








The wildlife of Namibia is composed of its flora and fauna. Namibia's endangered species include the wild dog, black rhino, oribi and puku.









The wildlife of Namibia is composed of its flora and fauna. Namibia's endangered species include the wild dog, black rhino, oribi and puku.
The puku antelope is limited to about 100 individuals along the Chobe River in Botswana and the Linyati marshes in Namibia. The black rhino and white rhino have suffered the most from poaching and are on the verge of extinction. If there had been no effort to save them in the last 20 years they most likely would have disappeared altogether. While both species occur naturally in Namibia, in many of the reserves they have been reintroduced. The country also has the largest population in southern Africa of cheetah not contained within national parks. There are over twenty species of antelope ranging from the largest, the eland, to the smallest, the Damara dik-dik. The gemsbok, a striking antelope with long symmetrical horns and distinctive black and white markings is featured on the Namibian coat of arms. Namibia also harbours a wealth of small mammals including mongoose, jackal as well as the less common antbear and honey badger, both solitary and nocturnal.
Namibia's parks and reserves range from the open bush of the centre and the north where wildlife is relatively plentiful, to the barren and inhospitable coastal strip with its huge sand dunes. The three main tourist attractions for wildlife in Namibia are Etosha National Park, Waterberg National Park and Cape Cross Seal Reserve.
Namibia has 115 species of fish (five endemic). [1] There are about 50 species of frogs (six endemic) [2] but neither caecilians nor salamanders. [1] Namibia is home to 250 species of reptiles with 59 endemic. [2] There were 1331 recorded species of arachnids with 164 endemic [2] but there are potentially 5650 species. [2] Records show 6331 species of insects (1541 of them are endemic). [2] but there are expected to be 35,000 species of insects. [2]
200 species of terrestrial mammals (14 of them are endemic) and 40 species of marine mammals are native to Namibia. [2]
There are 645 species of birds (14 of them are endemic). [2]
There were 26 species of freshwater snails recorded and 13 species of freshwater bivalves. [1] A number of land gastropods are also found in Namibia.

There are 4334 species of plants recorded (683 of them are endemic). [2]

Etosha National Park is a national park in northwestern Namibia and one of the largest national parks in Africa. It was proclaimed a game reserve in March 1907 in Ordinance 88 by the Governor of German South West Africa, Friedrich von Lindequist. It was designated as Wildschutzgebiet in 1958, and was elevated to the status of a national park in 1967 by an act of parliament of the Republic of South Africa. It spans an area of 22,270 km2 (8,600 sq mi) and gets its name from the large Etosha pan which is almost entirely within the park. With an area of 4,760 km2 (1,840 sq mi), the Etosha pan covers 23% of the total area of the national park. The area is home to hundreds of species of mammals, birds and reptiles, including several threatened and endangered species such as the black rhinoceros. Sixty-one black rhinoceros were killed during poaching in Namibia during 2022, 46 of whom were killed in Etosha.

The greater kudu is a large woodland antelope, found throughout eastern and southern Africa. Despite occupying such widespread territory, they are sparsely populated in most areas due to declining habitat, deforestation, and poaching. The greater kudu is one of two species commonly known as kudu, the other being the lesser kudu, T. imberbis.

The puku is a medium-sized antelope found in wet grasslands in southern Democratic Republic of Congo, Namibia, Tanzania, Zambia and more concentrated in the Okavango Delta in Botswana. Nearly one-third of all puku are found in protected areas, zoos, and national parks due to their diminishing habitat.

The Kaokoveld Desert is a coastal desert of northern Namibia and southern Angola.

Waterberg Plateau Park is a national park in central Namibia on the Waterberg Plateau, 68 kilometres (42 mi) south-east of Otjiwarongo. The plateau and the national park are named after the prominent table mountain that rises from the plateau, the Waterberg. The Waterberg Plateau is a particularly prominent location, elevating high above the plains of the Kalahari of Eastern Namibia. Waterberg Park and some 405 square kilometres (156 sq mi) of surrounding land were declared a Nature Reserve in 1972. As the plateau is largely inaccessible from beneath several of Namibia's endangered species were relocated in the early 1970s to protect them from predators and poaching to extinction. The programme was very successful and Waterberg now supplies other Namibian parks with rare animals. In 1989, the black rhinoceros was reintroduced to the area from Damaraland.

Khaudum National Park is an isolated Nature Reserve situated in the Kalahari Desert at the west of the Caprivi Strip in northeast of Namibia. It is a very remote and inaccessible reserve but is home to some magnificent animals, such as the lion and hyena. The park also has a campsite for visitors.
India is home to a large variety of wildlife. It is a biodiversity hotspot with its various ecosystems ranging from the Himalayas in the north to the evergreen rain forests in the south, the sands of the west to the marshy mangroves of the east. India lies within the Indomalayan realm and is the home to about 7.6% of mammal, 14.7% of amphibian, 6% of bird, 6.2% of reptilian, and 6.2% of flowering plant species. India's forest lands nurture about 500 species of mammals and more than 2000 bird species.

