Related Research Articles

The politics of Uganda occurs in an authoritarian context. Since assuming office in 1986 at the end of the Ugandan civil war, Yoweri Museveni has ruled Uganda as an autocrat. Political parties were banned from 1986 to 2006 in the wake of the 2005 Ugandan multi-party referendum which was won by pro-democracy forces. Since 2006, Museveni has used legal means, patronage, and violence to maintain power.
The history of Uganda comprises the history of the people who inhabited the territory of present-day Uganda before the establishment of the Republic of Uganda, and the history of that country once it was established. Evidence from the Paleolithic era shows humans have inhabited Uganda for at least 50,000 years. The forests of Uganda were gradually cleared for agriculture by people who probably spoke Central Sudanic languages.

Yoweri Kaguta Museveni is a Ugandan military officer, politician and revolutionary who has been serving as the ninth president of Uganda since 1986. His government is considered autocratic. After Museveni lost the election of 1980, he started the Ugandan Bush War which led to the removal of Milton Obote.

The National Resistance Movement has been the ruling party in Uganda since 1986.

The Uganda Electoral Commission (EC) provides national elections for a president and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term. The Parliament is composed of members directly elected to represent constituencies, and one woman representative for every district; as well representatives of special interest groups, including the army, youth, workers and persons with disabilities.

The Forum for Democratic Change, founded on 16 December 2004, is the main opposition party in Uganda. The FDC was founded as an umbrella body called Reform Agenda, mostly for disenchanted former members and followers of President Yoweri Museveni's National Resistance Movement (NRM). Party president Kizza Besigye, formerly a close ally of Museveni, was a presidential candidate in 2001, 2006, 2011 and 2016 presidential elections. In November 2012, Mugisha Muntu was elected as President of the FDC until November 2017 when he was defeated by Patrick Oboi Amuriat the current party President until 2022.

Human rights in Uganda as a state relates to the difficulties in the achievement of international rights standards for all citizens. These difficulties centre upon the provision of proper sanitation facilities, internal displacement, development of adequate infrastructure, as well as the mistreatment of the LGBT community, women, and children. Nonetheless, Uganda is, as per the Relief Web sponsored Humanitarian Profile – 2012, making considerable developments in this area.

Warren Kizza Besigye Kifefe, known as Colonel. Dr. Kizza Besigye, is a Ugandan physician, politician, and former military officer in the Uganda People's Defence Force. He served as the president of the Forum for Democratic Change (FDC) political party and was an unsuccessful candidate in Uganda's 2001, 2006, 2011, and 2016 presidential elections, losing all of them to the incumbent Yoweri Museveni, who has been President of Uganda since 26 January 1986. The results of the 2006 elections were contested in court, where the court found massive rigging and disenfranchisement. He allowed an early internal FDC election for a successor president, which took place on 24 November 2012.

General elections were held in Uganda on 23 February 2006. They were the first multi-party elections since President Yoweri Museveni took over power in 1986, and followed a referendum the previous year on scrapping the ban on party politics.

Norbert Mao is a Ugandan political activist and lawyer. He has been president of the Democratic Party since 2010, three time presidential candidate and he served as the Local Council 5 chairman for Gulu District. He is the current minister for Justice and Constitutional Affairs in the Ugandan government, an office he assumed on 21 July 2022. He was appointed to this position by Yoweri Museveni, the president of the Republic of Uganda. This appointment drew immense criticism from the Democratic Party, an opposition party he is currently serving as president. It was seen as a move by President Museveni to tame the Party and clip its wings to criticize his government. He's currently negotiating to transfer power from NRM to NUP

Eugene Ludovic Wamalwa is a Kenyan politician who was the former Cabinet Secretary of the Ministry of Defense. Prior to that before 29 September 2021, he was Cabinet Secretary of Devolution. He is also a former minister for Justice. He also served as Minister for Water and Irrigation. He belongs to the Azimio la Umoja - One Kenya Coalition Party, and was elected to represent the Saboti Constituency in the National Assembly of Kenya during the 2007 Kenyan parliamentary election, and serving for a one term of five years.

Robert Kyagulanyi Ssentamu, known by his stage name Bobi Wine, is a Ugandan politician, singer, and actor. He is a former Member of Parliament for Kyadondo County East constituency in Wakiso District, in Uganda's Central Region. He also leads the National Unity Platform political party. In June 2019, he announced his candidacy for the 2021 Ugandan presidential election. He participated in the 2021 election, in which he defeated the incumbent Yoweri Kaguta Museveni.

Presidential elections were held in Uganda on 12 March 2001. The incumbent Yoweri Museveni won 69% of the vote and was elected to a second term. All candidates were independents, as political parties were banned at the time. Voter turnout was 70.3%.

General elections were held in Uganda on 18 February 2011. Incumbent President Yoweri Museveni of the National Resistance Movement (NRM) was re-elected for a third time, having been in power since 1986. The NRM also won 263 of the 375 seats in Parliament.
The following lists events that happened during 2005 in Uganda.
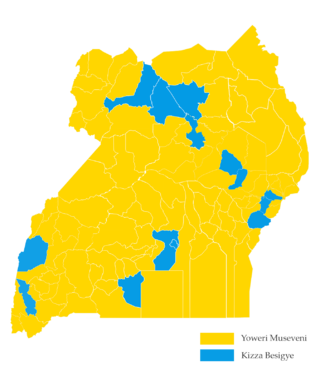
General elections were held in Uganda on 18 February 2016 to elect the President and Parliament. Polling day was declared a national holiday.

The Alliance for National Transformation (ANT), founded on 19 March 2019, is a political party in Uganda.

General elections were held in Uganda on 14 January 2021 to elect the President and the Parliament. The Electoral Commission announced Incumbent President Yoweri Museveni, the incumbent ruling since 1986, as the winner with 58.64% of the votes although the U.S. State Department qualified the electoral process as "fundamentally flawed" and Africa Elections Watch said they observed irregularities. The official voter turnout was 57% but is questioned since 409 polling stations have been announced to have 100% voter turnout.
Patrick Oboi Amuriat is an Ugandan engineer, politician and a founding member of Forum for Democratic Change (FDC) party and ran on its platform for the president of Uganda in the January 2021 presidential election. He served in the Ugandan parliament from 2001 to 2016 and chaired several committees and was a member of Parliamentary Advocacy Forum, PAFO.
Events in the year 2022 in Uganda.
References
- 1 2 3 "Uganda: Launch Independent Inquiry Into Killings". Human Rights Watch . 2011-05-08. Retrieved 2015-02-02.
- 1 2 Musaazi Namiti (2011-04-28). "Uganda walk-to-work protests kick up dust". Al Jazeera English. Retrieved 2015-02-02.
- 1 2 Ioannis Gatsiounis (2011-04-23). "Deadly Crackdown on Uganda's Walk-to-Work Protests". TIME. Archived from the original on April 11, 2014. Retrieved 2015-02-02.
- ↑ "Kizza Besigye held over Uganda 'Walk to Work' protest". BBC News. 2011-04-12. Retrieved 2015-02-02.