
Suffren was a predreadnought battleship built for the Marine Nationale in the first decade of the twentieth century. Completed in 1902, the ship was assigned to the Escadre de la Méditerranée for most of her career and often served as a flagship. She had an eventful career as she twice collided with French ships and twice had propeller shafts break before the start of World War I in 1914. Suffren was assigned to join the naval operations off the Dardanelles, where she participated in a series of attacks on the Ottoman fortifications guarding the straits.

The Type 1936A destroyers, also known as the Z23 class, were a group of fifteen destroyers built for the Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine from 1938 to 1943. They were known to the Allies as the Narvik class. In common with other German destroyers launched after the start of World War II, the Narviks were unnamed, known only by their hull numbers – Z23 to Z39.
The Le Hardi class consisted of twelve destroyers built for the Marine Nationale during the late 1930s. Only seven ships were ultimately completed while construction of the remaining five ships was interrupted by the French defeat in the Battle of France in May–June 1940 and were never finished. The seven ships that were seaworthy sailed for French North Africa to prevent their capture by the advancing Germans. Several ships later sailed for French West Africa where Le Hardi played a minor role in the Battle of Dakar in September. The Germans captured two ships that were still under construction and attempted to finish them both before abandoning the effort in 1943.

The 38 cm SK C/34 naval gun was developed by Germany mid to late 1930s. It armed the Bismarck-class battleships and was planned as the armament of the O-class battlecruisers and the re-armed Scharnhorst-class battleships. Six twin-gun mountings were also sold to the Soviet Union and it was planned to use them on the Kronshtadt-class battlecruisers, however they were never delivered. Spare guns were used as coastal artillery in Denmark, Norway and France. One gun and one barrel is currently on display at respectively Møvig Fortress outside Kristiansand and Bunkermuseum Hanstholm, Denmark.

The Type 35 torpedo boat was a class of a dozen torpedo boats built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine in the late 1930s. Although the first boats were completed a few months after the start of World War II in September 1939, none of them were able to participate in the Norwegian Campaign of April–June 1940. They began escorting convoys and minelayers as they laid their minefields in the North Sea and English Channel in July. Most of the boats were transferred to Norway in November where they made an unsuccessful attempt to attack shipping along the Scottish coast that saw one boat sunk.

The Canon de 138 mm Modèle 1927 was a medium-calibre gun of the French Navy used during World War II. It was derived from a German World War I design. It was used on the destroyers of the Aigle and Vauquelin classes and the Bougainville-class sloops.

The 3.7 cm SK C/30 was the German Kriegsmarine's primary 3.7 cm (1.5 in) anti-aircraft gun during the Second World War. It was superseded by the fully automatic 3.7 cm FlaK 43 late in the war.

The 15 cm SK C/28 was a German medium-caliber naval gun used during the Second World War. It served as the secondary armament for the Bismarck class and Scharnhorst-class battleships, Deutschland-class cruisers and the Graf Zeppelin-class aircraft carriers. A number of surplus weapons were used as coast-defense guns and eight were adapted to use Army carriages and used as heavy field guns as the 15 cm Schiffskanone C/28 in Mörserlafette

The Type 1936B destroyers were a group of five destroyers built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine between 1941 and 1942, of which only three were completed and saw service. Eight ships of this design were ordered, but the orders for three ships were cancelled before construction began. Z35 was the first ship of the class to be completed and was commissioned in mid-1943. Her sister ships, Z36 and Z43, followed in 1944. Z44 was sunk during an air raid in 1944 before she was completed while Z45 was never completed. Both ships were scrapped after the war.

The 8.8 cm SK C/35 was a German naval gun used in World War II.

The 15 cm TbtsK C/36 was a German medium-caliber naval gun deployed on Type 1936A (Mob) destroyers during the Second World War. It was designed because the Oberkommando der Marine thought that the 12.7 cm (5.0 in) guns of the Type 1936 and 1936A destroyers would potentially be inferior to those of possible enemies. The guns caused serious issues when actually placed upon ships however, as they added significant weight high up on the ships. To deal with this increase in weight, the destroyers had one gun removed, sometimes with a twin gun being used in order to keep five guns.

