
A SIM card is an integrated circuit (IC) intended to securely store an international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephone devices. Technically the actual physical card is known as a universal integrated circuit card (UICC); this smart card is usually made of PVC with embedded contacts and semiconductors, with the SIM as its primary component. In practice the term "SIM card" is still used to refer to the entire unit and not simply the IC.

Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 centimetres (1.6 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be used for the bootstrapping of capable wireless connections. Like other proximity card technologies, NFC is based on inductive coupling between two electromagnetic coils present on a NFC-enabled device such as a smartphone. NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s.
Network switching subsystem (NSS) is the component of a GSM system that carries out call out and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations. It is owned and deployed by mobile phone operators and allows mobile devices to communicate with each other and telephones in the wider public switched telephone network (PSTN). The architecture contains specific features and functions which are needed because the phones are not fixed in one location.

A mobile phone feature is a capability, service, or application that a mobile phone offers to its users. Mobile phones are often referred to as feature phones, and offer basic telephony. Handsets with more advanced computing ability through the use of native code try to differentiate their own products by implementing additional functions to make them more attractive to consumers. This has led to great innovation in mobile phone development over the past 20 years.
The Personal Handy-phone System (PHS), also marketed as the Personal Communication Telephone (PCT) in Thailand, and the Personal Access System (PAS) and commercially branded as Xiaolingtong in Mainland China, was a mobile network system operating in the 1880–1930 MHz frequency band, used mainly in Japan, China, Taiwan, and some other Asian countries and regions.

The Sony Ericsson K800i, and its variant, the Sony Ericsson K790, are mobile phone handsets manufactured by Sony Ericsson. Launched in July 2006, the phones are the successor to the Sony Ericsson K750i, and are the first to be tagged with the Sony Cyber-shot branding. Both of the phones feature a 3.2-megapixel digital camera complete with a xenon flash, a protective lens cover, and a new "BestPic" bracketing feature. The new "BestPic" feature takes 9 full quality snapshots of a subject in quick succession, allowing the user to choose the best shots from them. On the entertainment front, the phones have a media player supporting MP3, AAC/AAC+/eAAC+ and WMA music files and 3GP/MPEG-4 video files. The phones also feature a RDS FM radio, and a Memory Stick Micro (M2) slot for expandable solid state memory. The K790/K800 models are also the first Sony Ericsson mobile phones to use ATI's Imageon 2192 graphics engine, which delivers a full 3D gaming graphics for Java and full support for its 3.2-megapixel camera. It is the phone used by James Bond in the 2006 Casino Royale film and trailers.
Y!mobile is a Japanese mobile phone operator. Y!mobile is a brand used by SoftBank Corp., a subsidiary of Japanese telecommunications company SoftBank Group Corporation, that provides mobile telecommunications and ADSL services. The current CEO of the company is Ken Miyauchi. It was formed in 2014 through the merger of Willcom and eAccess, and uses the Y! moniker brand from Yahoo! Japan, which is partly-owned by SoftBank.
A Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card connector includes a connector body, the connector body defines a receptacle channel that extends inwardly from the front and the receptacle channel further defines a first hole and a second hole. Pluralities of terminals mount in the middle of the connector body; a switch terminal mounts in the connector body. The switch terminal has a fixing portion received in the first hole and a contacting portion received in the second hole, the contacting portion forms an arced surface, the top of the arced surface is inserted into the second hole and protrudes above the top surface of the housing base in the receiving cavity.

A mobile phone is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while the user is moving within a telephone service area, as opposed to a fixed-location phone. The radio frequency link establishes a connection to the switching systems of a mobile phone operator, which provides access to the public switched telephone network (PSTN). Modern mobile telephone services use a cellular network architecture and therefore mobile telephones are called cellphones in North America. In addition to telephony, digital mobile phones support a variety of other services, such as text messaging, multimedia messaging, email, Internet access, short-range wireless communications, satellite access, business applications, payments, multimedia playback and streaming, digital photography, and video games. Mobile phones offering only basic capabilities are known as feature phones ; mobile phones which offer greatly advanced computing capabilities are referred to as smartphones.

