two main classes of hormone receptors. Receptors for peptide hormones tend to be cell surface receptors built into the plasma membrane of cells and are thus referred to as trans membrane receptors. An example of this is insulin. Receptors for steroid hormones are usually found within the cytoplasm and are referred to as intracellular or nuclear receptors, such as testosterone. Upon hormone binding, the receptor can initiate multiple signaling pathways, which ultimately leads to changes in the behavior of the target cells.
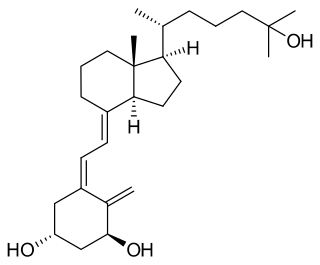
Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D, normally made in the kidney. A manufactured form is used to treat kidney disease with low blood calcium, hyperparathyroidism due to kidney disease, low blood calcium due to hypoparathyroidism, osteoporosis, osteomalacia, and familial hypophosphatemia. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.

Vitamin D toxicity, or hypervitaminosis D is the toxic state of an excess of vitamin D. The normal range for blood concentration is 20 to 50 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL).

Human iron metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that maintain human homeostasis of iron at the systemic and cellular level. Iron is both necessary to the body and potentially toxic. Controlling iron levels in the body is a critically important part of many aspects of human health and disease. Hematologists have been especially interested in systemic iron metabolism because iron is essential for red blood cells, where most of the human body's iron is contained. Understanding iron metabolism is also important for understanding diseases of iron overload, such as hereditary hemochromatosis, and iron deficiency, such as iron deficiency anemia.

Calbindins are three different calcium-binding proteins: calbindin, calretinin and S100G. They were originally described as vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding proteins in the intestine and kidney in the chick and mammals. They are now classified in different subfamilies as they differ in the number of Ca2+ binding EF hands.

The vitamin D receptor (VDR), also known as the calcitriol receptor and as NR1I1, is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, binds to the VDR, which then forms a heterodimer with the retinoid-X receptor. This then binds to hormone response elements on DNA resulting in expression or transrepression of specific gene products. The VDR not only regulates transcriptional responses but also involved in microRNA-directed post transcriptional mechanisms. In humans, the vitamin D receptor is encoded by the VDR gene.

X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH), is an X-linked dominant form of rickets that differs from most cases of rickets in that vitamin D supplementation does not cure it. It can cause bone deformity including short stature and genu varum (bow-leggedness). It is associated with a mutation in the PHEX gene sequence (Xp.22) and subsequent inactivity of the PHEX protein.

Vitamin D-binding protein (DBP), also/originally known as gc-globulin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GC gene.

Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins C1/C2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HNRNPC gene.

Cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A member 1 (abbreviated CYP24A1) is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes encoded by the CYP24A1 gene. It is a mitochondrial monooxygenase which catalyzes reactions including 24-hydroxylation of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3). It has also been identified as vitamin D3 24-hydroxylase.(EC 1.14.15.16)
Vitamin D deficiency, or hypovitaminosis D is defined as a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate sunlight exposure. Vitamin D deficiency can also be caused by inadequate nutritional intake of vitamin D, disorders limiting vitamin D absorption, and conditions impairing vitamin D conversion into active metabolites—including certain liver, kidney, and hereditary disorders. Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, leading to bone softening diseases such as rickets in children. It can also worsen osteomalacia and osteoporosis in adults, leading to an increased risk of bone fractures. Muscle weakness is also a common symptom of vitamin D deficiency, further increasing the risk of fall and bone fractures in adults. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with the development of schizophrenia.

Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (also known as cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).

Imerslund–Gräsbeck syndrome, is a rare autosomal recessive, familial form of vitamin B12 deficiency caused by malfunction of the "Cubam" receptor located in the terminal ileum. This receptor is composed of two proteins, amnionless (AMN), and cubilin. A defect in either of these protein components can cause this syndrome. This is a rare disease, with a prevalence about 1 in 200,000, and is usually seen in patients of European ancestry.
Vitamin D response element (VDRE) is a DNA sequence that is found in the promoter region of vitamin D regulated genes. The receptor for 1,25(OH)2D (VDR) binds to and regulates the expression of some genes.














