Related Research Articles

The Cooke Locomotive and Machine Works, located in Paterson, New Jersey, manufactured steam railroad locomotives from 1852 until it was merged with seven other manufacturers to form American Locomotive Company (ALCO) in 1901.
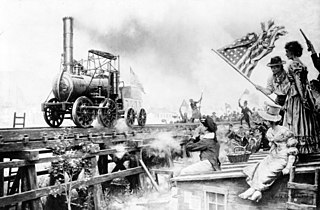
The Stourbridge Lion was a railroad steam locomotive. It was the first locomotive and the first foreign built locomotive to be operated in the United States, and one of the first locomotives to operate outside Britain. It takes its name from the lion's face painted on the front, and Stourbridge in England, where it was manufactured by the firm Foster, Rastrick and Company in 1829. The locomotive, obtained by the Delaware & Hudson Canal Company (D&H), was shipped to New York in May 1829, where it was tested raised on blocks. It was then taken to Honesdale, Pennsylvania for testing on the company's newly built track. The locomotive performed well in its first test in August 1829, but was found to be too heavy for the track and was never used for its intended purpose of hauling coal wagons. During the next few decades, a number of parts were removed from the abandoned locomotive until only the boiler and a few other components remained. These were acquired by the Smithsonian Institution in 1890 and are currently on display at the B&O Railroad Museum in Baltimore.
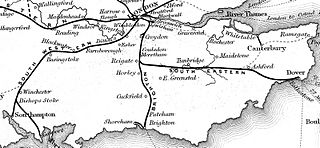
The London and Brighton Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in England which was incorporated in 1837 and survived until 1846. Its railway ran from a junction with the London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) at Norwood – which gives it access from London Bridge, just south of the River Thames in central London. It ran from Norwood to the South Coast at Brighton, together with a branch to Shoreham-by-Sea.

Amblecote is an affluent urban village in the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley in the West Midlands, England. It lies immediately north of the historic town of Stourbridge on the southwestern edge of the West Midlands conurbation. Historically, Amblecote was in the parish of Oldswinford, but unlike the rest of the parish it was in Staffordshire, and as such was administered separately.

Foster, Rastrick and Company was one of the pioneering steam locomotive manufacturing companies of England. It was based in Stourbridge, Worcestershire, now West Midlands. James Foster, an ironmaster, and John Urpeth Rastrick, an engineer, became partners in 1816, forming the company in 1819. Rastrick was one of the judges at the Rainhill Trials in 1829. The company was dissolved on 20 June 1831.

John Bloomfield Jervis was an American civil engineer. America's leading consulting engineer of the antebellum era (1820–60), Jervis designed and supervised the construction of five of America's earliest railroads, was chief engineer of three major canal projects, designed the famous, pioneering, DeWitt Clinton steam locomotive in 1831 while with the Mohawk & Hudson RR, designed the first locomotive with a swiveling 4-wheeled front bogie truck in 1832 for the M&H RR, designed and built the 41-mile Croton Aqueduct – New York City's fresh water supply from 1842 to 1891 – and was a consulting engineer for the Boston water system.
John Urpeth Rastrick was one of the first English steam locomotive builders. In partnership with James Foster, he formed Foster, Rastrick and Company, the locomotive construction company that built the Stourbridge Lion in 1829 for export to the Delaware and Hudson Railroad in America. From the 1830s he concentrated on civil engineering with his major project from 1838 being the construction of the London and Brighton Railway.

James Foster was a prominent Worcestershire ironmaster, coalmaster and senior partner in the important iron company of John Bradley & Co, Stourbridge, which was founded by his elder half-brother but greatly enlarged under his direction. As well as the Stourbridge ironworks, the business owned a number of coal and ironstone mines, furnaces, forges and other works in the Black Country and near Ironbridge. The business continued long after James Foster's death, ultimately being incorporated as John Bradley (Stourbridge) Ltd in the early 20th century. In the late 19th century, the company was a member of the Marked Bar Association, whose members were the makers of the highest quality bar iron of the time. Foster was also a partner in other companies including the engineering firm Foster, Rastrick and Company, which built the first steam locomotive to run on rails in the USA. He was also a banker and landowner as well as being elected Member of Parliament and appointed as Improvement Commissioner for Stourbridge, and High Sheriff of Worcestershire.
Wollaston is a village on the outskirts of Stourbridge in the English West Midlands. It is located in the south of the Dudley Metropolitan Borough, one mile west of Stourbridge town centre.

