Related Research Articles

Mikayel Nalbandian was a Russian-Armenian writer, poet, political theorist and activist.

The Hamidian massacres also called the Armenian massacres, were massacres of Armenians in the Ottoman Empire in the mid-1890s. Estimated casualties ranged from 100,000 to 300,000, resulting in 50,000 orphaned children. The massacres are named after Sultan Abdul Hamid II, who, in his efforts to maintain the imperial domain of the declining Ottoman Empire, reasserted pan-Islamism as a state ideology. Although the massacres were aimed mainly at the Armenians, in some cases they turned into indiscriminate anti-Christian pogroms, including the Diyarbekir massacres, where, at least according to one contemporary source, up to 25,000 Assyrians were also killed.

The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia, was an independent Armenian state that existed from May 1918 to December 2 1920 in the Armenian-populated territories of the former Russian Empire known as Eastern or Russian Armenia. The republic was established in May 1918, with its capital in the city of Yerevan, after the dissolution of the short-lived Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic. It was the first Armenian state since the Middle Ages.

The Turkish–Armenian War, known in Turkey as the Eastern Front of the Turkish War of Independence, was a conflict between the First Republic of Armenia and the Turkish National Movement following the collapse of the Treaty of Sèvres in 1920. After the provisional government of Ahmet Tevfik Pasha failed to win support for ratification of the treaty, remnants of the Ottoman Army's XV Corps under the command of Kâzım Karabekir attacked Armenian forces controlling the area surrounding Kars, eventually recapturing most of the territory in the South Caucasus that had been part of the Ottoman Empire prior to the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878) and was subsequently ceded by Soviet Russia as part of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk.
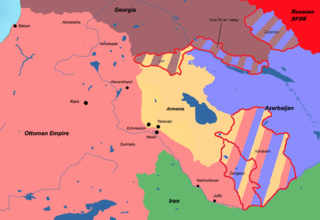
The Treaty of Batum was signed in Batum on 4 June 1918, between the Ottoman Empire and the three Transcaucasian states: the First Republic of Armenia, the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and the Democratic Republic of Georgia. It was the first treaty of the First Republic of Armenia and the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and had 14 articles.
Armenian revolutionary songs are songs that promote Armenian patriotism. The origins of these songs lay largely in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, when Armenian political parties were established to struggle for the political and civil rights of Armenians living in the Ottoman Empire.
The Armenian national movement included social, cultural, but primarily political and military movements that reached their height during World War I and the following years, initially seeking improved status for Armenians in the Ottoman and Russian Empires but eventually attempting to achieve an Armenian state.

The Armenian question was the debate following the Congress of Berlin in 1878 as to how the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire should be treated. The term became commonplace among diplomatic circles and in the popular press. In specific terms, the Armenian question refers to the protection and the freedoms of Armenians from their neighboring communities. The Armenian question explains the 40 years of Armenian–Ottoman history in the context of English, German, and Russian politics between 1877 and 1914. In 1915, the leadership of the Committee of Union and Progress, which controlled the Ottoman government, decided to end the Armenian question permanently by killing and expelling most Armenians from the empire, in the Armenian genocide.

Richard Hovannisian was an American historian and professor at the University of California, Los Angeles. He is known mainly for his four-volume history of the First Republic of Armenia.

The Kars oblast was a province (oblast) of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire between 1878 and 1917. Its capital was the city of Kars, presently in Turkey. The oblast bordered the Ottoman Empire to the west, the Batum Oblast to the north, the Tiflis Governorate to the northeast, and the Erivan Governorate to the east. The Kars oblast included parts of the contemporary provinces of Kars, Ardahan, and Erzurum Province of Turkey, and the Amasia Community of the Shirak Province of Armenia.
The Khaibalikend massacre was the mass killing of Armenian civilians in the villages of Ghaibalishen (Khaibalikend), Jamilli, and Karkijahan and Pahlul in Nagorno-Karabakh, from June 5 to 7, 1919. The villages were destroyed, and from 600 to 700 ethnic Armenians, including women and children, were murdered by armed ethnic Azeri and Kurdish irregulars and Azerbaijani soldiers. The massacre was organized by Nagorno-Karabakh's Governor-General Khosrov bek Sultanov and led by his brother, Sultan bek Sultanov.

