
Lakes of liquid ethane and methane exist on the surface of Titan, Saturn's largest moon. This was confirmed by the Cassini–Huygens space probe, as had been suspected since the 1980s. The large bodies of liquid are known as maria (seas) and the small ones as lacūs (lakes).
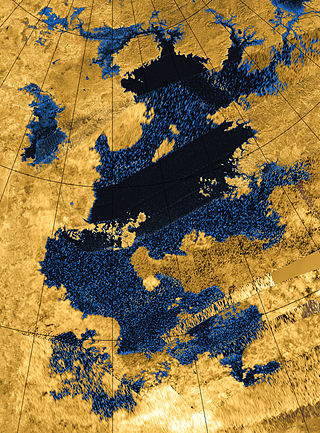
Kraken Mare is the largest known body of liquid on the surface of Saturn's moon Titan. It was discovered by the space probe Cassini in 2006, and was named in 2008 after the Kraken, a legendary sea monster. It covers an area slightly bigger than the Caspian Sea on Earth, making it the largest known lake in the Solar System.

A lake is a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers, such as Lake Ontario. Most lakes are freshwater and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume.

Punga Mare is a lake in the north polar region of Titan, the planet Saturn's largest moon. After Kraken Mare and Ligeia Mare, it is the third largest known body of liquid on Titan. It is composed of liquid hydrocarbons. Located almost adjacent to the north pole at 85.1° N, 339.7° W, it measures roughly 380 km (236 mi) across, greater than the length of Lake Victoria on Earth. Its surface area is ~61,000 km2. Its namesake is Punga, in Māori mythology ancestor of sharks, rays and lizards and a son of Tangaroa, the god of the sea.

Eyre Lacuna is a feature on Saturn's largest moon, Titan, believed to be a currently dry bed of an intermittent hydrocarbon lake.
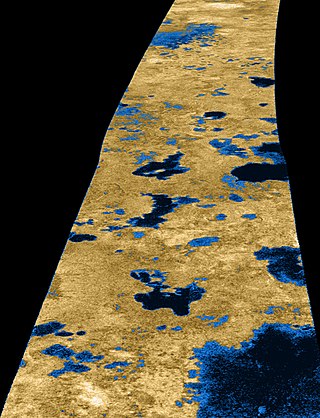
Mackay Lacus is the seventh largest of a number of hydrocarbon seas and lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. The lake is composed of liquid methane and ethane, and was detected by the Cassini space probe.

Abaya Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan.

Ngami Lacuna is a feature on Saturn's largest moon, Titan, believed to be a currently dry bed of an intermittent hydrocarbon lake.

Bolsena Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan.

Neagh Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. The lake is composed of liquid methane and ethane, and was detected by the Cassini space probe.

Sotonera Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan.

Hammar Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon seas and lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan.

Feia Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon seas and lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. It was named in 2007 on the basis of data taken by the space probe Cassini.

Koitere Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. The lake is composed of liquid methane and ethane, and was detected by the space probe Cassini.

Müggel Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon seas and lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan.

Ladoga Lacus is a geographical feature on Saturn's largest moon, Titan, named after Lake Ladoga, Russia. It is one of a number of "methane lakes" found in Titan's north polar region.

Sionascaig Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon seas and lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. The lake is located at latitude 41.52°S and longitude 278.12°W on Titan's globe, and is composed of liquid methane and ethane. The feature is named for the Earth lake, Loch Sionascaig, in Scotland.

Kutch Lacuna is a large intermittent lake on Titan.

Nakuru Lacuna is the largest intermittent lake on Titan.










