Related Research Articles

Abu Zubaydah is a Saudi Arabian currently held by the U.S. in the Guantanamo Bay detention camp in Cuba. He is held under the authority of Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Terrorists (AUMF).

Waterboarding is a form of torture in which water is poured over a cloth covering the face and breathing passages of an immobilized captive, causing the person to experience the sensation of drowning. In the most common method of waterboarding, the captive's face is covered with cloth or some other thin material and immobilized on their back at an incline of 10 to 20 degrees. Torturers pour water onto the face over the breathing passages, causing an almost immediate gag reflex and creating a drowning sensation for the captive. Normally, water is poured intermittently to prevent death. However, if the water is poured uninterruptedly it will lead to death by asphyxia, also called dry drowning. Waterboarding can cause extreme pain, damage to lungs, brain damage from oxygen deprivation, other physical injuries including broken bones due to struggling against restraints, and lasting psychological damage. Adverse physical effects can last for months, and psychological effects for years. The term "water board torture" appeared in press reports as early as 1976.

Mohammed Mani Ahmad al-Qahtani is a Saudi citizen who was detained as an al-Qaeda operative for 20 years in the United States's Guantanamo Bay detention camps in Cuba. Qahtani allegedly tried to enter the United States to take part in the September 11 attacks as the 20th hijacker and was due to be onboard United Airlines Flight 93 along with the four other hijackers. He was refused entry due to suspicions that he was trying to illegally immigrate. He was later captured in Afghanistan in the battle of Tora Bora in December 2001.

Mohamedou Ould Slahi is a Mauritanian citizen who was detained at Guantánamo Bay detention camp without charge from 2002 until his release on October 17, 2016.

Ammar Al-Baluchi is a Pakistani citizen in U.S. custody at Guantanamo Bay detention camp. Charges against him include "facilitating the 9/11 attackers, acting as a courier for Osama bin Laden and plotting to crash a plane packed with explosives into the U.S. consulate in Karachi."

The Salt Pit and Cobalt are the code names of an isolated clandestine CIA black site prison and interrogation center in Afghanistan. It is located north of Kabul and was the location of a brick factory prior to the Afghanistan War. The CIA adapted it for extrajudicial detention.
The five techniques are illegal interrogation methods which were originally developed by the British military in other operational theatres and then applied to detainees during the Troubles in Northern Ireland. They have been defined as prolonged wall-standing, hooding, subjection to noise, deprivation of sleep, and deprivation of food and drink.

The Office of Legal Counsel (OLC) is an office in the United States Department of Justice that assists the Attorney General's position as legal adviser to the President and all executive branch agencies. It drafts legal opinions of the Attorney General and provides its own written opinions and other advice in response to requests from the Counsel to the President, the various agencies of the Executive Branch, and other components of the Department of Justice. The Office reviews and comments on the constitutionality of pending legislation. The office reviews any executive orders and substantive proclamations for legality if the President proposes them. All proposed orders of the Attorney General and regulations that require the Attorney General’s approval are reviewed. It also performs a variety of special assignments referred by the Attorney General or the Deputy Attorney General.
Extrajudicial prisoners of the United States, in the context of the early twenty-first century War on Terrorism, refers to foreign nationals the United States detains outside of the legal process required within United States legal jurisdiction. In this context, the U.S. government is maintaining torture centers, called black sites, operated by both known and secret intelligence agencies. Such black sites were later confirmed by reports from journalists, investigations, and from men who had been imprisoned and tortured there, and later released after being tortured until the CIA was comfortable they had done nothing wrong, and had nothing to hide.
The US Army Field Manual on Interrogation, sometimes known by the military nomenclature FM 34-52, is a 177-page manual describing to military interrogators how to conduct effective interrogations while conforming with US and international law. It has been replaced by FM 2-22.3 Human Intelligence Collector Operations.
Torture in the United States includes documented and alleged cases of torture both inside and outside the United States by members of the government, the military, law enforcement agencies, intelligence agencies, health care services, and other public organizations.
"Enhanced interrogation techniques" or "enhanced interrogation" is a euphemism for the program of systematic torture of detainees by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) and various components of the U.S. Armed Forces at remote sites around the world, including Bagram, Guantanamo Bay, Abu Ghraib, and Bucharest authorized by officials of the George W. Bush administration. Methods used included beating, binding in contorted stress positions, hooding, subjection to deafening noise, sleep disruption, sleep deprivation to the point of hallucination, deprivation of food, drink, and medical care for wounds, as well as waterboarding, walling, sexual humiliation, subjection to extreme heat or extreme cold, and confinement in small coffin-like boxes. A Guantanamo inmate's drawings of some of these tortures, to which he himself was subjected, were published in The New York Times. Some of these techniques fall under the category known as "white torture". Several detainees endured medically unnecessary "rectal rehydration", "rectal fluid resuscitation", and "rectal feeding". In addition to brutalizing detainees, there were threats to their families such as threats to harm children, and threats to sexually abuse or to cut the throat of detainees' mothers.
This article deals with the activities of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) of the federal government of the United States that are violations of human rights.