The 12.7 cm SK C/34 was a German medium-caliber naval gun deployed on destroyers from 1934 through the Second World War. Some of these guns remained in service until 2003 in the coastal defense units of Norway.

The 10.5 cm SK C/32 (SK - SchnellladekanoneC - Construktionsjahr, was a widely used German naval gun on a variety of Kriegsmarine ships during World War II. Originally designed as a surface weapon, it was used in a number of other roles such as anti-aircraft and coastal defence; wet-mounts were developed for U-boats.

The Type 37 torpedo boat was a class of nine torpedo boats built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. Completed in 1941–1942, one boat helped to escort a commerce raider passing through the English Channel into the Atlantic Ocean in late 1941, but their first major action was in early 1942 when they formed part of the escort for a pair of battleships and a heavy cruiser through the Channel back to Germany in the Channel Dash. Two pairs of boats were sent to France at different times in mid-1942 and were part of the escort during an unsuccessful attempt to pass a different commerce raider back through the Channel in October. One boat was assigned to the Torpedo School as a training ship in mid-1942 and the others followed in the next year.
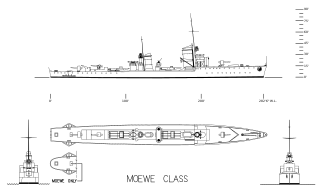
The Type 23 torpedo boat was a group of six torpedo boats built for the Reichsmarine during the 1920s. As part of the renamed Kriegsmarine, the boats made multiple non-intervention patrols during the Spanish Civil War in the late 1930s. During World War II, they played a minor role in the Norwegian Campaign of 1940, Albatros being lost when she ran aground. The Type 23s spent the next several months escorting minelayers as they laid minefields and escorting ships before the ships were transferred to France around September. Möwe was torpedoed during this time and did not return to service until 1942. They started laying minefields themselves in September and continued to do so for the rest of the war.

The Type 24 torpedo boat (also known as the was a group of six torpedo boats built for the Reichsmarine during the 1920s. As part of the renamed Kriegsmarine, the boats made multiple non-intervention patrols during the Spanish Civil War in the late 1930s. One was sunk in an accidental collision shortly before the start of World War II in September 1939 and the others escorted ships and searched for contraband for several months of the war. They played a minor role in the Norwegian Campaign of April 1940 and resumed their escort duties. After being transferred to France late in the year, the Type 24s started laying their own minefields in the English Channel.

The Type 1939 torpedo boats, also known as the Elbing class by the Allies, were a group of 15 torpedo boats that were built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II.
The Type 1941 torpedo boats were a group of 15 torpedo boats that were built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. Ordered in late 1942, none of the ships were finished before the German surrender on 8/9 May 1945, although four of the ships had been towed west to be completed earlier in that year. They were all either scuttled or demolished in the shipyard in 1945–1946.

The Type 1940 torpedo boats were a group of 24 torpedo boats that were intended to be built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. Although classed as fleet torpedo boats by the Germans, they were comparable to contemporary large destroyers. They were designed around surplus Dutch propulsion machinery available after the Germans conquered the Netherlands in May 1940 and were to be built in Dutch shipyards. Hampered by uncooperative Dutch workers and material shortages, none of the ships were completed before the Allies invaded Normandy on June 1944. The Germans towed the three ships that were most complete to Germany to be finished, but one was sunk en route by Allied fighter-bombers and no further work was done of the pair that did arrive successfully. The remaining ships in the Netherlands were later broken up for scrap and the two that reached Germany were scuttled in 1946.

The Type 44 torpedo boats were a group of six or nine torpedo boats that were designed for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. Ordered in 1944, none of the ships were laid down before the German surrender in May 1945.