
Tourette syndrome or Tourette's syndrome is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence. It is characterized by multiple movement (motor) tics and at least one vocal (phonic) tic. Common tics are blinking, coughing, throat clearing, sniffing, and facial movements. These are typically preceded by an unwanted urge or sensation in the affected muscles known as a premonitory urge, can sometimes be suppressed temporarily, and characteristically change in location, strength, and frequency. Tourette's is at the more severe end of a spectrum of tic disorders. The tics often go unnoticed by casual observers.

A tic is a sudden, repetitive, nonrhythmic motor movement or vocalization involving discrete muscle groups. Tics can be invisible to the observer, such as abdominal tensing or toe crunching. Common motor and phonic tics are, respectively, eye blinking and throat clearing.
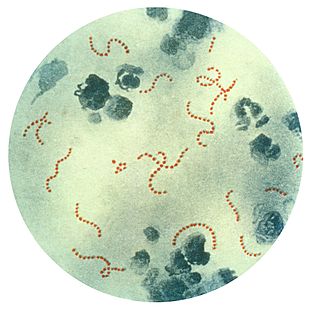
Pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections (PANDAS) is a controversial hypothetical diagnosis for a subset of children with rapid onset of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or tic disorders. Symptoms are proposed to be caused by group A streptococcal (GAS), and more specifically, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal (GABHS) infections. OCD and tic disorders are hypothesized to arise in a subset of children as a result of a post-streptococcal autoimmune process. The proposed link between infection and these disorders is that an autoimmune reaction to infection produces antibodies that interfere with basal ganglia function, causing symptom exacerbations, and this autoimmune response results in a broad range of neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Tourette syndrome is an inherited neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence, characterized by the presence of motor and phonic tics. The management of Tourette syndrome has the goal of managing symptoms to achieve optimum functioning, rather than eliminating symptoms; not all persons with Tourette's require treatment, and there is no cure or universally effective medication. Explanation and reassurance alone are often sufficient treatment; education is an important part of any treatment plan.
Arthur K. Shapiro, M.D., was an American psychiatrist and expert on Tourette syndrome. His "contributions to the understanding of Tourette syndrome completely changed the prevailing view of this disorder"; he has been described as "the father of modern tic disorder research" and is "revered by his colleagues as the first dean of modern Tourette syndrome researchers".
Habit reversal training (HRT) is a "multicomponent behavioral treatment package originally developed to address a wide variety of repetitive behavior disorders".
The Yale–Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS) is a test to rate the severity of obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) symptoms.
The obsessive–compulsive spectrum is a model of medical classification where various psychiatric, neurological and/or medical conditions are described as existing on a spectrum of conditions related to obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). "The disorders are thought to lie on a spectrum from impulsive to compulsive where impulsivity is said to persist due to deficits in the ability to inhibit repetitive behavior with known negative consequences, while compulsivity persists as a consequence of deficits in recognizing completion of tasks." OCD is a mental disorder characterized by obsessions and/or compulsions. An obsession is defined as "a recurring thought, image, or urge that the individual cannot control". Compulsion can be described as a "ritualistic behavior that the person feels compelled to perform". The model suggests that many conditions overlap with OCD in symptomatic profile, demographics, family history, neurobiology, comorbidity, clinical course and response to various pharmacotherapies. Conditions described as being on the spectrum are sometimes referred to as obsessive–compulsive spectrum disorders.

Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental and behavioral disorder in which an individual has intrusive thoughts and/or feels the need to perform certain routines repeatedly to the extent where it induces distress or impairs general function. As indicated by the disorder's name, the primary symptoms of OCD are obsessions and compulsions. Obsessions are persistent unwanted thoughts, mental images, or urges that generate feelings of anxiety, disgust, or discomfort. Common obsessions include fear of contamination, obsession with symmetry, and intrusive thoughts about religion, sex, and harm. Compulsions are repeated actions or routines that occur in response to obsessions. Common compulsions include excessive hand washing, cleaning, arranging things, counting, seeking reassurance, and checking things. Many adults with OCD are aware that their compulsions do not make sense, but they perform them anyway to relieve the distress caused by obsessions. Compulsions occur so often, typically taking up at least one hour per day, that they impair one's quality of life.
James Frederick Leckman, M.D., is a child psychiatrist and psychoanalyst and the Neison Harris Professor of Child Psychiatry, Psychiatry, Psychology and Pediatrics at the Yale School of Medicine, recognized for his research in Tourette syndrome (TS) and obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD).
The University of Florida Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Program is a treatment and research clinic in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Florida. The clinic is located in Gainesville, Florida.

Wayne Goodman is an American psychiatrist and researcher who specializes in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). He is the principal developer, along with his colleagues, of the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS), which is considered to be the gold standard for assessing OCD.

The Spence Children's Anxiety Scale (SCAS) is a psychological questionnaire designed to identify symptoms of various anxiety disorders, specifically social phobia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder/agoraphobia, and other forms of anxiety, in children and adolescents between ages 8 and 15. Developed by Susan H. Spence and available in various languages, the 45 question test can be filled out by the child or by the parent. Alternatively, an abbreviated form of the test has been developed, with only 19 questions. It has shown equally valid results while reducing stress and response burden in younger participants. There is also another 34 question version of the test specialized for children in preschool between ages 2.5 and 6.5. Any form of the test takes approximately 5 to 10 minutes to complete. The questionnaire has shown good reliability and validity in recent studies.
The Dimensional Obsessive-Compulsive Scale (DOCS) is a 20-item self-report instrument that assesses the severity of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) symptoms along four empirically supported theme-based dimensions: (a) contamination, (b) responsibility for harm and mistakes, (c) incompleteness/symmetry, and (d) unacceptable (taboo) thoughts. The scale was developed in 2010 by a team of experts on OCD led by Jonathan Abramowitz, PhD to improve upon existing OCD measures and advance the assessment and understanding of OCD. The DOCS contains four subscales that have been shown to have good reliability, validity, diagnostic sensitivity, and sensitivity to treatment effects in a variety of settings cross-culturally and in different languages. As such, the DOCS meets the needs of clinicians and researchers who wish to measure current OCD symptoms or assess changes in symptoms over time.
John Piacentini, PhD, ABPP, is an American clinical child and adolescent psychologist, and professor of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA in Los Angeles, California. He is the director of the Center for Child Anxiety, Resilience, Education and Support (CARES), and the Child OCD, Anxiety and Tic Disorders Program at UCLA’s Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior.
The Tourette's Disorder Scale (TODS) is a psychological measure used to assess tics and co-occurring conditions in tic disorders.
The Premonitory Urge for Tics Scale (PUTS) is a psychological measure used to assess premonitory urges preceding tics in tic disorders. It is not recommended for children ten and under.
The Motor tic, Obsessions and compulsions, Vocal tic Evaluation Survey (MOVES) is a psychological measure used to screen for tics and other behaviors. It measures "motor tics, vocal tics, obsessions, compulsions, and associated symptoms including echolalia, echopraxia, coprolalia, and copropraxia".
The Autism – Tics, AD/HD, and other Comorbidities (A–TAC) is a psychological measure used to screen for other conditions occurring with tics. Along with tic disorders, it screens for autism spectrum disorders, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and other conditions with onset in childhood. The A-TAC has been reported as valid and reliable for detecting most disorders in children. One telephone survey found it was not validated for eating disorders.