Samsung Galaxy is a series of computing and mobile computing devices that are designed, manufactured and marketed by Samsung Electronics. The product line includes the Samsung Galaxy S series of high-end phones, Samsung Galaxy Z series of high-end foldables, Samsung Galaxy A series of Mid-range phones, the Samsung Galaxy Book, the Samsung Galaxy Tab series, the Samsung Galaxy Watch, the Samsung Galaxy Buds and the Samsung Galaxy fit.
Mobile security, or mobile device security, is the protection of smartphones, tablets, and laptops from threats associated with wireless computing. It has become increasingly important in mobile computing. The security of personal and business information now stored on smartphones is of particular concern.

Xiaomi Mi1,, is a high-end, Android smartphone produced by Xiaomi. The device uses a Qualcomm Snapdragon S3 as its CPU and an Adreno 220 as its GPU. The device is initially sold at a price of ¥1999. When it was released, the device received more than 300,000 pre-orders in the first 34 hours.
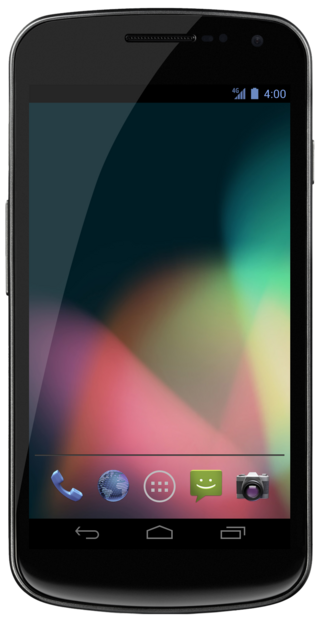
The Galaxy Nexus (GT-I9250) is a touchscreen Android smartphone co-developed by Google and Samsung Electronics. It is the third smartphone in the Google Nexus series, a family of Android consumer devices built by an original equipment manufacturer partner. The phone is the successor to Google's previous flagship phones, the Nexus One and Nexus S.

The WIMM One is a developer device for the WIMM platform produced by WIMM Labs. It is a wearable computing device running a modified version of the Android operating system. It comes preloaded with several apps. Additional applications can be downloaded from the micro app store or side-loaded over USB.
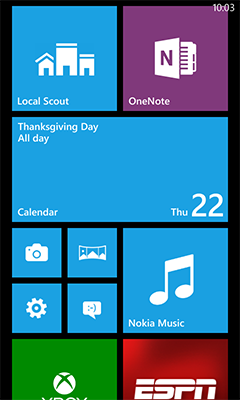
Windows Phone 8 is the second generation of the Windows Phone mobile operating system from Microsoft. It was released on October 29, 2012, and, like its predecessor, it features a flat user interface based on the Metro design language. It was succeeded by Windows Phone 8.1, which was unveiled on April 2, 2014.
The HTC Rhyme is a multi-touch, slate-format Android 2.3 smartphone designed and produced by HTC. The Rhyme was released in the United States exclusively by Verizon Wireless on September 22, 2011, with releases in Asia and Europe beginning in October 2011. The Rhyme is a mid-range smartphone, distinguished by its use of an updated HTC Sense 3.5 user experience, and a selection of bundled accessories; such as a charging dock, wireless speakers, and an LED "charm" that can be used as a notification light. While it was not explicitly marketed as such by HTC, the Rhyme was primarily developed and targeted towards women.

Samsung Galaxy Core GT-I8260 single sim card slot model and Samsung Galaxy Core GT-I8262 dual sim card variant are smartphone manufactured by Samsung Electronics that runs on the open source Android 4.1.2 Jelly Bean operating system. Announced by Samsung in early May 2013, the Dual-SIM model has been released in mid-to-late May 2013, and the single-SIM version for July 2013.
Google Fi Wireless, formerly Project Fi and Google Fi, is an American MVNO telecommunications service by Google that provides telephone calls, SMS, and mobile broadband using cellular networks and Wi-Fi. Google Fi uses the T-Mobile network. Google Fi is a service for US residents only, as of late 2023.

The Sony Xperia 1 is an Android smartphone made by Sony. Part of Sony's flagship Xperia series, the device was announced to the public at a press conference held at the annual 2019 Mobile World Congress event on February 25, 2019. It’s the world's first smartphone with an ultrawide 21:9 aspect ratio 4K HDR OLED display, dubbed Cinema Wide, and Sony's first triple-lens camera system featuring Eye AF eye-tracking technology seen in the company's Alpha line of professional-grade cameras. The Xperia 1 was later joined by a more compact device, the Xperia 5, which was revealed on 5 September 2019. Compared to the Xperia 1, the Xperia 5 has a smaller 1080p screen, a smaller battery, and a non-centrally aligned camera module.