The Zakatal okrug was a special administrative district (okrug) of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, part of the Tiflis Governorate from 1893 to 1905. The administrative centre of the district was Zakataly, and it corresponded to most of the contemporary districts of Balakan, Zaqatala and Qax of Azerbaijan. The Zakatal okrug was established from the territories of the erstwhile Free Jamaats of Jar-Balakan, bordering the Tiflis Governorate to the west, the Elizavetpol Governorate to the south and the Dagestan Oblast to the north. The district was the smallest independent administrative unit of the Russian Empire, similarly to the Sukhumi okrug.

Armash was a small Armenian-populated town located in the Ottoman Empire, near the Sea of Marmara. With its seminary and monastery of Charkhapan Surb Astvatsatsin, Armash served as the spiritual center of Armenians in western Asia Minor until 1915, when its inhabitants were rounded up and sent on death marches to the Syrian desert by orders of the leaders of the Committee of Union and Progress party.
Anarchism in Armenia emerged as part of the Armenian national liberation movement, with its roots in various heretical Christian sects that practiced in the region. It took on an organized form with the establishment of the Armenian Revolutionary Federation in 1890, before being suppressed by the various empires and authoritarian regimes that ruled over Armenia during the 20th century. It eventually re-emerged in the 21st century, as part of the anti-establishment movement that spread throughout the country in the wake of its independence.

The Zangezur uezd was a county (uezd) of the Elizavetpol Governorate of the Russian Empire with its administrative center in Gerusy from 1868 until its formal abolition and partition between the Soviet republics of Armenia and Azerbaijan in 1921. The area of the Zangezur uezd corresponded to most of the contemporary Syunik province of Armenia, and Lachin, Gubadly, Zangilan, and Shusha districts of Azerbaijan.

The Kagizman okrug was a district (okrug) of the Kars Oblast of the Russian Empire, existing between 1878 and 1918. Its capital was the town of Kagyzman, presently in the Kars Province of Turkey. The okrug bordered with the Kars okrug to the north, the Olti okrug to the northwest, the Erivan Governorate to the east, and the Erzurum Vilayet of the Ottoman Empire to the west.
In the aftermath of World War I and during the Armenian–Azerbaijani and Russian Civil wars, there were mutual massacres committed by Armenians and Azerbaijanis against each other. While a significant portion of the Muslim population of the Erivan Governorate were displaced during the internecine conflict due to the actions of Armenian irregulars and militias, the government of Armenia pursued a policy of ethnic homogenisation in affected areas. Starting in 1918, Armenian partisans expelled and massacred thousands of Azerbaijani Muslims in Zangezur and destroyed their settlements in an effort to "re-Armenianize" the region. These actions were cited by Azerbaijan as a reason to start a military campaign in Zangezur. Ultimately, Azerbaijan took in and resettled tens of thousands of Muslim refugees from Armenia. The total number of killed is a matter of scholarly dispute. By the outset of Armenia's independence, the country's Turkic population was more than 10 thousand.
The First Republic of Armenia was the first independent Armenian state since the Cilician Kingdom of Armenia, proclaimed on 28 May 1918 in the territory of present Armenia. The republic lasted until 2 December 1920 when it was partitioned by the Russian SFSR and the Turkish Nationalist forces. In the two and a half years of its existence, the republic was composed of 9 mostly Dashnak-dominated cabinets.
References
- ↑ ( Hovannisian 1971 , pp. 10)
- ↑ ( Nalbandian 1963 , pp. 128)
- ↑ ( Nalbandian 1963 , pp. 128)
- ↑ ( Nalbandian 1963 , pp. 128–129)