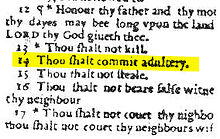The Great Bible of 1539 was the first authorised edition of the Bible in English, authorised by King Henry VIII of England to be read aloud in the church services of the Church of England. The Great Bible was prepared by Myles Coverdale, working under commission of Thomas Cromwell, Secretary to Henry VIII and Vicar General. In 1538, Cromwell directed the clergy to provide "one book of the Bible of the largest volume in English, and the same set up in some convenient place within the said church that ye have care of, whereas your parishioners may most commodiously resort to the same and read it."
This article is a summary of the literary events and publications of 1631.

Miserere is a setting of Psalm 51 by Italian composer Gregorio Allegri. It was composed during the reign of Pope Urban VIII, probably during the 1630s, for the exclusive use of the Sistine Chapel during the Tenebrae services of Holy Week, and its mystique was increased by unwritten performance traditions and ornamentation. It is written for two choirs, of five and four voices respectively, singing alternately and joining to sing the ending in one of the most recognised and enduring examples of polyphony, in this case in a 9-part rendition.
Early Modern English Bible translations are those translations of the Bible which were made between about 1500 and 1800, the period of Early Modern English. This was the first major period of Bible translation into the English language including the King James Version and Douai Bibles. The Reformation and Counter-Reformation led to the need for Bibles in the vernacular with competing groups each producing their own versions.

Throughout history, printers' errors, unconventional translations and translation mistakes have appeared in a number of published Bibles. Bibles with features considered to be erroneous are known as Bible errata, and were often destroyed or suppressed due to their contents being considered heretical by some.

A typographical error, also called a misprint, is a mistake made in the typing of printed or electronic material. Historically, this referred to mistakes in manual typesetting. Technically, the term includes errors due to mechanical failure or slips of the hand or finger, but excludes errors of ignorance, such as spelling errors, or changing and misuse of words such as "than" and "then". Before the arrival of printing, the copyist's mistake or scribal error was the equivalent for manuscripts. Most typos involve simple duplication, omission, transposition, or substitution of a small number of characters.

A printer's devil was a young apprentice in a printing establishment who performed a number of tasks, such as mixing tubs of ink and fetching type. Notable writers including Benjamin Franklin, Walt Whitman, Ambrose Bierce, Bret Harte, and Mark Twain served as printer's devils in their youth.

Matthew 5:19 is the nineteenth verse of the fifth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament and is part of the Sermon on the Mount. Jesus has reported that he came not to destroy the law, but fulfil it. In this verse he perhaps continues to reinforce this claim.

Matthew 5:27 and Matthew 5:28 are the twenty-seventh and twenty-eighth verses of the fifth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament and is part of the Sermon on the Mount. These verses begin the second antithesis: while since Matthew 5:21 the discussion has been on the commandment: "You shall not murder", it now moves to the commandment: "You shall not commit adultery".

The Ten Commandments, or the Decalogue, are a set of biblical principles relating to ethics and worship originally from the Jewish tradition that play a fundamental role in Judaism and Christianity. The text of the Ten Commandments appears in three different versions in the Bible: at Exodus 20:2–17, Deuteronomy 5:6–21, and the "Ritual Decalogue" of Exodus 34:11–26.

Watson Heston was an American editorial cartoonist who peaked in popularity during the Golden Age of Freethought in the late 19th century.
Events from the 1630s in England.
Events from the year 1631 in England.
Robert Barker was a printer to James I of England and son of Christopher Barker, who had been printer to Queen Elizabeth I. He was most notably the printer of the King James Bible, one of the most influential and important books ever printed in the English language. He and co-publisher Martin Lucas published the infamous "Wicked Bible", which contained a typographical error omitting the word not from the sentence Thou shalt not commit adultery.

"Thou shalt not take the name of the LORD thy God in vain" is the second or third of God's Ten Commandments to man in Judaism and Christianity.

"Thou shalt not steal" is one of the Ten Commandments of the Jewish Torah, which are widely understood as moral imperatives by legal scholars, Jewish scholars, Catholic scholars, and Post-Reformation scholars.

"Thou shalt not commit adultery" is found in the Book of Exodus of the Hebrew Bible. It is considered the sixth commandment by Roman Catholic and Lutheran authorities, but the seventh by Jewish and most Protestant authorities. What constitutes adultery is not plainly defined in this passage of the Bible, and has been the subject of debate within Judaism and Christianity. The word fornication means illicit sex, prostitution, idolatry and lawlessness.

Thou shalt not kill, You shall not murder or Do not murder (CSB), is a moral imperative included as one of the Ten Commandments in the Torah.

"I am the LORD thy God" is the opening phrase of the Ten Commandments, which are widely understood as moral imperatives by ancient legal historians and Jewish and Christian biblical scholars.

Psalm 71 is the 71st psalm of the Book of Psalms, beginning in English in the King James Version: "In thee, O LORD, do I put my trust: let me never be put to confusion". It has no title in the Hebrew version. In the slightly different numbering system used in the Greek Septuagint and Latin Vulgate translations of the Bible, this psalm is Psalm 70. In Latin, it is known as "In te Domine speravi".