
The glucose tolerance test is a medical test in which glucose is given and blood samples taken afterward to determine how quickly it is cleared from the blood. The test is usually used to test for diabetes, insulin resistance, impaired beta cell function, and sometimes reactive hypoglycemia and acromegaly, or rarer disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. In the most commonly performed version of the test, an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), a standard dose of glucose is ingested by mouth and blood levels are checked two hours later. Many variations of the GTT have been devised over the years for various purposes, with different standard doses of glucose, different routes of administration, different intervals and durations of sampling, and various substances measured in addition to blood glucose.

Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Symptoms may also include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that do not heal. Often symptoms come on slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the limbs which may lead to amputations. The sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon.

Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a person without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and of needing a Caesarean section. Babies born to individuals with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at increased risk of macrosomia, of having hypoglycemia after birth, and of jaundice. If untreated, diabetes can also result in stillbirth. Long term, children are at higher risk of being overweight and of developing type 2 diabetes.

World Water Day is an annual United Nations (UN) observance day held on the 22nd of March that highlights the importance of fresh water. The day is used to advocate for the sustainable management of freshwater resources. The theme of each year focuses on topics relevant to clean water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH), which is in line with the targets of Sustainable Development Goal 6. The UN World Water Development Report (WWDR) is released each year around World Water Day.

World Health Day is a global health awareness day celebrated every year on 7 April, under the sponsorship of the World Health Organization (WHO), as well as other related organizations.
Slowly evolving immune-mediated diabetes, or latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA), is a form of diabetes that exhibits clinical features similar to both type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D), and is sometimes referred to as type 1.5 diabetes. It is an autoimmune form of diabetes, similar to T1D, but patients with LADA often show insulin resistance, similar to T2D, and share some risk factors for the disease with T2D. Studies have shown that LADA patients have certain types of antibodies against the insulin-producing cells, and that these cells stop producing insulin more slowly than in T1D patients. Since many people develop the disease later in life, it is often misdiagnosed as type 2 diabetes.

A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, heart diseases, cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's disease, cataracts, and others. NCDs may be chronic or acute. Most are non-infectious, although there are some non-communicable infectious diseases, such as parasitic diseases in which the parasite's life cycle does not include direct host-to-host transmission.
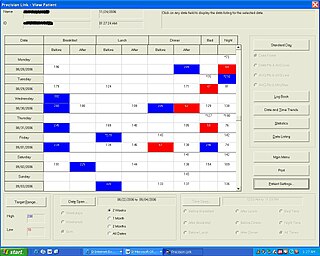
Diabetes Management Software refers to software tools that run on personal computers and personal digital assistants to help persons with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes manage the data associated with:
Sir Kurt George Matthew Mayer Alberti, is a British doctor. His long-standing special interest is diabetes mellitus, in connection with which he has published many research papers and served on many national and international committees. He was President of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) and President of the International Diabetes Federation (IDF). In the 1970s, Alberti published recommendations for the management of diabetic ketoacidosis, a serious metabolic emergency which affects people suffering from severe insulin deficiency. This 'Alberti regime' rationalised the use of insulin and fluid therapy in this condition to the undoubted benefit of many patients.
Prediabetes is a component of metabolic syndrome and is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that fall below the threshold to diagnose diabetes mellitus. It usually does not cause symptoms but people with prediabetes often have obesity, dyslipidemia with high triglycerides and/or low HDL cholesterol, and hypertension. It is also associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Prediabetes is more accurately considered an early stage of diabetes as health complications associated with type 2 diabetes often occur before the diagnosis of diabetes.

Frederick Madison Allen was an American physician who is best remembered for his carbohydrate-restricted low-calorie diet for sufferers of diabetes mellitus. He was known for pioneering the "starvation diet".
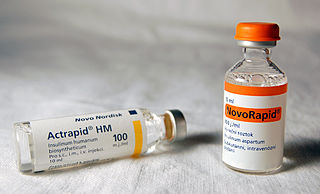
As a medication, insulin is any pharmaceutical preparation of the protein hormone insulin that is used to treat high blood glucose. Such conditions include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. Insulin is also used along with glucose to treat hyperkalemia. Typically it is given by injection under the skin, but some forms may also be used by injection into a vein or muscle. There are various types of insulin, suitable for various time spans. The types are often all called insulin in the broad sense, although in a more precise sense, insulin is identical to the naturally occurring molecule whereas insulin analogues have slightly different molecules that allow for modified time of action. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2021, it was the 179th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.
The St. Vincent Declaration is a set of goals for the health care of people with diabetes mellitus published as the product of an international conference held in St. Vincent, Italy, on 10–12 October 1989.

Insulin degludec (INN/USAN) is an ultralong-acting basal insulin analogue that was developed by Novo Nordisk under the brand name Tresiba. It is administered via subcutaneous injection to help control the blood sugar level of those with diabetes. It has a duration of action that lasts up to 42 hours, making it a once-daily basal insulin, that is one that provides a base insulin level, as opposed to the fast- and short-acting bolus insulins.
Researcher - Dr. Dinesh Kacha Research Article - Diabetes Reversal Through Ayurvedic Lifestyle

The Diabetes Center Mergentheim (DCM) is a large and modern treatment center for people with diabetes mellitus in Germany. The center includes the Diabetes-Clinic, the Diabetes-Academy, FIDAM, the Diabetes-Medical Practice, ConDiaZ and InsulinJA.
This article provides a global overview of the current trends and distribution of metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome refers to a cluster of related risk factors for cardiovascular disease that includes abdominal obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and elevated cholesterol.

Globally, an estimated 537 million adults are living with diabetes, according to 2019 data from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes was the 9th-leading cause of mortality globally in 2020, attributing to over 2 million deaths annually due to diabetes directly, and to kidney disease due to diabetes. The primary causes of type 2 diabetes is diet and physical activity, which can contribute to increased BMI, poor nutrition, hypertension, alcohol use and smoking, while genetics is also a factor. Diabetes prevalence is increasing rapidly; previous 2019 estimates put the number at 463 million people living with diabetes, with the distributions being equal between both sexes icidence peaking around age 55 years old. The number is projected to 643 million by 2030, or 7079 individuals per 100,000, with all regions around the world continue to rise. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 85-90% of all cases. Increases in the overall diabetes prevalence rates largely reflect an increase in risk factors for type 2, notably greater longevity and being overweight or obese. The prevalence of African Americans with diabetes is estimated to triple by 2050, while the prevalence of whites is estimated to double. The overall prevalence increases with age, with the largest increase in people over 65 years of age. The prevalence of diabetes in America is estimated to increase to 48.3 million by 2050.

Diabetes mellitus, often known simply as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to the hormone's effects. Classic symptoms include thirst, polyuria, weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Untreated or poorly treated diabetes accounts for approximately 1.5 million deaths every year.
Santé Diabète (SD) is a French Non-governmental organization (NGOs) whose headquarters is in Grenoble (France) which is working on strengthening health systems to improve the prevention and management of diabetes in Africa. As part of a chronic disease like diabetes, improving the quality of care saves thousands of lives but also improves the quality of life for people living with diabetes.