Steven Gill Bradbury is an American attorney and government official who served as the General Counsel of the United States Department of Transportation. He previously served as Acting Assistant Attorney General (AAG) from 2005 to 2007 and Principal Deputy AAG from 2004 to 2009, heading the Office of Legal Counsel (OLC) in the U.S. Department of Justice during President George W. Bush's second term.
Rafiq Bin Bashir Bin Jalud al Hami is a citizen of Tunisia, who was formerly held for over seven years without charge or trial in the United States's Guantanamo Bay detention camps, in Cuba. His Guantanamo Internment Serial Number was 892. The Department of Defense reports that he was born on 14 March 1969, in Tunisia.

Gul Rahman was an Afghan man, suspected by the United States of being a militant, who was a victim of torture. He died in a secret CIA prison, or black site, located in northern Kabul, Afghanistan known as the Salt Pit. He had been captured October 29, 2002.

A set of legal memoranda known as the "Torture Memos" were drafted by John Yoo as Deputy Assistant Attorney General of the United States and signed in August 2002 by Assistant Attorney General Jay S. Bybee, head of the Office of Legal Counsel of the United States Department of Justice. They advised the Central Intelligence Agency, the United States Department of Defense, and the President on the use of enhanced interrogation techniques: mental and physical torment and coercion such as prolonged sleep deprivation, binding in stress positions, and waterboarding, and stated that such acts, widely regarded as torture, might be legally permissible under an expansive interpretation of presidential authority during the "War on Terror".

John Anthony Rizzo was an American attorney who worked as a lawyer in the Central Intelligence Agency for 34 years. He was the deputy counsel or acting general counsel of the CIA for the first nine years of the War on Terror, during which the CIA held dozens of detainees in black site prisons around the globe.

The Committee Study of the Central Intelligence Agency's Detention and Interrogation Program is a report compiled by the bipartisan United States Senate Select Committee on Intelligence (SSCI) about the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)'s Detention and Interrogation Program and its use of torture during interrogation in U.S. government communiqués on detainees in CIA custody. The report covers CIA activities before, during, and after the "War on Terror". The initial report was approved on December 13, 2012, by a vote of 9–6, with seven Democrats, one Independent, and one Republican voting in favor of the report and six Republicans voting in opposition.
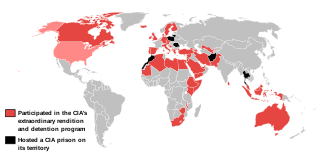
CIA black sites refer to the black sites that are controlled by the CIA and used by the U.S. government in its War on Terror to detain enemy combatants.
References
- 1 2 Gordon, Rebecca (2014). Mainstreaming Torture: Ethical Approaches in the Post-9/11 United States. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-933643-2.
- ↑ https://arpa.com/misc/usdoj-orig-2002-05-bradbury-memo-ts-noforn-un.pdf [ dead link ]
- ↑ Gorman, Siobhan; Perez, Evan (April 17, 2009). "CIA Memos Released; Immunity for Harsh Tactics" . The Wall Street Journal . Retrieved February 12, 2017.
- ↑ Borger, Julian (March 14, 2022). "CIA black site detainee served as training prop to teach interrogators torture techniques". The Guardian . Retrieved March 15, 2022.