
The Battle of Monte Cassino, also known as the Battle for Rome, was a series of four military assaults by the Allies against German forces in Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II. The objective was to break through the Winter Line and facilitate an advance towards Rome.

The Battle of Anzio was a battle of the Italian Campaign of World War II that commenced January 22, 1944. The battle began with the Allied amphibious landing known as Operation Shingle, and ended on June 4, 1944, with the liberation of Rome. The operation was opposed by German and by Italian Repubblica Sociale Italiana (RSI) forces in the area of Anzio and Nettuno.

The Garigliano is a river in central Italy.

The Bernhardt Line, or Reinhard Line, was a German Army defensive line in Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II. Having reached the Bernhardt Line at the start of December 1943, it took until mid-January 1944 for the US Fifth Army to fight its way to the next line of defences, the Gustav Line. The Bernhardt Line was defended by XIV Panzer Corps, part of the German Tenth Army.
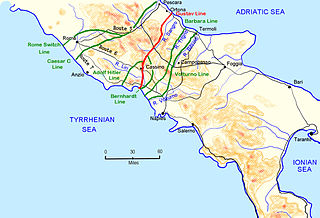
The Winter Line was a series of German and Italian military fortifications in Italy, constructed during World War II by Organisation Todt and commanded by Albert Kesselring. The series of three lines was designed to defend a western section of Italy, focused around the town of Monte Cassino, through which ran the important Highway 6 which led uninterrupted to Rome. The primary Gustav Line ran across Italy from just north of where the Garigliano River flows into the Tyrrhenian Sea in the west, through the Apennine Mountains to the mouth of the Sangro River on the Adriatic coast in the east. The two subsidiary lines, the Bernhardt Line and the Hitler Line, ran much shorter distances from the Tyrrehnian Sea to just northeast of Cassino where they would merge into the Gustav Line. Relative to the Gustav Line, the Hitler Line stood to the northwest and the Bernhardt Line to the southeast of the primary defenses.

Albert Kesselring was a German military officer and convicted war criminal who served in the Luftwaffe during World War II. In a career which spanned both world wars, Kesselring reached the rank of the Generalfeldmarschall and became one of Nazi Germany's most highly decorated commanders.

The 2nd Polish Corps, 1943–1947, was a major tactical and operational unit of the Polish Armed Forces in the West during World War II. It was commanded by Lieutenant General Władysław Anders and fought with distinction in the Italian Campaign, in particular at the Battle of Monte Cassino. By the end of 1945, the corps had grown to well over 100,000 soldiers.

The 2nd New Zealand Division, initially the New Zealand Division, was an infantry division of the New Zealand Military Forces during the Second World War. The division was commanded for most of its existence by Lieutenant-General Bernard C. Freyberg. It fought in Greece, Crete, the Western Desert and Italy. In the Western Desert Campaign, the division played a prominent role in the defeat of German and Italian forces in the Second Battle of El Alamein and the British Eighth Army's advance to Tunisia.

The Italian campaign of World War II, also called the Liberation of Italy following the German occupation in September 1943, consisted of Allied and Axis operations in and around Italy, from 1943 to 1945. The joint Allied Forces Headquarters (AFHQ) was operationally responsible for all Allied land forces in the Mediterranean theatre and it planned and led the invasion of Sicily in July 1943, followed in September by the invasion of the Italian mainland and the campaign in Italy until the surrender of the Axis forces in Italy in May 1945.

The Gothic Line was a German and Italian defensive line of the Italian Campaign of World War II. It formed Field Marshal Albert Kesselring's last major line of defence along the summits of the northern part of the Apennine Mountains during the fighting retreat of the Axis forces in Italy against the Allied Armies in Italy, commanded by General Sir Harold Alexander.

The 90th Light Infantry Division was a light infantry division of the German Army during World War II that served in North Africa as well as Sardinia and Italy. The division played a major role in most of the actions against the British Eighth Army in the Western Desert Campaign and eventually surrendered to the Allies in the final stages of the Tunisia Campaign in May 1943. It was re-constituted later in 1943 and deployed to Sardinia and when the expected Allied invasion of Sardinia failed to materialise, the division was moved to Italy. It was engaged in actions against the Allies in Italy from 1943 to April 1945 when the division was listed as "destroyed" in the Po River valley.

The 334th Infantry Division was a German Army infantry division in World War II. Originally formed in November 1942, it surrendered to the Allies at the conclusion of the Tunisian Campaign in May 1943. The division was reconstituted on 3 June 1943 in France within the 1st Army, with the staff of the 80th Infantry Division as well as remnants of the old division and replacement units. It spent the remainder of the war serving on the Italian Front.

Fridolin von Senger und Etterlin was a general in the army of Nazi Germany during World War II.
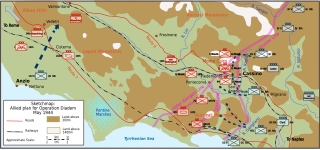
Operation Diadem, also referred to as the Fourth Battle of Monte Cassino or, in Canada, the Battle of the Liri Valley, was an offensive operation undertaken by the Allies of World War II in May 1944, as part of the Italian Campaign of World War II. Diadem was supported by air attacks called Operation Strangle. The opposing force was the German 10th Army.

Michał Waszyński was first a film director in Poland, then in Italy, and later a producer of major American films, mainly in Spain. Known for his elegance and impeccable manners, he was known by his acquaintances as "the prince".

X Corps was a corps of the British Army that served in the First World War on the Western Front before being disbanded in 1919. The corps was re-formed in 1942 during the Second World War and saw service in the North African Campaign and the Italian Campaign where it came under command of the US Fifth Army and the British Eighth Army.

The Battle of San Pietro Infine was a major engagement from 8–17 December 1943, in the Italian Campaign of World War II involving Allied forces attacking from the south against heavily fortified positions of the German "Winter Line" in and around the town of San Pietro Infine, just south of Monte Cassino about halfway between Naples and Rome.

The French Expeditionary Corps (FEC) (French: Corps Expéditionnaire Français, CEF), also known as the French Expeditionary Corps in Italy (FECI) (French: Corps Expéditionaire Français en Italie, CEFI), was an expeditionary force of the French Liberation Army. Created in 1943, the corps fought in the Italian Campaign of World War II, under the command of General Alphonse Juin. Consisting of 112,000 men divided into four divisions, all but one of the divisions were colonial units, mostly Moroccans and Algerians drawn from the Army of Africa and led by French officers. Overall approximately 60% of the Expeditionary Corps was composed of colonial troops.

The Spring 1945 offensive in Italy, codenamed Operation Grapeshot, was the final Allied attack during the Italian Campaign in the final stages of the Second World War. The attack in the Lombard Plain by the 15th Allied Army Group started on 6 April 1945 and ended on 2 May with the surrender of all Axis forces in Italy.

The Fallschirmjäger were the paratrooper branch of the German Luftwaffe before and during World War II. They were the first paratroopers to be committed in large-scale airborne operations. They were commanded by Kurt Student, the Luftwaffe's second-in-command.