The Stourbridge Line is a shortline railroad that operates 25 miles (40 km) of former Erie Lackawanna Railroad trackage between Honesdale and Lackawaxen, Pennsylvania, where it connects with Norfolk Southern Railway. The line was previously owned by the Lackawaxen-Honesdale Shippers Association and operated under contract by Robey Railroads. The operation was contracted to the Morristown & Erie Railway in January, 2009; service ended in 2011. Service was resumed by the Delaware, Lackawaxen & Stourbridge Railroad (DL&S) on May 9, 2015.
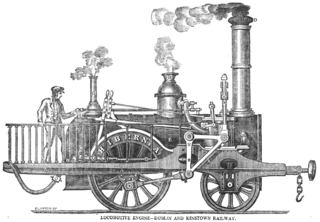
Hibernia was a steam locomotive designed by Richard Roberts and built by Sharp, Roberts and Company in 1834 for the Dublin and Kingstown Railway (D&KR). The locomotive had vertical cylinders driving via bell cranks.

John Kennedy was a Scottish textile industrialist in Manchester.

The Agenoria was an early steam locomotive built by the Foster, Rastrick and Co partnership of Stourbridge, England. It first ran on 2 June 1829 along the Kingswinsford Railway which was a 3-mile long (4.8 km) line linking mines in the Shut End area of the Black Country with a canal basin at Ashwood on the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal. It was withdrawn from service around 1864 and was donated to the Science Museum (London) in December 1884. It is now on display at the National Railway Museum in York.
This article lists events relating to rail transport that occurred during the 1780s.
The Chillington Iron Works opened in 1822. Foster, Rastrick and Company in Stourbridge played a role in equipping the works. An extensive 2 ft 6 in gauge tramway connected the ironworks with the Birmingham canal at Chillington Wharf, but had disappeared by the turn of the century. Steam locomotives from John Smith Village Foundry at Coven, were purchased for use on the line.
Hazledine and Company was an ironworks in Bridgnorth, Shropshire, England. It was set up about 1792 by three brothers: John Hazledine (1760–1810), Robert Hazledine (1768–1837) and Thomas Hazledine (1771–1842). Sources differ about the partnership - Discover Shropshire claims that the partners were John Hazledine, William Hallen and John Wheeler.
John Bradley & Co was a company established in 1800 by John Bradley at Stourbridge in the West Midlands area of England. The company developed into a large industrial concern with furnaces, ironworks and mines. Under James Foster, John Bradley's half brother, it was instrumental in bringing the first commercial steam locomotive into the Midlands area in 1829. The firm stayed under family control until the early years of the 20th century when first the mining (1913) and then the ironworks (1919) were sold off. Part of the business continued to trade under the name John Bradley & Co. (Stourbridge) Ltd until after the Second World War.

The Earl of Dudley’s Railway or Pensnett Railway, was a 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge railway that developed from a single 3-mile (4.8 km) line opened in 1829 to, at its maximum extent, a 40-mile (64 km) long network around the Earl of Dudley’s Iron Works at Round Oak near Brierley Hill.
References
- ↑ "British locomotive manufacturers". steamindex.com. 25 March 2021. Foster Rastrick & Co. Stourbridge. Retrieved 3 April 2024.
- Bedwell, Carolyn (2002), John Urpeth Rastrick . Retrieved April 4, 2005.
- Bedwell, Carolyn (2002), John Urpeth Rastrick – Chronology . Retrieved April 22, 2005 — date for Foster, Rastrick and Company formation.
- Senate House Library, University of London, John Bradley & Co (Stourbridge) Ltd., Ironfounders Archived 2018-01-14 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved April 22, 2005 — info on Foster, Rastrick and Company, verifies Foster family connections.