Related Research Articles

Tai chi is an ancient Chinese martial art. Initially developed for combat and self-defense, for most practitioners it has evolved into a sport and form of exercise. As an exercise, tai chi is performed as gentle, low-impact movement in which practitioners perform a series of deliberate, flowing motions while focusing on deep, slow breaths. Often referred to as "meditation in motion," tai chi aims to concentrate and balance the body's qi, providing benefits to mental and physical health.

Georges André Malraux was a French novelist, art theorist, and minister of cultural affairs. Malraux's novel La Condition Humaine (1933) won the Prix Goncourt. He was appointed by President Charles de Gaulle as information minister (1945–46) and subsequently as France's first cultural affairs minister during de Gaulle's presidency (1959–1969).

Sun Tzu was a Chinese military general, strategist, philosopher, and writer who lived during the Eastern Zhou period. Sun Tzu is traditionally credited as the author of The Art of War, an influential work of military strategy that has affected both Western and East Asian philosophy and military thought. Sun Tzu is revered in Chinese and East Asian culture as a legendary historical and military figure. His birth name was Sun Wu and he was known outside of his family by his courtesy name Changqing. The name Sun Tzu—by which he is more popularly known—is an honorific which means "Master Sun".

The Art of War is an ancient Chinese military treatise dating from the late Spring and Autumn period. The work, which is attributed to the ancient Chinese military strategist Sun Tzu, is composed of 13 chapters. Each one is devoted to a different set of skills or art related to warfare and how it applies to military strategy and tactics. For almost 1,500 years, it was the lead text in an anthology that was formalized as the Seven Military Classics by Emperor Shenzong of Song in 1080. The Art of War remains the most influential strategy text in East Asian warfare, has influenced both East Asian and Western military theory and thinking, and has found a variety of applications in myriad competitive non-military endeavors across the modern world including espionage, culture, politics, business, and sports.

Chinese art is visual art that originated in or is practiced in China, Greater China or by Chinese artists. Art created by Chinese residing outside of China can also be considered a part of Chinese art when it is based on or draws on Chinese culture, heritage, and history. Early "Stone Age art" dates back to 10,000 BC, mostly consisting of simple pottery and sculptures. After that period, Chinese art, like Chinese history, was typically classified by the succession of ruling dynasties of Chinese emperors, most of which lasted several hundred years. The Palace Museum in Beijing and the National Palace Museum in Taipei contains extensive collections of Chinese art.
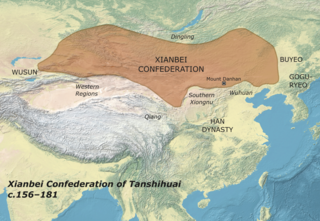
The Xianbei were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multilingual, multi-ethnic confederation consisting of mainly Proto-Mongols, and, to a minor degree, Tungusic and Turkic peoples. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the Wuhuan and Xianbei when they were defeated by the Xiongnu at the end of the third century BC. Following the split, the Xianbei people did not have a direct contact with the Han dynasty, residing to the north of the Wuhuan. In the first century BC, the Xianbei began actively engaging in the struggle between the Han and Xiongnu, culminating in the Xianbei replacing the Xiongnu on the Mongolian Plateau.

The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BCE with the purpose of protecting him in his afterlife.

Ip Man, also known as Yip Man, was a Chinese martial arts grandmaster. He became a teacher of the martial art of Wing Chun when he was 20. He had several students who later became martial arts masters in their own right, the most famous among them being Bruce Lee.

Ink wash painting ; is a type of Chinese ink brush painting which uses washes of black ink, such as that used in East Asian calligraphy, in different concentrations. It emerged during the Tang dynasty of China (618–907), and overturned earlier, more realistic techniques. It is typically monochrome, using only shades of black, with a great emphasis on virtuoso brushwork and conveying the perceived "spirit" or "essence" of a subject over direct imitation. Ink wash painting flourished from the Song dynasty in China (960–1279) onwards, as well as in Japan after it was introduced by Zen Buddhist monks in the 14th century. Some Western scholars divide Chinese painting into three periods: times of representation, times of expression, and historical Oriental art. Chinese scholars have their own views which may be different; they believe that contemporary Chinese ink wash paintings are the pluralistic continuation of multiple historical traditions.

A necklace is an article of jewellery that is worn around the neck. Necklaces may have been one of the earliest types of adornment worn by humans. They often serve ceremonial, religious, magical, or funerary purposes and are also used as symbols of wealth and status, given that they are commonly made of precious metals and stones.

The Kushan Empire was a syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Eastern Iran and Northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath, near Varanasi, where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great.

Xu Beihong, also known as Ju Péon, was a Chinese painter.

Landscape painting, also known as landscape art, is the depiction in painting of natural scenery such as mountains, valleys, rivers, trees, and forests, especially where the main subject is a wide view—with its elements arranged into a coherent composition. In other works, landscape backgrounds for figures can still form an important part of the work. Sky is almost always included in the view, and weather is often an element of the composition. Detailed landscapes as a distinct subject are not found in all artistic traditions, and develop when there is already a sophisticated tradition of representing other subjects.

Tyrus Wong was a Chinese-born American artist. He was a painter, animator, calligrapher, muralist, ceramicist, lithographer and kite maker, as well as a set designer and storyboard artist. One of the most-influential and celebrated Asian-American artists of the 20th century, Wong was also a film production illustrator, who worked for Disney and Warner Bros. He was a muralist for the Works Progress Administration (WPA), as well as a greeting card artist for Hallmark Cards. Most notably, he was the lead production illustrator on Disney's 1942 film Bambi, taking inspiration from Song dynasty art. He also served in the art department of many films, either as a set designer or storyboard artist, such as Rebel Without a Cause (1955), Around the World in 80 Days (1956), Rio Bravo (1959), The Music Man (1962), PT 109 (1963), The Great Race (1965), Harper (1966), The Green Berets (1968), and The Wild Bunch (1969), among others.

The Ryerss Mansion, also known as the Burholme Mansion, is an historic, American mansion that is located in the Fox Chase neighborhood of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.

Susan Stuart Goodrich Frackelton (1848–1932) was an American painter, specializing in painting ceramics. She was a leader in the Arts and Crafts movement in the United States and author of Tried by Fire, the "most popular handbook for decorators of chinaware", having reached a national audience.
Gideon Nye Jr. was an American diplomat, art collector, writer and merchant in the East Indian and China trade, known both for his art collection and for his books on China.
Ah Xian is a Chinese-born artist based in Sydney, Australia.

Chinese Souls #2 is a quilt by American artist Nancy Crow, located at the Indianapolis Museum of Art, in Indianapolis, Indiana. It was created in 1992 as part of a series of memorial quilts she began in response to an atrocity she witnessed in China in 1990.

He Xiangning was a Chinese revolutionary, feminist, politician, painter, and poet. Together with her husband Liao Zhongkai, she was one of the earliest members of Sun Yat-sen's revolutionary movement Tongmenghui. As Minister for Women's Affairs in Sun's Nationalist government in Guangzhou (Canton), she advocated equal rights for women and organized China's first rally for International Women's Day in 1924. After her husband's assassination in 1925 and Chiang Kai-shek's persecution of the Communists in 1927, she stayed away from party politics for two decades, but actively worked to organize resistance against the Japanese invasion of China.
References
- ↑ Jantzen, Hans (1959). Ottonische Kunst[Ottonian Art] (in German) (2 ed.). Hamburg: Rowohlt. p. 115.