The wildlife of the Democratic Republic of the Congo includes its flora and fauna, comprising a large biodiversity in rainforests, seasonally flooded forests and grasslands.

Namibia is one of few countries in the world to specifically address habitat conservation and protection of natural resources in their constitution. Article 95 states, "The State shall actively promote and maintain the welfare of the people by adopting international policies aimed at the following: maintenance of ecosystems, essential ecological processes, and biological diversity of Namibia, and utilization of living natural resources on a sustainable basis for the benefit of all Namibians, both present and future.".

Tourism in Namibia is a major industry, contributing N$7.2 billion to the country's gross domestic product. Annually, over one million travelers visit Namibia, with roughly one in three coming from South Africa, then Germany and finally the United Kingdom, Italy and France. The country is among the prime destinations in Africa and is known for ecotourism which features Namibia's extensive wildlife.

Angolan mopane woodlands are situated in southwestern Angola, extending into northern Namibia. This ecosystem surrounds Etosha Pan, which is considered a separate ecoregion. The mopane trees are the main type of vegetation.

The Central Zambezian miombo woodlands ecoregion spans southern central Africa. Miombo woodland is the predominant plant community. It is one of the largest ecoregions on the continent, and home to a great variety of wildlife, including many large mammals.

Tanzania contains some 20 percent of the species of Africa's large mammal population, found across its reserves, conservation areas, marine parks, and 17 national parks, spread over an area of more than 42,000 square kilometres (16,000 sq mi) and forming approximately 38 percent of the country's territory. Wildlife resources of Tanzania are described as "without parallel in Africa" and "the prime game viewing country". Serengeti National Park, the country's second largest national park area at 14,763 square kilometres (5,700 sq mi), is located in northern Tanzania and is famous for its extensive migratory herds of wildebeests and zebra while also having the reputation as one of the great natural wonders of the world. The Ngorongoro Conservation Area, established in 1959, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and inhabited by the Maasai people. Its Ngorongoro Crater is the largest intact caldera in the world.

Bwabwata National Park is a protected area in northeastern Namibia that was established in 2007 and covers 6,274 km2 (2,422 sq mi). It was created by merging Caprivi Game Park and Mahango Game Reserve. It is situated in the Zambezi and Kavango East regions, extending along the Caprivi Strip. It is bounded by the Okavango River to the west and the Kwando River to the east. Angola lies to the north and Botswana to the south.

Mudumu is a National Park in Caprivi Region in north-eastern Namibia. The park was established in 1990. It covers an area of 737 square kilometres (285 sq mi). The Kwando River forms the western border with Botswana. Various communal area conservancies and community forests surround Mudumu National Park.
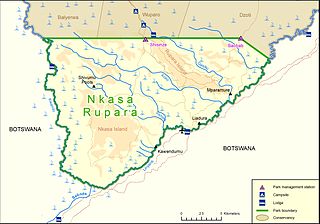
Nkasa Rupara National Park, also Nkasa Lupala National Park, formerly Mamili National Park, is a national park in Namibia. It is centered on the Nkasa and Rupara islands on the Kwando/Linyanti River in the south-western corner of East Caprivi. Botswana lies to the west, south and east, and Sangwali village to the north. It is Namibia's largest formally protected wetland area. It is one of Namibia’s protected areas that benefits local communities surrounding parks. The unfenced park forms a trans-boundary link for wildlife migration between Angola, Botswana, Namibia and Zambia. Nkasa Rupara is part of the Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area.

NamParks or the Namibian National Parks Programme is a programme of the Namibian Ministry of Environment and Tourism (MET). It was established in 2006 and is supported by the Federal Republic of Germany through KfW. It works in Bwabwata, Khaudum, Mudumu and Nkasa Rupara national parks in north eastern Namibia. The parks are part of a larger conservation area, the Kavango–Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area. They contain biodiversity and habitat that are not found elsewhere in Namibia. They are also important for tourism. Partners believe that investment in the north eastern parks contributes to the ecological and economic development of the KAZA TFCA.
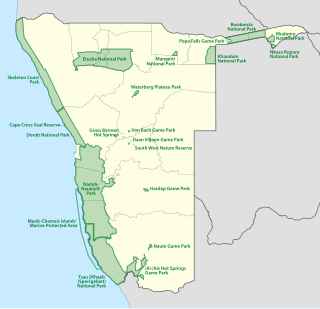
The protected areas of Namibia include its national parks and reserves. With the 2010 declaration of Dorob National Park, Namibia became the first and only country to have its entire coastline protected through a national parks network. Protected areas are subdivided into game reserves and/or nature reserves, such as special protected area, wilderness areas, natural areas, and development areas. There are also recreation reserves. Facilities in the national parks are operated by Namibia Wildlife Resorts. Over 19% of Namibia is protected, an area of some 130,000 square kilometres. However, the Ministry of Environment & Tourism auctions limited hunting rights within its protected areas. The Namibia Nature Foundation, an NGO, was established in 1987 to raise and administer funds for the conservation of wildlife and protected area management. Communal Wildlife Conservancies in Namibia help promote sustainable natural resource management by giving local communities rights to wildlife management and tourism.